[ad_1]
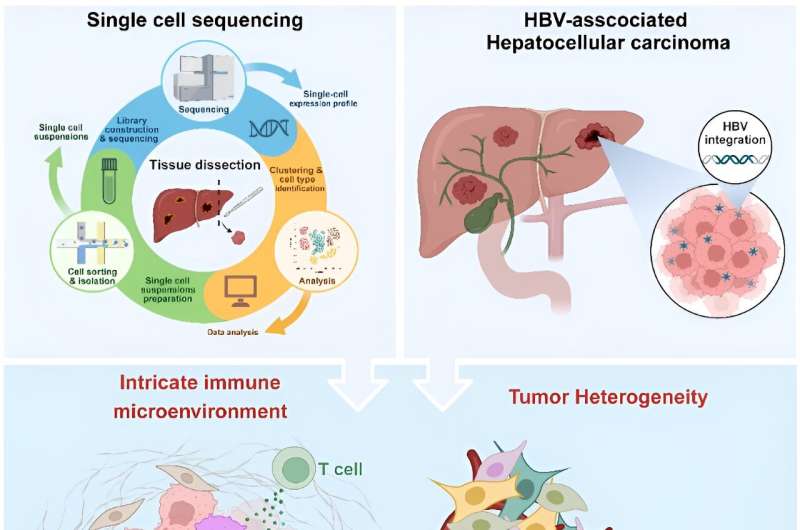
The intricate immune microenvironment, tumor cell plasticity, and dynamics of tumor evolution pose daunting challenges to the definition of tumor ecosystems in HBV-HCC. Single-cell sequencing holds nice promise for reinforcing the understanding of the tumor immune microenvironment and tumor heterogeneity of HBV-HCC, opening new views on the HBV-HCC tumor ecosystem. Credit score: MedComm – Oncology (2023). DOI: 10.1002/mog2.60
HBV-related HCC poses a major international well being problem, characterised by its mobile range and sophisticated tumor immune microenvironment. The growing unmet want in HBV-HCC therapy highlights the necessity for a deeper understanding of the function of the intricate immune microenvironment, tumor cell plasticity, and dynamics of tumor evolution in HBV-associated hepatic carcinogenesis.
Single-cell sequencing has emerged as a revolutionary device in cancer researchoffering a complete image of the most cancers’s development and the various pathways concerned. The appliance of single-cell sequencing in HBV-HCC has been instrumental in dissecting tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment and heterogeneity, providing an unprecedentedly detailed perception into the HBV-HCC tumor ecosystem.
A new review printed in MedComm—Oncology commences with an outline of the progress made in HCC analysis by scRNA-seq evaluation, and systematically introduces the fundamental workflow, limitations, and enhancements of scRNA-seq. One of many focal factors of this assessment is how scRNA-seq has enhanced our understanding of malignant tumor cell heterogeneity in HBV-HCC.
Tumor heterogeneity serves as a pivotal assist for the survival and additional evolution of HBV-HCC below varied selective pressures. The lack of know-how of ITH in HBV-HCC has existed as a troublesome difficulty for a few years. scRNA-seq has revolutionized the exploration of tumor heterogeneity in HBV-HCC, opening up a spread of recent avenues to visualise intratumoral and intertumoral heterogeneity, monitor tumor development, and forestall additional mobile deterioration.
The research of the genetic range and clonal construction of tumor cells inside HBV-HCC by single-cell sequencing not solely lays a theoretical basis for exact scientific classification but additionally presents potential exact therapeutic choices based mostly on molecular characterization. This will facilitate the invention of novel biomarkers for analysis and prognostic efficacy.
Along with heterogeneity, the assessment emphasizes immune profiling inside the HBV-HCC tumor microenvironment. Not like different tumors, the mobile and molecular immune imbalance in HBV-HCC is notably complicated.
On the one hand, TME of HBV-HCC is flooded with considerable antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and immune cellsthrough which suppressive immune cells and tumor cells drive the dysfunction of effector cells. Then again, liver harm induced by power liver irritation upon extended publicity to HBV an infection propels the dysregulation of TME.
scRNA-seq has make clear the chaos and dynamics of the immune microenvironment, figuring out varied cell fractions exerting an influential function within the growth of HBV-HCC, corresponding to CD69+ CD103+ HBV-specific Trm cells, LAYN+ Tregs, CCL18+ M2 macrophages, LAMP3+ DCs and TANs. It proposed a attainable implementation of immune escape mechanisms, contributing to the identification of potential immune targets and the advance of immunotherapy.
This complete assessment not solely sheds gentle on the present state of HBV-HCC analysis but additionally charts a course for future investigations. It underscores the pivotal function of integrating single-cell information with different omics information in advancing our understanding and therapy of HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.
This integrative strategy is essential to unraveling the complexity of HBV-HCC and creating simpler therapies. Lastly, the authors summarize the present limitations and potential options of single-cell sequencing in HBV-HCC analysis.
This assessment serves as a pivotal useful resource for readers looking for novel insights into single-cell sequencing in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HBV-HCC) analysis. It methodically assembles the core analytical approaches at the moment employed in HBV-HCC single-cell research, shedding gentle on the roles of assorted mobile subpopulations and the evolutionary dynamics of clones within the growth and development of HBV-HCC.
By presenting this info in a structured and accessible format, the assessment not solely gives a useful reference for future HBV-HCC investigations but additionally guides the scientific neighborhood towards deeper insights and simpler interventions within the battle towards HBV-HCC.
Extra info:
Dandan Yin et al, Novel insights into HBV‐hepatocellular carcinoma at single‐cell sequencing, MedComm—Oncology (2023). DOI: 10.1002/mog2.60
Supplied by
Sichuan Worldwide Medical Alternate and Promotion Affiliation
Quotation:
Novel insights into HBV-hepatocellular carcinoma at single-cell sequencing (2023, December 14)
retrieved 15 December 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-12-insights-hbv-hepatocellular-carcinoma-single-cell-sequencing.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post