[ad_1]
Credit score: Cell Studies Drugs (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101359
Medical doctors have almost a dozen new focused medicine to deal with sufferers with acute myeloid leukemia, or AML, but three of 4 sufferers nonetheless die inside 5 years. Some sufferers succumb inside only a month or two, regardless of the battery of medication used to deal with the aggressive blood illness, the place blood cells do not develop correctly.
A brand new examine attracts on a area of science referred to as proteogenomics to attempt to enhance the outlook. In a paper published Jan. 16 in Cell Studies Drugsscientists report new findings about how drug resistance in some AML sufferers develops and the way docs would possibly sometime cease or sluggish the method.
The analysis comes from a staff of researchers from the Division of Power’s Pacific Northwest Nationwide Laboratory and Oregon Well being & Science College. For almost a decade, OHSU and PNNL researchers have labored collectively to fill a important hole in our data of how most cancers and different illnesses occur. At one finish of the spectrum, our physique’s genes can go awry, creating mutations that may be dangerous or lethal. On the different finish of the spectrum is an actual individual whose life is affected and even ended in consequence.
What occurs within the center, between the genes and the individual’s well being?
The reply: a dizzying variety of complicated molecular processes that scientists are grappling to know. On the middle are the physique’s proteins and a area of examine referred to as proteogenomics.
Sorting the info with machine studying
The PNNL-OHSU staff is learning 1000’s of proteins that would play a job in AML. Proteins are the physique’s molecular workhorses, ferrying vitamins and different provides forwards and backwards between cells, turning genes on or off, and sustaining dozens of fundamental physique processes.
Though genes get the glory, they do little on to maintain our our bodies going. That is the job of proteins. For almost 20 years, examine writer Karin Rodland of OHSU, previously of PNNL, has been a pioneer exploring the position of proteins in well being and illness, constructing a program with OHSU and PNNL colleagues to check AML.
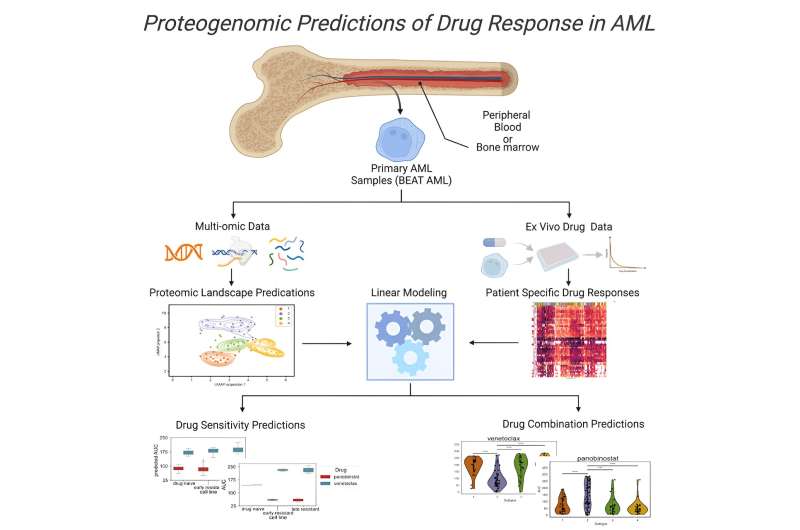
Within the newest examine, a staff led by Sara Gosline, an information scientist and computational biologist at PNNL, did an exhaustive examine of the protein exercise in 210 sufferers with AML. Altogether, the staff measured ranges of almost half one million items of proteins from greater than 9,000 proteins in sufferers’ blood samples.
The staff mixed these findings with in depth information already recognized concerning the illness—the genes and mutations concerned, the molecular messengers that point out which genes are lively, and the results of 46 medicine on AML sufferers, together with details about how the illness progressed in these sufferers.
“We have been ready to have a look at patterns of drug responses in lots of of individuals by together with protein and gene measurements collectively, and this gave us a stage of element that hasn’t been potential in prior research,” mentioned Gosline. “It is a nice instance the place we’re in a position to put our rising data of protein signaling and machine studying fashions to profit sufferers sooner or later.”
Gosline and colleagues, together with first writer James Pino of PNNL, deployed synthetic intelligence, utilizing a number of machine studying algorithms to make sense of the info.
Beating drug resistance
Whereas the examine yielded a load of knowledge about what occurs within the physique of an AML affected person, one discovering stood out, pointing to a potential option to sidestep or delay drug resistance for some sufferers.
The staff confirmed that remedy with quizartinib, permitted final 12 months to deal with AML, can shift how most cancers cells reply to different medicine usually utilized in mixture to deal with sufferers.
Particularly, the staff discovered that when sufferers on quizartinib cease responding to venetoclax, docs would possibly think about switching to a different drug, panobinostat. It is an instance of how proteogenomic info may alter the roadmap that docs use to navigate which medicines sufferers obtain at totally different phases of the illness.
“The issue is that most cancers retains evolving,” mentioned Gosline. “You hit the tumor with one drug and the tumor adjustments. That is what occurs when sufferers expertise drug resistance and the medicines cease working. Our examine helps us perceive precisely how this occurs and what could be performed in response. Which remedy is finest to show to?”
AML poses a selected problem, mentioned examine writer Cristina Tognon at OHSU.
“Once you deal with a tumor with a drug, you’re placing stress on the tumor cells as they struggle to determine a option to escape that stress and survive. It is a large drawback in AML sufferers. What’s much more troublesome is that in AML, there are lots of mutations at work; the illness does not are available in only one taste,” mentioned Tognon, who’s an affiliate analysis professor and scientific director of the Druker Laboratory at OHSU.
In the end, the staff targeted on 147 proteins and particular molecular places referred to as phosphosites that play a key position in figuring out which proteins are turned on and that are off.
Utilizing simply the protein information, the staff sorted the samples into 4 distinct teams that predicted how the sufferers fared. Sufferers whose samples positioned them in one of many teams had a greater prognosis than the others, surviving way over 5 years. Medical doctors hope that the sort of info will finally develop into accessible within the clinic. That might permit some sufferers who don’t want aggressive therapies with extreme unintended effects to keep away from them whereas assuring that sufferers who’ve the worst prognosis are handled as aggressively as potential.
“There may be potential for medical functions to be derived from this work, for instance, diagnostics, similar to protein biomarkers to foretell responses to therapies, and the design of recent drug mixtures which may outperform present ones,” mentioned OHSU’s Jeff Tyner, professor of drugs on the OHSU Faculty of Drugs and Knight Most cancers Institute.
The work is the most recent of greater than 200 research which have checked out protein exercise in lots of types of most cancers, together with colon, mind, endometrial, mind, blood and ovarian cancers. An OHSU-PNNL staff mentioned the rising position of proteins for treating sufferers with precision drugs in a recent article within the Annual Evaluations of Pharmacology and Toxicology. An increasing number of, scientists are utilizing proteomics—the examine of proteins—to bridge the hole between genomics (the examine of genes) to phenomics (phenotypes or observable traits).
Extra info:
James C. Pino et al, Mapping the proteogenomic panorama allows prediction of drug response in acute myeloid leukemia, Cell Studies Drugs (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101359
Sunil Okay. Joshi et al, Mass Spectrometry–Primarily based Proteogenomics: New Therapeutic Alternatives for Precision Drugs, Annual Evaluate of Pharmacology and Toxicology (2023). DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-022723-113921
Offered by
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Quotation:
Proteins counsel a path to cut back drug resistance in a type of most cancers (2024, February 2)
retrieved 3 February 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-02-proteins-path-drug-resistance-cancer.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post