[ad_1]
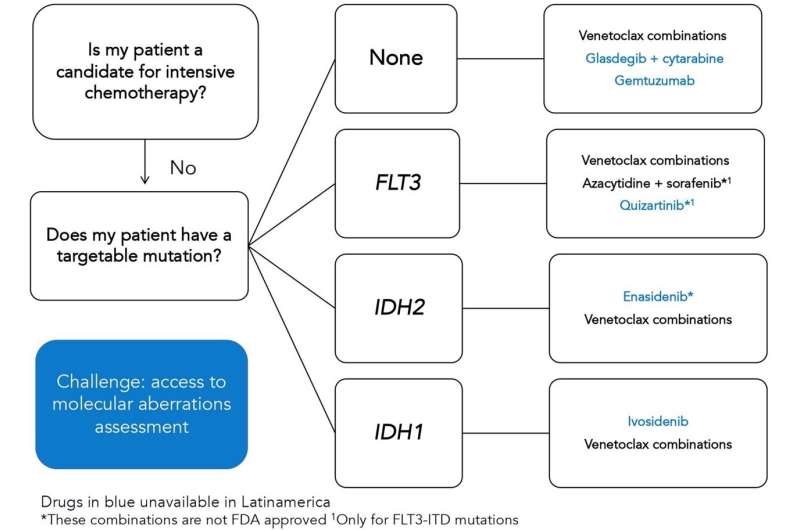
Tailored therapy algorithm for sufferers with acute myeloid leukemia who judged to not be candidates for intensive chemotherapy. Credit score: Hematology (2023). DOI: 10.1080/16078454.2022.2158015
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a most cancers kind that originates within the bone marrow. Regardless of being thought-about a uncommon illness, it’s the most typical kind of acute leukemia and progresses quickly, necessitating speedy therapy.
Whereas many developments have been made within the illness’s therapy, these sources aren’t totally accessible in underdeveloped nations. This case has prompted Latin American scientists to hunt a complete understanding of AML on their continent, primarily specializing in the therapies and diagnostic strategies obtainable for this inhabitants.
The research, published in the Hematology Science Journalprimarily based on the evaluate of epidemiological data and was coordinated by the D’Or Institute for Analysis and Training (IDOR), in partnership with the College of São Paulo (USP), the Autonomous College of Nuevo Leon, and the Nationwide Institute of Medical Sciences and Diet Salvador Zubirán.
It additionally had the help of collaborators in 15 Latin American nations. “Research like this present alternatives for glorious scientific collaborations as a result of usually one nation has extra experience in sure strategies or therapies. This alternate of information generates human sources for Latin America,” says the analysis coordinator, Dr. Eduardo Rego, a hematologist researcher at IDOR and a professor on the College of São Paulo (USP).
Leukemia happens when the bone marrow, accountable for producing blood cells equivalent to red blood cells (erythrocytes) and white blood cells (leukocytes), begins to supply and launch immature cells known as blasts into the bloodstream in a disordered method. These blasts don’t perform like grownup cells and start to hurt different organs within the physique. Within the case of AML, it’s noticed a proliferation of myeloid cells, normally leukocytes, and, extra hardly ever, mast cells or macrophages.
AML analysis is extra frequent in adults, particularly the aged, however it could actually additionally happen in youngsters.
Specialised instruments are employed for the analysis of the illness, equivalent to move cytometry (used to depend and classify cells within the blood), cytogenetic evaluations (which embrace studying the karyotype and figuring out chromosomal abnormalities), and molecular checks (with mutation evaluation) to information applicable therapies.
Present suggestions embrace utilizing 8-color flow cytometry to determine immunological markers, however this useful resource will not be at all times obtainable in Latin America, the place most laboratories nonetheless work with 4 colours, lowering the accuracy of the examination to determine residual illness in affected person samples.
Moreover, whereas complete genetic testing is already a actuality in developed nations, some Latin American nations nonetheless wrestle with standardizing karyotype checks, the method accountable for learning the affected person’s chromosomal abnormalities. In keeping with the research, between 2010 and 2018, a profitable karyotype evaluation was carried out in 46% to 61% of instances, indicating the necessity for higher coaching of groups in Latin America.
That is along with the accessibility limitations of those checks, which might even surpass the therapy prices.
The provision of therapies for acute myeloid leukemia additionally varies between high- and low-income nations, displaying heterogeneity even amongst Latin American nations.
In one of many major therapies for AML, intensive induction chemotherapy, whose foremost goal is to remove a big portion of cancerous blasts, the early mortality charge varies between 3% and 6%, in accordance with latest medical trials. Nevertheless, when carried out in low- and middle-income countriesthese charges improve; in Brazil, it reaches 41% amongst older adults.
The authors consider that this disparity could possibly be decreased by means of pressing therapy measures for sufferers with extremely elevated white blood cell counts, as they’ve the very best mortality charge throughout induction therapy. One other challenge is the affected person’s profile, as many have already got comorbidities that worsen the illness.
Moreover, therapy delays as a result of ready for genomic outcomes and shortages of chemotherapy as a result of mismanagement of presidency sources are additionally fixed obstacles confronted in Latin American nations.
“One attention-grabbing side of this research is that we in contrast facets of acute myeloid leukemia not solely between Latin America and developed nations but in addition amongst Latin American nations themselves. It is a extremely heterogeneous situation, even inside Brazil. Within the nation, we’ve a larger focus of sources within the Southeast area, which additionally displays within the availability of AML therapies,” the researcher notes.
Along with chemotherapy, one other important therapy for extreme instances of AML is bone marrow transplantation, now known as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. On this method, the illness is handled extra aggressively with identified marrow-toxic medicine, and restoration happens from the affected person’s younger cells or from donor cells. When a affected person’s cells are used, it’s known as autologous transplantation, and when cells come from a donor, it’s known as allogeneic.
In Latin America, the haploidentical donation has been a big facilitator of allogeneic transplants. On this methodology, solely 50% compatibility is required for the transplant, which is normally performed by a first-degree relative of the affected person.
This medical advance avoids ready for a extra suitable volunteer, a problem that’s tough to beat when most Latin American nations lack unrelated donor registries, with Brazil being an exception by means of the Brazilian Registry of Volunteer Bone Marrow Donors (REDOME).
Within the absence of donors, the research additionally considers that autologous transplantation ought to be an efficient and economical possibility in Latin America, because it reduces the possibility of antagonistic results equivalent to the necessity for blood transfusion and hospitalizations.
The article mentions that this technique was studied in earlier analysis, the place autologous transplants have been carried out in sufferers after chemotherapy therapy. The general survival of members at two years ranged from 74% to 79%, with a disease-free survival of 61%.
Primarily based on the specifics of AML analysis and therapy in Latin America, the authors emphasize that scientific collaborations led by Latin American researchers are paramount to raised adapting therapies to the wants of those nations. Additionally they stress the significance of investing in medical schooling and accessible therapies in Latin America and different low- and middle-income nations going through comparable challenges and disparities associated to the illness.
Extra data:
Andrés Gómez-De León et al, Acute myeloid leukemia: challenges for analysis and therapy in Latin America, Hematology (2023). DOI: 10.1080/16078454.2022.2158015
Offered by
D’Or Institute for Analysis and Training
Quotation:
Useful resource shortages and technological lag stay obstacles for acute myeloid leukemia therapy in Latin America (2024, January 5)
retrieved 5 January 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-01-resource-shortages-technological-lag-obstacles.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post