[ad_1]
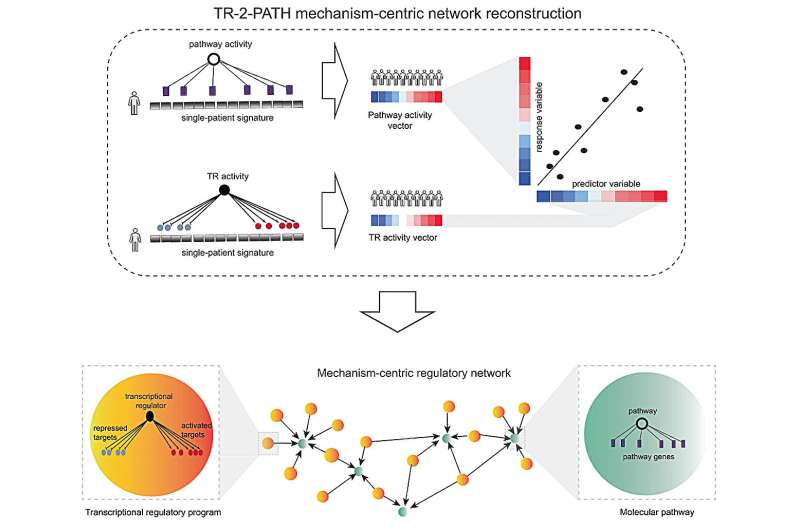
Reconstruction of a mechanism-centric regulatory community for CRPC sufferers. a Schematic illustration of the TR-2-PATH workflow. (First row) Single-patient pathway enrichment evaluation and single-patient transcriptional regulatory evaluation identifies pathway exercise vector and transcriptional regulatory exercise vector respectively, pairs of that are then subjected to linear regression evaluation to reconstruct a mechanism-centric regulatory community. (Second row) Within the community, transcriptional regulatory applications are represented as orange nodes and molecular pathways as inexperienced nodes. An edge (black arrow) illustrates {that a} important relationship was outlined between a transcriptional regulatory program and molecular pathway. Credit score: Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-44686-5
Rutgers researchers can predict which sufferers will profit from a well-liked prostate most cancers drug—they usually have devised a technique which will make the remedy work longer.
“This work ought to assist medical doctors know which sufferers’ prostate cancers will and will not reply to the androgen deprivation remedy enzalutamidewhich might gradual prostate cancer development by disrupting androgen receptor signaling,” stated Antonina Mitrofanova, affiliate professor of Biomedical and Well being Informatics, affiliate dean for analysis on the Rutgers Faculty of Well being Professions, researcher at Rutgers Most cancers Institute of New Jersey, and lead creator of the examine.
“We hope this will get efficient remedy to extra sufferers in much less time, and we hope follow-up analysis makes the profit that many sufferers obtain from enzalutamide work longer.”
For the examine published in Nature CommunicationsMitrofanova’s group developed computational algorithms to find why the prostate cancer drug enzalutamide (offered below the model title Xtandi) by no means works for some sufferers and why it will definitely stops working in others.
The researchers analyzed superior prostate most cancers affected person information to map interactions amongst molecular pathways and their upstream transcription elements (proteins that regulate the expression of a number of genes) in prostate most cancers cells. Their consideration centered on the MYC pathway due to its recognized function in prostate most cancers. They found that one other protein and transcription issue, NME2, works intently with MYC in superior prostate most cancers cells that resist enzalutamide and proceed to unfold.
Evaluation of medical data discovered that sufferers with elevated ranges of MYC and NME2 have been 5 instances much less possible than others to profit from enzalutamide. The evaluation additionally discovered that protein ranges climbed considerably in most sufferers who solely responded to the drug quickly.
The Rutgers group labored with colleagues at Northwestern College, Sarki Abdulkadir and Vishal Kothari, to verify these findings with experiments on cancerous tissues and laboratory mice. Their work once more confirmed that elevated ranges of MYC and NME2 have been related to poor response to enzalutamide, each in tissue samples and reside mice.
This analysis additionally demonstrated that MYC and NME2 may rise in response to enzalutamide utilization—which explains why the drug may ultimately cease working. However there was a silver lining: Decreasing NME2 and, thus, MYC ranges restored the efficacy of enzalutamide in cancers that had grown proof against its results.
Any enchancment in prostate most cancers remedy would produce widespread advantages, the researchers stated. Prostate most cancers is the second most typical most cancers in the USA and the fourth most typical most cancers worldwide.
This examine marks a big step towards understanding and treating superior prostate most cancers, by which the most cancers has unfold past the prostate itself and turns into proof against the older androgen deprivation therapies which are sometimes used as preliminary therapies for the illness.
The outcomes from the examine point out sufferers with elevated ranges of MYC and NME2 who grow to be proof against enzalutamide should still reply to various medicines, resembling abiraterone (ZYTIGA), which do not cease working when MYC and NME2 ranges rise and will considerably profit from therapeutic focusing on of MYC axes, restoring efficacy of enzalutamide and making it work longer for these sufferers.
“The outcomes from each the computational evaluation and the lab experiments have been sturdy,” stated Mitrofanova. “However we hope to observe this work with a trial in human sufferers. That is the following step.”
Extra data:
Sukanya Panja et al, Mechanism-centric regulatory community identifies NME2 and MYC applications as markers of Enzalutamide resistance in CRPC, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-44686-5
Supplied by
Rutgers University
Quotation:
New technique to spice up prostate most cancers remedy efficacy (2024, January 22)
retrieved 22 January 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-01-strategy-boost-prostate-cancer-treatment.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post