[ad_1]
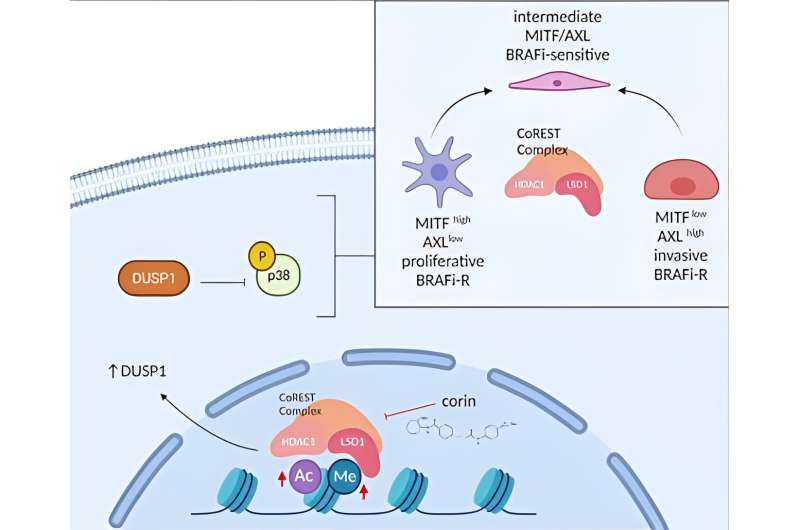
Credit score: Journal of Medical Investigation (2024). DOI: 10.1172/JCI171063
One of many main challenges in most cancers analysis and medical care is knowing the molecular foundation for therapeutic resistance as a significant reason for long-term remedy failures. In instances of melanoma, the principle focused therapeutic technique is directed in opposition to the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Sadly, within the overwhelming majority of those sufferers, resistance to MAPK inhibitor therapies develops inside one 12 months of remedy.
In a brand new research from Boston College Chobanian & Avedisian Faculty of Drugs, researchers have recognized a selected epigenetic pathway concerned within the improvement of therapy resistance in melanoma and have recognized a promising chemical reagent that may efficiently resensitize therapy-resistant cancers to focused therapies.
The work is published within the Journal of Medical Investigation.
“Though the cancer research neighborhood has been very profitable in creating particular focused therapies for the genetic occasions driving many cancers, most sufferers are unable to be cured of their cancers resulting from acquired resistance mechanisms. We’re excited in regards to the broader implications this research has for the potential remedy of sufferers with acquired resistance to most cancers therapies,” mentioned co-corresponding writer Rhoda Alani, MD, the Herbert Mescon Chair of Dermatology on the college.
In collaboration with investigators from Brigham and Ladies’s Hospital and Harvard Medical Faculty, the researchers used each cancer cell lines grown within the lab and human melanoma tumors grown in experimental fashions to guage the epigenetic influences related to melanoma development, and their response to focused therapies.
They decided {that a} important resistance mechanism for melanoma entails the epigenetic mediator, CoREST, and that this remedy resistance will be focused by corin, a not too long ago designed dual-functioning small molecule inhibitor of CoREST. The research supplies the molecular rationale for the way CoREST complicated concentrating on will be harnessed for an essential therapeutic aim in a broad vary of epigenetic contexts, together with melanoma.
Alani expects the medical implications for this analysis to be important as it’s probably that comparable epigenetic occasions are related to remedy resistance in different cancers, and that the event of novel high-specificity epigenetic inhibitors like corin might permit for the resensitization of those tumors to efficient focused therapies and potential illness remission.
The researchers hope this research will result in the event of extra particular focused epigenetic therapies for most cancers and different ailments with minimal unwanted effects.
“We additionally anticipate that these research will end result within the improved efficacy of anticancer focused medicine whereas limiting the event of drug resistance in cancers by way of the mixed use of focused epigenetic therapies,” added Alani, who is also chief of dermatology at Boston Medical Middle.
Along with Alani, the opposite corresponding writer is Philip Cole, MD, Ph.D., (Brigham and Ladies’s Hospital and Harvard Medical Faculty).
Extra data:
Muzhou Wu et al, The CoREST Repressor Complicated Mediates Phenotype Switching and Remedy Resistance in Melanoma, Journal of Medical Investigation (2024). DOI: 10.1172/JCI171063
Supplied by
Boston University School of Medicine
Quotation:
Researchers establish crucial pathway liable for melanoma drug resistance (2024, February 1)
retrieved 1 February 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-02-critical-pathway-responsible-melanoma-drug.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post