[ad_1]
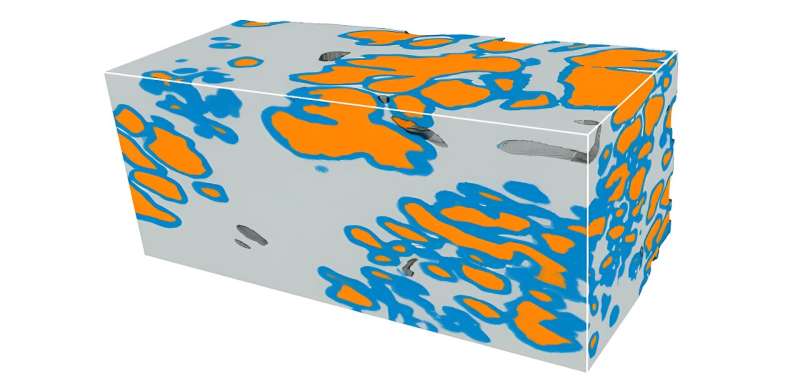
Microscopic glands of the prostate are segmented (coloured) with the brand new deep-learning pipeline; the picture exhibits a prostate most cancers tissue quantity, measuring roughly 1 x 1 x 2 mm in dimension. The prostate glands type a branching-tree community; orange areas characterize the lumen (inside) of the glands, blue areas characterize the epithelium (edges) of the glands, and grey areas are the encompassing stroma. The morphology of prostate glands, as seen on 2D histology slides, is presently the premise for figuring out how aggressive a most cancers is (prognostication), and what remedies are required for particular person sufferers. Precisely segmenting and characterizing these glands in 3D inside the context of enormous 3D pathology datasets has the potential to enhance these prognostic determinations and significant therapy selections. Credit score: Rui Wang, College of Washington.
Prostate most cancers stands as a prevalent risk to males’s well being, rating second in cancer-related deaths in america. Every year, roughly 250,000 males within the U.S. obtain a prostate most cancers prognosis. Whereas most instances have low morbidity and mortality charges, a subset of instances calls for aggressive therapy.
Urologists assess the necessity for such therapy primarily by way of the Gleason rating, which evaluates prostate gland look on histology slides. Nevertheless, there’s appreciable variability in interpretation, resulting in each undertreatment and overtreatment.
The present technique, based mostly on histology slides, has limitations. Solely a small fraction of the biopsy is seen in 2D, risking missed essential particulars, and interpretations of complicated 3D glandular constructions may be ambiguous when seen on 2D tissue sections. Furthermore, standard histology destroys tissue, limiting downstream analyses.
To deal with these shortcomings, researchers have developed nondestructive 3D pathology methodsproviding full imaging of biopsy specimens whereas preserving tissue integrity.
Current developments embody methods for acquiring 3D pathology datasets, enabling improved risk assessment for prostate most cancers.
Research published in Journal of Biomedical Optics harnesses the total energy of 3D pathology by growing a deep-learning mannequin to enhance the 3D segmentation of glandular tissue constructions which might be vital for prostate most cancers danger evaluation.
The analysis workforce, led by Professor Jonathan T. C. Liu from the College of Washington in Seattle, skilled a deep-learning mannequin, nnU-Web, instantly on 3D prostate gland segmentation knowledge obtained from earlier complicated pipelines.
Their mannequin effectively generates correct 3D semantic segmentation of the glands inside their 3D datasets of prostate biopsies, which had been acquired with open-top light-sheet (OTLS) microscopes developed inside their group. The 3D gland segmentations present worthwhile insights into the tissue composition, which is essential for prognostic analyses.
Liu says, “Our outcomes point out nnU-Web’s outstanding accuracy for 3D segmentation of prostate glands even with restricted coaching knowledge, providing a less complicated and sooner various to our earlier 3D gland-segmentation strategies. Notably, it maintains good efficiency with lower-resolution inputs, probably decreasing useful resource necessities.”
The brand new deep-learning-based 3D segmentation mannequin represents a major step ahead in computational pathology for prostate most cancers. By facilitating correct characterization of glandular constructions, it holds promise for guiding vital therapy selections to enhance affected person outcomes finally.
This development underscores the potential of computational approaches in enhancing medical diagnostics. Transferring ahead, it holds promise for personalised drugs, paving the best way for simpler and focused interventions.
Transcending the constraints of standard histology, computational 3D pathology gives the power to unlock worthwhile insights into disease progression and to tailor interventions to particular person affected person wants. As researchers proceed to push the boundaries of medical innovation, the hunt to overcome prostate cancer enters a brand new period of precision and chance.
Extra info:
Rui Wang et al, Direct three-dimensional segmentation of prostate glands with nnU-Web, Journal of Biomedical Optics (2024). DOI: 10.1117/1.JBO.29.3.036001
Quotation:
Researchers use microscopy plus deep studying to advance prostate most cancers prognosis (2024, March 11)
retrieved 11 March 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-03-microscopy-deep-advance-prostate-cancer.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post