[ad_1]
Rural Black residents of the South have larger mortality, or loss of life, charges than rural Black residents elsewhere, and so did Hispanic residents of the agricultural South and West, in keeping with a brand new examine by two researchers within the Penn State Faculty of Well being and Human Growth.
These populations have larger mortality charges than their city counterparts or individuals from the identical ethnic/racial groups who stay elsewhere. Rural residents throughout america have had larger mortality charges than city residents for the reason that late twentieth century, in keeping with U.S. census knowledge.
The researchers discovered that this phenomenon, referred to as the “rural mortality drawback,” was not common however diverse based mostly on race, ethnicity and the place within the nation individuals lived.
Danielle Rhubart, assistant professor of biobehavioral well being and demography, and Alexis Santos, assistant professor of human development and family studies and demography, carried out the examine and revealed their leads to a analysis observe in Demography.
Public well being enhancements and remedy advances for most cancers and coronary heart illness within the Nineteen Eighties and ’90s led to reductions within the mortality charges in america as a complete, in keeping with the researchers. In rural areas, nevertheless, mortality charges decreased at a slower charge.
Prior analysis by Penn State school and others documented this phenomenon at a nationwide stage, however Santos and Rhubart stated they wished to develop a extra nuanced image of who was experiencing the agricultural morality drawback.
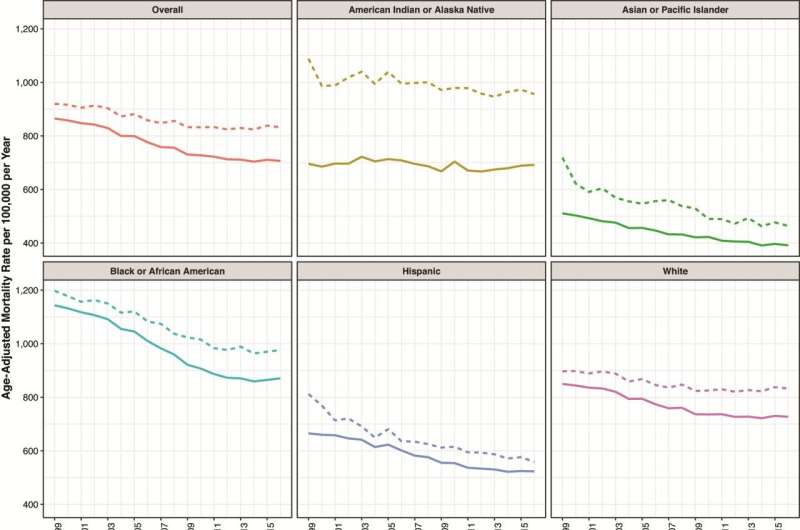
The researchers examined all deaths in america from 1999 to 2016 utilizing knowledge from the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention’s Huge-ranging On-line Knowledge for Epidemiological Analysis (WONDER) platform.
They cross-referenced the information with info from the Nationwide Heart for Well being Statistics to calculate age-adjusted loss of life charges for each age group, damaged down by area, racial/ethnic group and rural/city residence.
The nation was divided into 4 areas—Northeast, South, Midwest and West—and 5 racial/ethnic groups had been recognized—American Indian or Alaska Native, Asian or Pacific Islander, Black, Hispanic/Latino and white.
For every racial/ethnic group, the researchers discovered the loss of life charges had been larger in rural areas than in city areas. Individuals who recognized as American Indian or Alaska Native noticed the best annual impact, with these in rural areas experiencing a further 300 deaths annually for each 100,000 individuals in comparison with those that stay in city areas. Rural Hispanic residents had been the least affected, with round 25 further deaths annually for each 100,000 rural residents.
The agricultural mortality drawback was current for every racial or ethnic group on the nationwide stage, the researchers stated, however issues turned extra difficult after they examined every racial/ethnic inhabitants on a regional foundation.
“In areas of the nation with the most important share of an ethnic or racial group, we discovered these teams had larger mortality charges,” stated Santos.
Outcomes confirmed that the agricultural mortality drawback for Black populations solely existed within the South. Rural Black residents of the West, Midwest or Northeast truly had decrease mortality charges than their city counterparts, however 80% of rural Black people within the nation stay within the South, in keeping with U.S. census knowledge. The mortality drawback within the South was massive sufficient to create a nationwide mortality drawback for rural Black residents.
The agricultural mortality drawback was solely persistent throughout all areas for white and American Indian or Alaska Native populations. Rhubart stated that she was not stunned by the regional variations, as earlier analysis from the Penn State Interdisciplinary Community on Rural Inhabitants Well being and Getting old had demonstrated that rural America is just not a monolith.
“Our examine constructed on that work to point out that race, ethnicity and area all intersect to have very actual impacts on individuals’s well being in rural America,” stated Rhubart, principal investigator of the newly shaped working group on rural inhabitants well being within the Social Science Analysis Institute. “To deal with the foundation causes of the agricultural mortality drawback, we should first perceive how race, ethnicity and area all intersect with well being and mortality.”
Rhubart pointed to the complexity of those intersections and stated that efficient options will necessitate comparable complexity, particularly as many questions stay. As a result of their knowledge resulted in 2016, Rhubart and Santos are wanting to learn the way the COVID-19 pandemic might have affected these outcomes and whether or not the impacts of the pandemic have lingered. Most of all, they stated they wish to perceive the causes for the regional differences they detected.
“At this level, we have now recognized some necessary variations in mortality rates,” Santos stated. “The following step is for researchers to uncover what’s driving these variations in order that the underlying causes might be addressed. We wish to see individuals throughout the nation residing lengthy, wholesome lives no matter their backgrounds.”
Extra info:
Danielle Rhubart et al, Analysis Word Exhibiting That the Rural Mortality Penalty Varies by Area, Race, and Ethnicity in america, 1999–2016, Demography (2023). DOI: 10.1215/00703370-11078239
Quotation:
Research finds mortality charges amongst rural US residents range based mostly on race, ethnicity, area (2024, January 24)
retrieved 24 January 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-01-mortality-rural-residents-vary-based.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post