[ad_1]
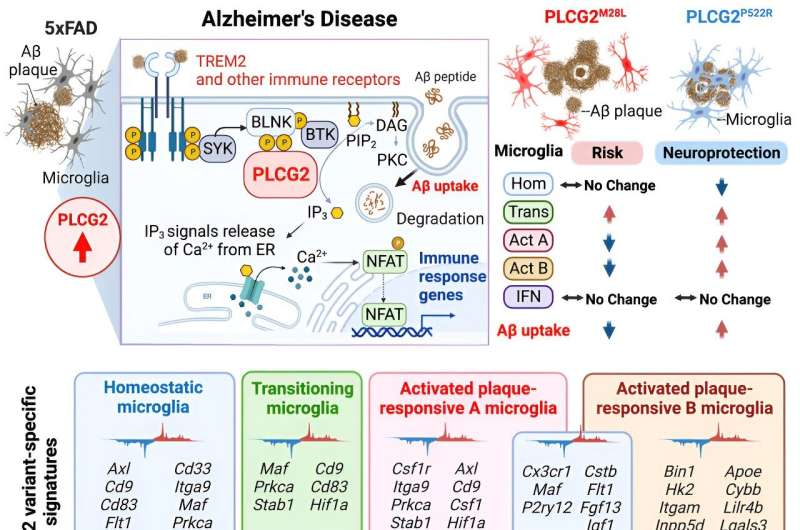
A examine led by specialists from Indiana College College of Drugs has shed new gentle on the genetic underpinnings of Alzheimer’s illness. The workforce’s analysis, rooted in human genetics research, has unearthed a essential mutation inside a key gene working within the mind’s immune cells, probably elevating the chance of Alzheimer’s illness.
The analysis workforce included a number of IU investigators inside Stark Neurosciences Analysis Institute—Gary Landreth, Ph.D., the Martin Professor of Alzheimer’s Analysis; Bruce Lamb, Ph.D., government director of Stark Neuroscience Analysis Institute; Stephanie Bissel, Ph.D., assistant professor of genetics; Kwangsik Nho, Ph.D., affiliate professor of radiology and imaging sciences; and Adrian Oblak, Ph.D., assistant professor of radiology and imaging sciences.
Their analysis was recently published in the journal Immunity.
Andy Tsai, Ph.D., a graduate of the Medical Neurosciences Graduate Program, was the driving force behind the analysis, encompassing his Ph.D. thesis. Tsai, now a postdoctoral fellow at Stanford College Medical College, has considerably contributed to unraveling the mysteries of Alzheimer’s illness.
The focus of the investigation revolved across the phospholipase C gamma 2 (PLCG2) gene, intricately entwined inside microglia—central to the mind’s immune response. This genetic anomaly, found by way of evaluation of the gene’s organic workings, showcased the impression of particular uncommon variants. The examine discovered that the M28L variant heightened the susceptibility to Alzheimer’s illness, whereas the P522R variant exhibited a risk-reducing impact.
Revolutionary mouse fashions of Alzheimer’s illness developed by the MODEL-AD Heart allowed researchers to substantiate their findings. Immune cells harboring risk-reducing gene variants demonstrated a discount in amyloid plaques, whereas these carrying the risk-elevating variants exhibited a surge in plaque accumulation. The examine unveiled particular gene clusters orchestrating these alterations in immune cell habits inside microglia.
Microglia, usually thought to be the mind’s first line of protection in opposition to infections, toxins and injury, has garnered consideration for its important position in influencing illness susceptibility.
“The microglial response impacts neurons which then impacts the capability to be taught and type new reminiscences,” Landreth mentioned.
Intensive collaboration inside Stark Neurosciences Analysis Institute enabled a complete analysis of the gene’s implications. This included a comparability between preclinical information from animal fashions and real-world human information on Alzheimer’s illness.
“This represents a collaboration that might’ve solely been achieved at Stark,” Landreth mentioned. “We used human genetics to analyze and determine a mechanism, and certainly we’ve.”
The examine’s paramount significance lies in explaining the essential position of microglial immune responses and their potential to impression illness danger, positively or negatively. This discovery guarantees to reshape the understanding of Alzheimer’s illness and carve a path towards focused therapeutics, which is being pursued by the TREAT-AD Heart.
Extra info:
Andy P. Tsai et al, Genetic variants of phospholipase C-γ2 alter the phenotype and performance of microglia and confer differential danger for Alzheimer’s illness, Immunity (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.08.008
Quotation:
Researchers determine new gene mutation that alters Alzheimer’s illness danger (2023, September 6)
retrieved 6 September 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-09-gene-mutation-alzheimer-disease.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post