[ad_1]
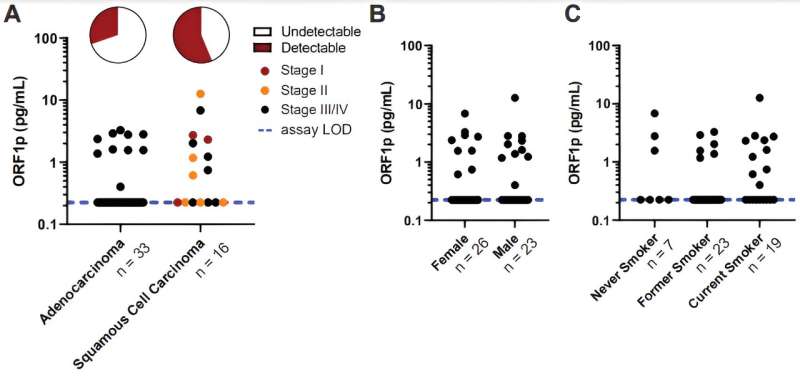
Circulating ORF1p ranges in lung most cancers affected person cohort, as labeled by (A) illness subtype, (B) gender, and (C) smoking standing. Blue dashed line signifies the assay restrict of detection, accounting for the four-fold dilution issue. Credit score: (2023). DOI: 10.1101/2023.01.25.525462
Diagnostic instruments for well timed, correct and cheap early most cancers detection that may assess danger or monitor response to therapy might assist sufferers get the care they want sooner and enhance present care methods. However present most cancers evaluation strategies have restricted specificity and sensitivity and may be prohibitively costly.
In a research led by investigators from Mass Normal Brigham, the Wyss Institute for Biologically Impressed Engineering at Harvard College and Dana-Farber Most cancers Institute, in collaboration with researchers from throughout the nation and past the U.S., researchers have developed a low-cost, ultrasensitive blood check to detect minute ranges of a cancer biomarker that’s extremely particular to a number of widespread cancers.
Every check may be carried out with merely half a drop of blood (25 microliters). The software confirmed promise for early most cancers detection and illness monitoring, and will doubtlessly be used along side different instruments for detection, danger stratification and therapy.
Outcomes are revealed in Cancer Discovery.
“Most cancers biomarker detection is a burgeoning space of analysis and remains to be a younger subject,” mentioned co-corresponding creator David Walt, Ph.D., of the Division of Pathology at Brigham and Girls’s Hospital. Walt can also be a core college member on the Wyss Institute. “Our outcomes present that we are able to detect ranges of this pan-cancer biomarker within the blood of sufferers with many sorts of cancers.”
The brand new research leverages a single-molecule-based detection expertise often called SIMOA that was developed by the Walt lab. The check is designed to detect the open studying body 1 protein (ORF1p), a transposable aspect protein that is recognized to happen in lots of cancers however not in corresponding regular tissue, and that may point out excessive danger of most cancers lethality.
Researchers have lengthy sought a delicate, correct check to detect ORF1p. The authors describe their first investigation of the check as a pilot experiment that wound up working higher than that they had imagined, which was adopted by a sequence of engineering enhancements and iterations in affected person samples.
“We had been shocked by how effectively this check labored in detecting the biomarker’s expression throughout most cancers varieties,” mentioned lead creator Martin Taylor, M.D., Ph.D., of the Division of Pathology at Massachusetts Normal Hospital. “It is created extra questions for us to discover and sparked curiosity amongst collaborators throughout many establishments.”
Teaming up with investigators throughout Mass Normal Brigham, Dana-Farber, Beth Israel Deaconess, and MIT in Boston and from Rockefeller College, College of Pennsylvania, College of Washington (Seattle), Johns Hopkins, Groningen (Netherlands), and Canon Medical, the researchers examined blood samples from sufferers with several types of cancers, together with ovarian and colorectal most cancers.
The ultrasensitive evaluation software efficiently quantified ORF1p in most cancers affected person blood samples, however solely in very uncommon “wholesome” sufferers, supporting the specificity for most cancers detection. Research in tissue samples from ~200 colon cancer and 75 esophageal biopsies, obtained from sufferers at completely different illness phases, confirmed that ORF1p tissue expression was prevalent in carcinomas and high-risk precursor lesions.
“Our outcomes bolster the rising concept that ORF1p expression is a ‘hallmark of most cancers’ expressed beginning early within the illness course of. Pervasive expression of ORF1p in carcinomas and the shortage of expression in regular tissues makes ORF1p in contrast to different protein biomarkers, which have regular expression ranges. This distinctive biology makes it extremely particular,” mentioned Taylor.
A limitation of the research is that the outcomes do not present key items of knowledge, reminiscent of the placement of the cancerous tissues within the physique. As well as, the ultrasensitive evaluation software is not profitable in figuring out all cancers and their subtypes. The group envisions that the software may very well be used along with different checks to enhance total early detection testing strategies, and to permit medical doctors to watch affected person response to most cancers remedy in actual time and make changes if wanted.
“The check may be very particular, nevertheless it would not inform us sufficient data for use in a vacuum,” mentioned Walt. “It is thrilling to see the early success of this ultrasensitive evaluation software, however there may be extra work to be finished.”
The research’s pathology researchers are actually working with clinicians to check the check’s accuracy in bigger trial cohorts and completely different affected person populations with the intention to perceive if the evaluation of the ORF1p biomarker can be helpful for the care of their sufferers. They’re additionally working to find out whether or not the biomarker can be utilized to stratify the chance of most cancers in sufferers.
“We have recognized for the reason that Nineteen Eighties that transposable parts had been energetic in some cancers, and practically 10 years in the past we reported that ORF1p was a pervasive most cancers biomarker, however till now, we’ve not had the power to detect it in blood checks,” mentioned co-corresponding creator Kathleen Burns, M.D., Ph.D., Chair of the Division of Pathology at Dana-Farber.
“Having a expertise able to detecting ORF1p in blood opens so many potentialities for medical purposes. We had been lucky to assemble this super group to push the bounds of those assays and acquire and check these treasured samples. There’s plenty of pleasure as our work continues.”
Extra data:
Martin S. Taylor et al, Ultrasensitive detection of circulating LINE-1 ORF1p as a selected multi-cancer biomarker, Most cancers Discovery (2023). DOI: 10.1101/2023.01.25.525462
Supplied by
Mass General Brigham
Quotation:
Ultrasensitive blood check detects ‘pan-cancer’ biomarker (2023, October 5)
retrieved 6 October 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-10-ultrasensitive-blood-pan-cancer-biomarker.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post