[ad_1]
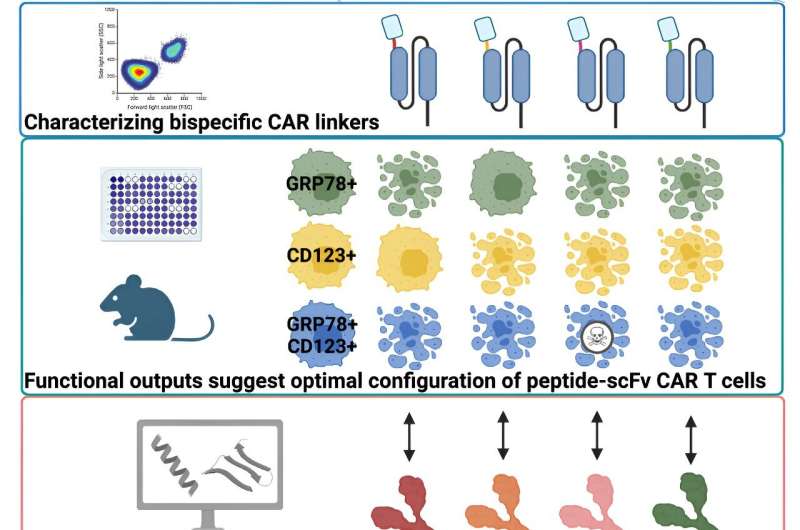
Graphical Summary. Credit score: Cell Stories Drugs (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101422
St. Jude Kids’s Analysis Hospital scientists have improved chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T–cell immunotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), demonstrating higher efficacy within the lab.
To beat widespread issues with CAR T cells, the researchers created a further means for the remedy to seek out and eradicate cancer cellsutilizing a small peptide. The research additionally confirmed how a computational method incorporating AlphaFold predicted protein fashions may assist perceive how construction impacts antigen recognition and remedy efficacy.
Their findings are published within the journal Cell Stories Drugs.
Immunotherapy that reprograms a affected person’s personal immune cells to focus on a cancer-specific protein, CAR T–cell remedy, has proven success in treating some relapsed leukemias. Nonetheless, generally the therapy is unsuccessful as a result of most cancers cells that should not have the focused protein can nonetheless develop, escaping the remedy and inflicting a relapse. The relapse charge for AML is excessive, resulting in a poor prognosis for the illness total.
The St. Jude group thought it may be doable to beat the issue of immune escape in AML fashions by concentrating on two totally different cancer-related proteins as an alternative of only one.
Others have tried an analogous method however have encountered issues with the construction of the bispecific CAR. The scientists overcame these issues by including a small peptide to the CAR to function the binder for the second focused protein, then confirmed their outcomes with computational structural evaluation of their improved constructs.
“Probably the most thrilling points of the research is that this method may be broadly extrapolated to different tumors,” stated senior corresponding creator Paulina Velasquez, MD, St. Jude Division of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Mobile Remedy. “We targeted on leukemia, however combining bispecific CAR design with computational predictions may be broadly extrapolated for different tumors akin to strong and mind tumors.”
Bettering twin concentrating on by including a second, small barcode scanner
The CAR the researchers created is a singular design. It’s a single moleculewhich incorporates the area of an antibody that binds a selected goal (its antigen) and one brief peptide that binds a separate goal.
“The 2 totally different binding domains of the CAR are like having two barcode scanners as an alternative of 1, searching for their acceptable barcode, the focused cancer-related proteins,” Velasquez stated. “Usually, a CAR has a single barcode scanner. Right here, we positioned two barely totally different barcode scanners on prime of one another, and if both one detects an acceptable goal barcode, the anti-cancer immunotherapy response prompts.”
The 2 binding domains are related by a linker to permit for the binding of two totally different cancer-related proteins. This differs enormously from earlier dual-targeting approaches within the area, which usually used two full antibody-based binding segments.
“We confirmed the worth find inventive methods to carry out dual-antigen concentrating on,” stated first creator Jaquelyn Zoine, Ph.D., St. Jude Division of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Mobile Remedy.
“Prior bispecific CAR approaches use two antibody-based single-chain variable fragments, that are bodily giant molecules and might get in one another’s means, generally resulting in poor or inefficient binding. Our method as an alternative added a small peptide, enabling our CAR to interact both platform to stop immune escape.”
The twin-targeted CARs carried out higher than single-targeted CARs in each in vitro and in vivo experiments, demonstrating promise for bettering CAR T–cell perform.
Untangling two-target constructs’ efficiency with synthetic intelligence
“We confirmed a proof of precept to clarify and probably broaden the CAR design repertoire,” stated co-author M. Madan Babu, Ph.D., FRS, St. Jude Middle of Excellence for Knowledge-Pushed Discovery director, and the George J Pedersen Endowed Chair in Organic Knowledge Science within the Division of Structural Biology. “However then comes the problem. How do we all know what linkers to decide on? How do we all know how a lot bodily flexibility is required?”
For the reason that bodily construction of the concentrating on molecule and its linker that bridges the 2 binding domains could cause inside interference that stops binding to the targets on the most cancers cell, figuring out what sort of linkers had been extra widespread ineffective therapies may result in future enchancment. Computational construction predictions and evaluating constructions with experimental outcomes confirmed to the St. Jude group that shorter, extra versatile linkers would work higher of their fashions.
“If we now have a inflexible linker connecting the barcode scanners, it might probably solely scan a restricted quantity on the most cancers cell, making it much less efficient find the targets,” Babu stated. “We discovered when you have got a linker of enough flexibility and shorter size so it would not fold onto itself, it might probably scan a a lot bigger quantity and is extra more likely to discover the goal proteins on the most cancers cell. Then you have got a simpler pair of barcode scanners that work collectively.”
“We’re certainly one of few teams on this planet to make use of AI-based construction prediction instruments for CAR design,” stated second creator Kalyan Immadisetty, St. Jude Division of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Mobile Remedy. Immadisetty confirmed the affiliation between brief, versatile linkers and better anti-cancer efficacy by evaluating 3D-modeled constructions. This info supported the efficiency of the CAR in actual experimental outputs.
“We had been excited that the structural predictions supported our experiments that knowledgeable us a brief and versatile linker could be one of the best configuration,” Zoine stated. “Whereas we carried out the experiments, Immadisetty discovered the structural elements correlating virtually precisely with what we had been exhibiting functionally, even after we switched one of many concentrating on antibody binding domains. We’ve got now launched the concept these AI prediction instruments may be prolonged to different CAR constructs.”
“Most significantly, others can now use our computational approach for designing their CARs,” Immadisetty stated. “And hopefully, it can assist them perceive the efficacy of their CAR expertise and result in total enhancements for leukemia and different malignancies.”
Extra info:
Jaquelyn T. Zoine et al, Peptide-scFv antigen recognition domains successfully confer CAR T cell multiantigen specificity, Cell Stories Drugs (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101422
Supplied by
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital
Quotation:
Novel bispecific design improves CAR T–cell immunotherapy for childhood leukemia (2024, February 12)
retrieved 13 February 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-02-bispecific-car-tcell-immunotherapy-childhood.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post