[ad_1]
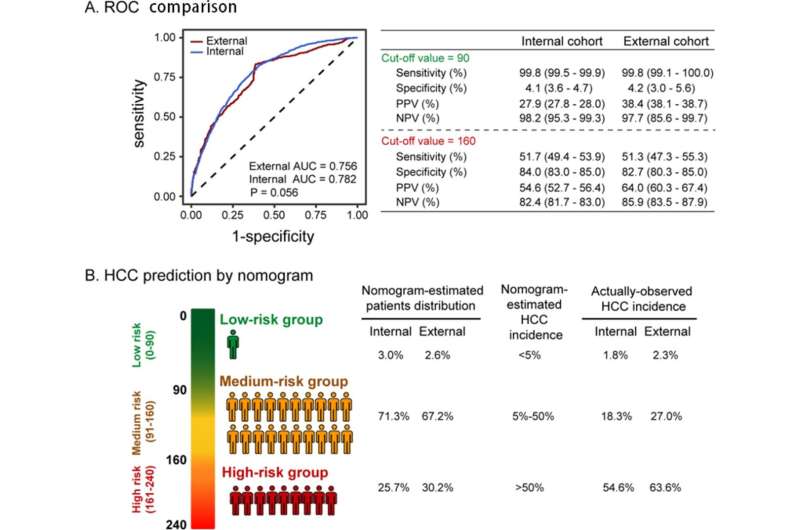
(A) Validation of the nomogram scores. The nomogram rating of every affected person in each inside and exterior cohort was calculated and plotted by ROC. (B) HCC threat stratification by the nomogram. Sufferers with ALD might be categorized into low-risk group (0–90 factors) with lower than 5% chance of HCC, intermediate-risk group (91–160 factors) with about 20.0–50% chance of HCC and high-risk group (161–240 factors) with over 50% chance of HCC. ALD, alcohol-associated liver illness; AUC, space below the curve; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; NPV, detrimental predictive worth; PPV, constructive predictive worth; ROC, receiver working attribute curve. Credit score: Chang B, Tian H, Huang A, et al.
Liver most cancers is the sixth most typical most cancers and the third most frequent reason behind cancer-related dying globally. Nonetheless, its distribution and causes range tremendously throughout totally different areas. Whereas areas like Jap Asia and sub-Saharan Africa see probably the most circumstances, the explanations behind them differ considerably.
In high-income countriesliver most cancers has been on the decline because of widespread new child hepatitis B vaccination and antiviral medication. In the meantime, low-income countries witness a worrying rise, typically linked to elevated hepatitis B and C infections and injectable drug use.
Whereas viral hepatitis stays a serious concern, one other issue is gaining consideration: alcohol consumption. Research present that continual alcohol consumption can straight trigger about 10% of most cancers circumstances in males and three%, respectively, in ladies. In reality, a examine on the Mayo Clinic revealed that alcoholic cirrhosis was the primary offender in 29% of sufferers with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the commonest liver most cancers kind.
However the examine does not simply sound the alarm; it additionally provides a possible answer. Researchers recognized key threat components for HCC in individuals with alcohol-related liver diseasetogether with heavy drinkingage, diabetes, male intercourse, and liver cirrhosis. Based mostly on these components, they developed a novel software known as a nomogram that may predict HCC threat with excessive accuracy and ease of use.
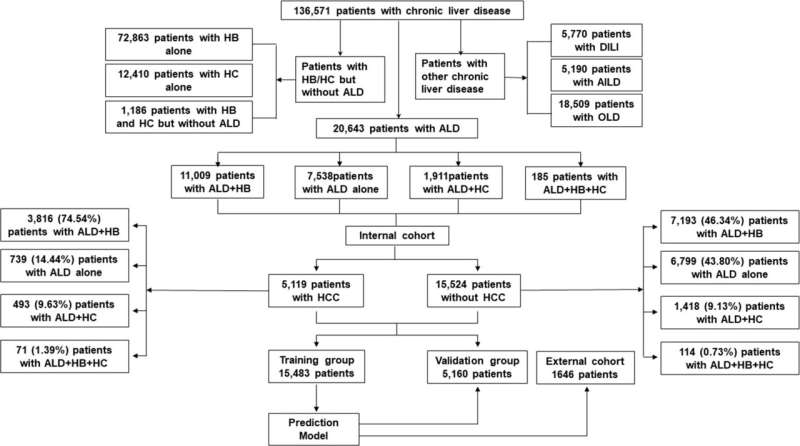
AILD, autoimmune-induced liver illness (together with autoimmune hepatitis, major biliary cirrhosis and first sclerosing cholangitis); ALD, alcohol-associated liver illness; DILI, drug-induced liver damage; HB, hepatitis B; HC, hepatitis C; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; OLD, different liver ailments (together with non-alcoholic fatty liver illness, Wilson’s illness, Buddi-Chiari syndrome, liver damage with unknown causes, and so on). Credit score: Chang B, Tian H, Huang A, et al.
This nomogram might be a game-changer for medical doctors, permitting them to personalize therapy plans and determine people on the highest threat for HCC. Early intervention might save lives and stop pointless struggling.
This examine underscores the rising public well being concern of alcohol-related liver most cancers. The newly developed nomogram provides a helpful software for medical doctors to determine high-risk people and personalize therapy plans, probably saving lives and stopping pointless struggling.
Whereas the examine gives helpful insights, it acknowledges limitations like its retrospective nature and the necessity for additional validation in bigger, potential research. Moreover, incorporating different components like smoking, genetics, and dietary habits might additional enhance the prediction mannequin.
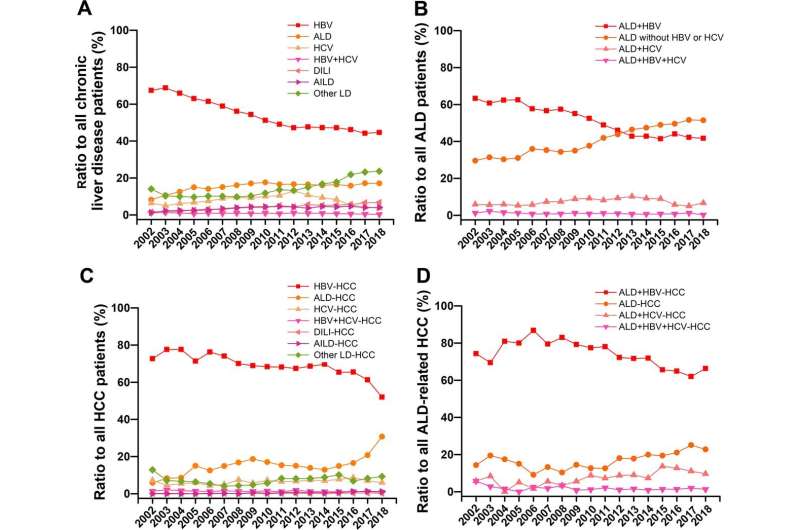
(A) Change of aetiology in the whole enrolled sufferers with continual liver ailments. (B) Change of aetiology within the sufferers with alcohol-associated liver illness (ALD). (C) Change of aetiology within the sufferers with HCC. (D) Change of aetiology within the sufferers with ALD-related HCC. AILD, autoimmune-induced liver illness; DILI, drug-induced liver damage; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HCV, hepatitis C virus. Credit score: Chang B, Tian H, Huang A, et al.
The researchers additionally spotlight the necessity for future analysis on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its hyperlink to liver most cancers, as this space stays under-investigated.
Total, this examine shines a lightweight on the rising risk of alcohol-related liver cancer and provides a promising software for early detection and intervention. Additional analysis and public well being efforts are essential to fight this rising well being problem.
The findings are published within the journal eGastroenterology.
Extra data:
Binxia Chang et al, Prevalence and prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma in alcohol-associated liver illness: a retrospective examine of 136 571 sufferers with continual liver ailments, eGastroenterology (2024). DOI: 10.1136/egastro-2023-100036
Supplied by
First Hospital of Jilin College
Quotation:
Rising alcohol-related liver most cancers prompts new prediction software (2024, March 5)
retrieved 6 March 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-03-alcohol-liver-cancer-prompts-tool.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post