[ad_1]
Graphical summary. Credit score: Nucleic Acids Analysis (2023). DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad1164
Technological developments have enabled scientists to comprehensively discover genetic management components, unraveling the complexities of gene activation mechanisms in our genetic code. New proof challenges the simplistic view that cis-regulatory components (CREs) are mere on/off switches for genes, emphasizing their capacity to exhibit advanced behaviors, such because the simultaneous enhancement of gene exercise and initiation of gene transcription (e.g., simultaneous enhancer and promoter actions).
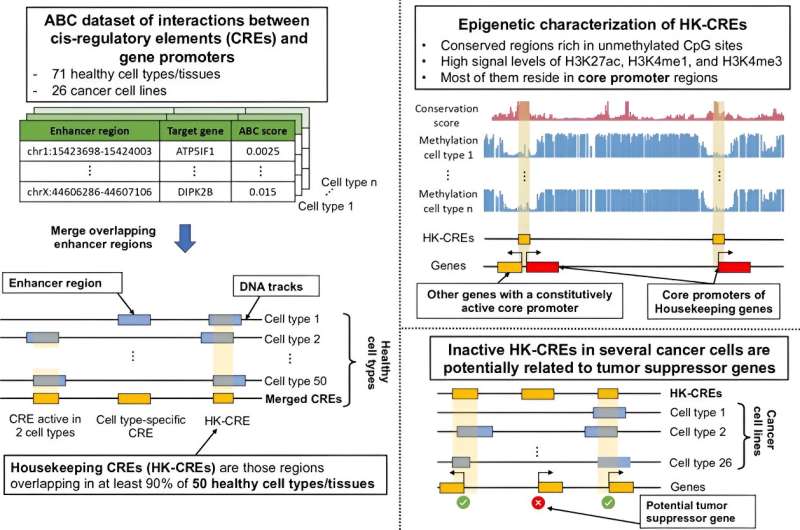
These switches aren’t solely necessary for the enhancement of particular genes however are essential for the essential capabilities that maintain our cells wholesome. Now, a examine carried out in Japan has revealed the existence of round 11,000 very important genetic switches lively in each cell sort—housekeeping cis-regulatory components (HK-CREs)—that play a task in sustaining the soundness and performance of our cells, far past the regulation of housekeeping genes.
The analysis is published in Nucleic Acids Analysis. This examine was carried out by scientists from the Laboratory of Practical Evaluation in silico (Nakai-lab) at The Institute of Medical Science, The College of Tokyo, Japan: Professor Kenta Nakai, head of the laboratory, and Dr. Martin Loza, Assistant Professor, in collaboration with Dr. Alexis Vandenbon, Affiliate Professor, from the Institute of Life and Medical Sciences, Kyoto College, Japan.
Discussing his motivation behind this examine, Dr. Loza states, “Given the numerous affiliation between cancer and mutations in epigenetic elements, each small perception we achieve could possibly be key within the ongoing battle in opposition to this illness, which has tragically claimed innumerable lives. Via intensive bioinformatics analyses, we aimed to emphasise HK-CREs profound influence on elementary mobile processes, together with their potential as important housekeeping tumor suppressors.”
The analysis staff discovered that HK-CREs weren’t solely confined to regulating the well-studied housekeeping genes (HKGs), which solely constituted lower than 20% of the genes related to these components. As a substitute, these components predominantly resided inside core promoter areas of many extra genes (round 8,000), indicating a broader regulatory position past typical housekeeping gene capabilities.
By using bioinformatics analyses and levering various public datasets, the staff validated the robustness of HK-CREs throughout 50 randomly chosen wholesome cell sorts, confirming the situation of HK-CREs throughout the genome. These components had been extremely conserved, residing in unmethylated CpG-rich areas, a trait strongly related to their housekeeping regulatory perform.
Sharing his issues concerning the evaluation, Dr. Loza states, “By leveraging bioinformatics analyses of multiomics knowledge, we provide an method to harnessing publicly out there datasets for exploring various organic mechanisms. We anticipate that using comparable workflows can considerably streamline analyses, slicing again each time and monetary investments wanted for complete research involving new knowledge.”
The staff remarked on the intricate cooperative interactions amongst housekeeping core promoters (HK-CPs), forming advanced regulatory networks by means of promoter–promoter interactions. These observations trace on the important affect of such interactions not solely on HKGs but additionally on genes particular to numerous cell sorts.
Turning their consideration to cancer cellsresearchers found a subset of HK-CREs displaying lowered exercise in various most cancers subtypes attributable to aberrant methylation, significantly these linked to zinc finger genes clustered in sub-telomere areas of chromosome 19. Figuring out genes comparable to ZNF135, ZNF154, ZNF667, and ZNF667-AS1 below the affect of those foundational core promoters, the analysis suggests their potential as housekeeping tumor suppressor genes.
“Genes detected in our examine have exhibited decreased exercise in a number of cancer cell linesand survival evaluation throughout numerous most cancers initiatives have revealed important will increase in survival likelihood in various most cancers sorts like pancreas adenocarcinoma and uveal melanoma,” states Dr. Loza.
In essence, the outcomes of this analysis have uncovered a beforehand unknown class of HK-CREs vital for mobile stability, extending their affect past housekeeping gene regulation.
“Our discovery on housekeeping tumor suppressor genes unveils a novel avenue in most cancers remedy, harnessing the intrinsic components throughout the DNA of each cell. Future approaches to most cancers therapy, specializing in these housekeeping tumor suppressor genessupply a singular answer that would probably goal a broad vary of cancers, sidestepping the challenges related to personalised drugs,” says Dr. Loza.
“Our findings on housekeeping cis-regulatory components fill a giant hole within the present data relating to gene regulatory processes. We anticipate that our findings will improve the understanding of those processes and function a helpful useful resource for researchers striving to uncover components inherent within the genome for combating numerous illnesses.”
Extra info:
Martin Loza et al, Epigenetic characterization of housekeeping core promoters and their significance in tumor suppression, Nucleic Acids Analysis (2023). DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad1164
Offered by
University of Tokyo
Quotation:
Research reveals essential ‘housekeeping’ genetic components and their potential to combat most cancers (2024, January 5)
retrieved 5 January 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-01-reveals-crucial-housekeeping-genetic-elements.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post