[ad_1]
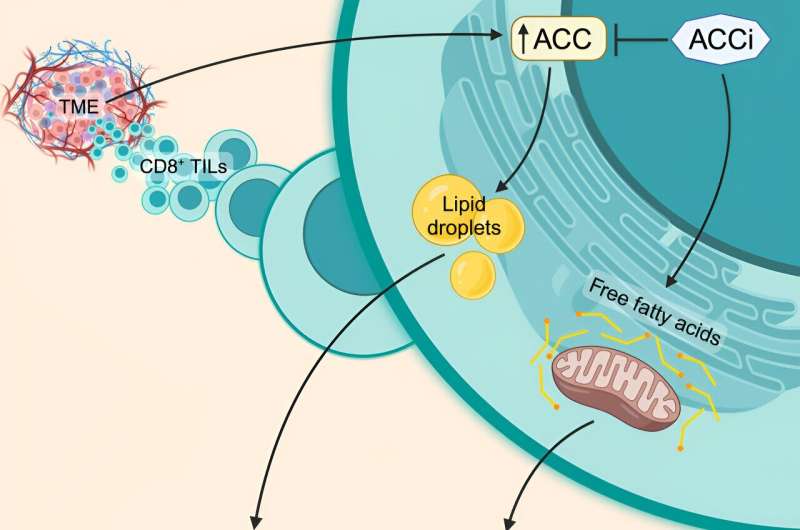
Graphical Summary. Credit score: Cell Metabolism (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.02.009
T cells are sometimes referred to as “assassins” or “killers” as a result of they’ll orchestrate and perform missions to seek out micro organism, viruses, and most cancers cells all through the physique. Mighty as they might be, current analysis has proven that when T cells infiltrate the setting of a stable tumor, they lose the vitality wanted to fight the most cancers.
A analysis group led by Jessica Thaxton, Ph.D., MsCR, affiliate professor of cell biology and physiology and co-leader of the Most cancers Cell Biology Program on the UNC Lineberger Complete Most cancers Middle, aimed to know why T cells don’t maintain vitality in tumors.
Utilizing their experience in tumor immunity and metabolism, the Thaxton Lab, led by Katie Hurst, MPH, and 4th 12 months graduate scholar Ellie Hunt, discovered {that a} metabolic enzyme referred to as Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase (ACC) causes T cells to retailer fats fairly than burning fats for vitality.
“Our discovery fills a long-standing hole in information concerning why T cells in stable tumors do not appropriately generate vitality,” stated Thaxton. “We inhibited the expression of ACC in mouse most cancers fashions, and we noticed that T cells have been capable of persist significantly better in stable tumors.”
The brand new findings and immunotherapeutic methods, which have been published in Cell Metabolismmight be used to make a number of varieties of T-cell therapies simpler for sufferers, probably encompassing each checkpoint and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies.
Within the area of most cancers immunotherapy, it has lengthy been recognized that T cells aren’t capable of create their mobile vitality, referred to as adenosine triphosphate or ATP, when they’re inside a stable tumor.
In 2019, Thaxton’s lab studied a T cell with optimum antitumor operate. In a publication in Most cancers Immunology AnalysisHurst and Thaxton used a proteomics display to determine enzymes related to the optimum antitumor metabolism of those T cells. By this display, the 2 found that ACC expression might restrict the flexibility of T cells to make ATP in tumors. ACC, a key molecule that’s concerned in lots of metabolic pathwaysblocks cells from breaking down fats and utilizing it as gas for vitality in mitochondria.
“Acetyl-CoA carboxylase can drive the stability between storing lipids versus breaking down these lipids and feeding them into the citric acid cycle for vitality,” stated Thaxton. “If ACC is flipped ‘on’, cells typically retailer lipid. If ACC is ‘off’, cells have a tendency to make use of the lipid of their mitochondria to make ATP.”
Utilizing Hunt’s experience in confocal imaging, the analysis group was capable of observe lipid shops in T cells remoted from a number of varieties of cancers. The commentary, in addition to different experiments, confirmed the group’s speculation that T cells have been storing lipids as an alternative of breaking them down.
Thaxton’s group then used CRISPR Cas9-mediated gene deletion to see what would occur in the event that they “deleted” ACC from the image. There was a fast discount within the quantity of lipid storage in T cells, and the group was capable of visualize fats relocating to the mitochondria for use to generate vitality.
Thaxton now hypothesizes that T cells may have a “delicate stability” of lipids to persist in solid tumors with a certain quantity of lipid devoted to most cancers cell assassination and low ranges of fat being maintained in shops.
The newest findings may show to be helpful in enhancing chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies. This cutting-edge know-how takes T cells out of cancer patientsmodifies them within the lab to seek out tumor cells, after which re-infuses the cells to combat the affected person’s most cancers. Preliminary knowledge from Thaxton’s lab demonstrates that even the manufactured T cells include extra lipid shops.
The lab is beginning to take a look at affected person samples to know how researchers can probably flip the ACC metabolic change immediately in affected person tumors, negating the necessity to take out and reinfuse cells again into the physique. However researchers should first decide how this might have an effect on different immune cell populations within the physique, reminiscent of macrophages.
Extra info:
Elizabeth G. Hunt et al, Acetyl-CoA carboxylase obstructs CD8+ T cell lipid utilization within the tumor microenvironment, Cell Metabolism (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.02.009
Quotation:
Researchers acquire perception into why T cells lose vitality in stable tumors (2024, March 15)
retrieved 17 March 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-03-gain-insight-cells-energy-solid.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post