[ad_1]
Successful on the battlefield takes a mix of exact intelligence and resolute troopers. However with regards to the battle in opposition to most cancers, the immune system’s fighters—the T cells—shortly lose their capability to kill and develop into exhausted, whereas the intelligence-providing dendritic cells are scarce. This is likely one of the causes that the good promise of immunotherapy—a brand new technology of remedies that harness the physique’s personal immune system for preventing most cancers—has not been absolutely realized.
In a research published right now in Cell, Weizmann Institute of Science researchers current a newly developed antibody that connects T cells to dendritic cells, creating a strong immune response to cancerous growths. The analysis opens a brand new avenue in immunotherapy: the event of remedies that hyperlink up varied cells within the immune system to create a crack fight staff for defeating cancer and different illnesses.
One of the vital distinguished immunotherapies makes use of antibodies that block PD-1, a regulatory “checkpoint” receptor discovered on the floor of T cells. When this receptor is expressed in T cells, a protein widespread within the tumor setting can connect to it, switching the T cells right into a state referred to as exhaustion. PD-1 antibodies stop this protein from attaching to T cells and repressing them, however many most cancers sufferers fail to answer this therapy; in lots of others, the effectiveness is short-lived.
To develop a more practical immunotherapy, researchers from the laboratories of Dr. Rony Dahan and Prof. Ido Amit in Weizmann’s Techniques Immunology Division began by asking why present remedies fall brief. To reply this query, they sampled T cells from two mouse fashions of most cancers that had undergone PD-1 antibody therapy.
“Utilizing superior applied sciences akin to single-cell DNA sequencing and large knowledge algorithms, we examined virtually 130,000 T cells, a few of which responded to the therapy and a few of which didn’t,” Amit explains. “Surprisingly, the group of T cells that did reply to the therapy expressed genes pointing towards an interplay with a uncommon inhabitants of dendritic cells.”
Dendritic cells acquire intelligence from throughout the physique by swallowing molecules belonging to malignant cells. They then current their findings to T cells, thereby warning them concerning the cancerous development and prompting them to take motion.
PD-1 antibodies are supposed to assist with activating the T cells that battle cancerous growths, however when the researchers examined a most cancers mannequin from a mouse missing dendritic cells, they found that the antibody therapy had misplaced its effectiveness solely. In different phrases, they revealed that dendritic cells are very important to the multiplication and activation of particular T cells within the battle in opposition to most cancers and are subsequently essential for the therapy as a complete to achieve success.
These findings uncovered a key weak point in present remedies: the truth that the related inhabitants of dendritic cells is never current in most cancerous growths and in most sufferers at present being handled with PD-1 antibodies. Below these circumstances, interplay between these cells and the T cells that they activate hardly ever takes place.
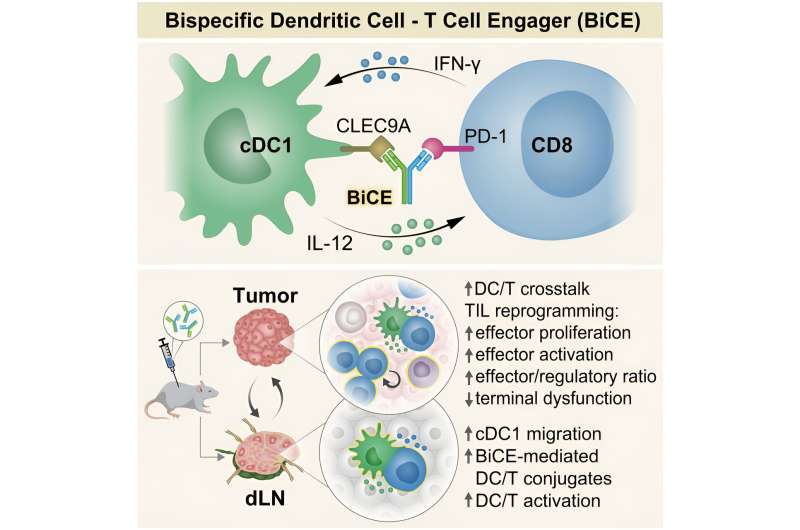
This understanding paved the way in which for the engineering of a brand new antibody known as BiCE (Bispecific DC-T Cell Engager), whose two arms have been designed to attach two several types of cells: One arm binds to T cells, inhibiting the PD-1 receptor, simply as present remedies do; the opposite arm recruits the dendritic cells from the uncommon inhabitants that’s very important for activating the T cells.
The event of the brand new therapy was led by doctoral analysis college students Yuval Shapir Itai, from Dahan’s laboratory, and Oren Barboy, from Amit’s laboratory.
Having created their antibody, the researchers studied its mechanism of motion. Once they used fluorescent markers to label the antibody and the immune cells of mice with pores and skin most cancers who had been given the brand new therapy, they have been in a position to observe how the antibody bodily linked the T cells to the dendritic cells, growing the variety of such mobile pairs across the cancerous development and within the adjoining lymph nodes.
Additionally they found that the mobile pairs created by the antibody have been energetic and that they triggered an immune response in opposition to the expansion. Furthermore, within the wake of the therapy, the dendritic cells that had been adjoining to the cancerous development migrated to the lymph nodes and linked to the T cells there, with a view to share intel and activate them.
New hope for untreatable illnesses
The effectiveness of this new therapy was examined in a number of mouse fashions of most cancers, together with aggressive breast, lung and pores and skin cancers. Therapy with the brand new antibody, as in comparison with the prevailing therapy, considerably diminished the expansion price of pores and skin and lung cancers.
In distinction, breast tumors that didn’t reply to the prevailing therapy additionally failed to answer the brand new antibody. Researchers consider that that is due to the very small variety of energetic dendritic cells round these tumors.
Due to this fact, they tried combining their new antibody with an present therapy that enhances the exercise of dendritic cells across the development. This mixed therapy was discovered to be more practical than the prevailing choices. It proved that even in cancers that had not responded to immunotherapy till now, the synergy between T cells and energetic dendritic cells creates a strong immune response in opposition to the tumor.
The subsequent stage of the research was to look at whether or not, alongside a strong immune response in opposition to the first cancerous development, the brand new antibody additionally manages to stop the illness from returning. Many most cancers sufferers endure such a recurrence even after the first development has been eliminated and any identified metastases have been handled.
The principle hazard is the existence of tiny remnants of the illness that escape detection and begin creating later, inflicting the tumor to recur. BiCE, not like present remedies, has been discovered to be efficient in thwarting the event of metastases within the lungs after the elimination of the first tumor.
This is perhaps proof that the antibody manages to create a systemic immune response in opposition to the most cancers all through all the physique and that, after therapy, it leaves behind immune cells that keep in mind how you can establish the most cancers and reply accordingly.
Yeda Analysis and Improvement, which is liable for commercializing the mental property of Weizmann Institute scientists, has filed a patent software and is working to develop an revolutionary therapy based mostly on the Weizmann antibody.
“We’re presenting a brand new method that places the emphasis on a system view of immunotherapy,” says Dahan. “As an alternative of taking a look at one avenue, we engineer antibodies that function a communication platform between whichever immune cells we select.”
“This growth provides hope not solely to cancer patients, who have to have their immune techniques activated to battle off the expansion but additionally to folks with different illnesses, akin to autoimmune illnesses, through which sufferers want a suppression of the immune response in opposition to their very own physique.”
“There are methods of suppressing all the immune system, however our new method ought to make it potential to suppress or activate a focused immune response with out the broad and harmful ramifications of general suppression and activation of the immune system.”
Extra data:
Yuval Shapir Itai et al, Bispecific dendritic-T cell engager potentiates anti-tumor immunity, Cell (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.12.011
Quotation:
Standing united: When immune cells be a part of forces, most cancers remedy is more practical (2024, January 18)
retrieved 18 January 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-01-immune-cells-cancer-therapy-effective.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post