[ad_1]
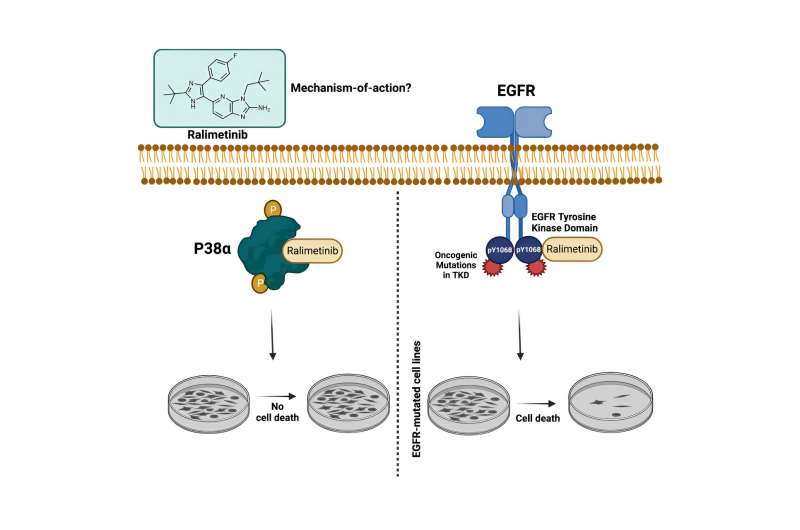
Graphical summary. Credit score: Cell Chemical Biology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.09.013
Most cancers medicine typically do not behave as anticipated in medical trials. A examine printed Oct. 11 within the journal Cell Chemical Biology explores why medicine below improvement are unlikely to work as a consequence of inadequate genetic evaluation.
Most cancers medicine, that are designed to focus on a single mutated protein and never affect regular tissue, fail for 2 causes. “They’re too poisonous for sufferers to securely take, or sufferers can safely take them, however they do not truly shrink a affected person’s tumor,” stated the examine’s senior creator Jason Sheltzer, Ph.D., assistant professor of surgical procedure and genetics, and member of Yale Most cancers Heart. Uncovering the mechanisms behind a mischaracterized drug may make clear its poor efficiency in clinical trials.
Most cancer drugs fail to obtain U.S. Meals and Drug Administration approval. To grasp why, Debanjan Bhattacharjee, Ph.D., and Jaweria Bakar from the Sheltzer Lab studied a p38a inhibitor drug referred to as ralimetinib.
“Once we examined this drug in our lab, we discovered that it was concentrating on a unique pathway,” stated Sheltzer. Not one of the sufferers responded for the reason that mobile sensitivity to ralimetinib exhibited the strongest correlation with EGFR inhibitors. “For those who take a look at the most cancers sorts the place this drug was examined versus the cancer types which might be identified to be pushed by EGFR, there may be simply no overlap,” stated Sheltzer.
“Oftentimes, researchers will develop a drug, they usually see that the drug kills cancer cells. And that shall be sufficient to encourage a trial. However there isn’t any genetic understanding of the way it kills most cancers cells or why it kills most cancers cells. And with out that genetic understanding, you do not truly know which cancer patients to offer it to, as a result of you do not know which biomarkers or genetic alterations to search for in a affected person’s tumor in an effort to give them that drug,” stated Sheltzer.
Scientists want a multi-modal method to focus on the underlying mechanisms of the illness. “If we had this genetic understanding of the drug sooner, then it might need been given to a unique set of sufferers who would have been extra more likely to reply,” stated Sheltzer. Scientists can collect proof utilizing a mixture of instruments together with CRISPR, pharmacogenomic profiling, and structural analysis.
Though additional testing is required, a genetics-first method has broad purposes within the struggle towards most cancers. Genetic evaluation in a multidisciplinary setting is key for bettering the success charge of recent therapies.
Extra data:
Debanjan Bhattacharjee et al, Inhibition of a decrease efficiency goal drives the anticancer exercise of a medical p38 inhibitor, Cell Chemical Biology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.09.013
Offered by
Yale University
Quotation:
Research explains why many most cancers medicine fail throughout medical trials (2023, October 25)
retrieved 25 October 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-10-cancer-drugs-clinical-trials.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post