[ad_1]
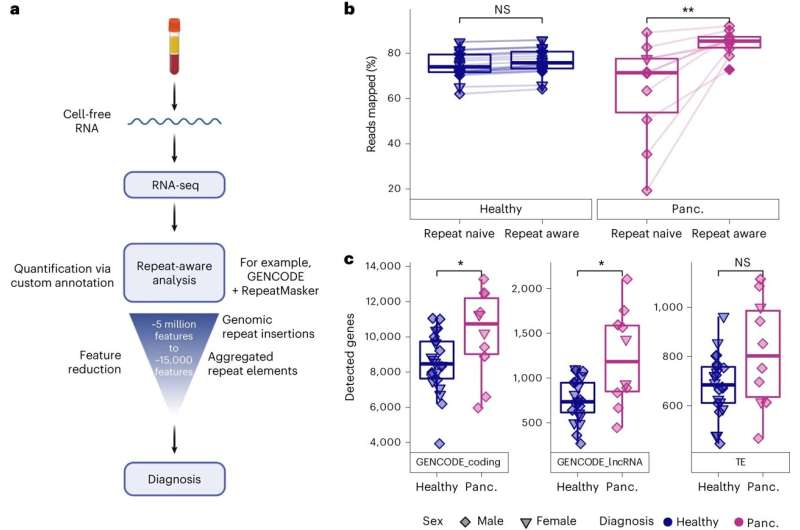
Cell-free RNA transcriptome profiling utilizing repeat-aware COMPLETE-seq. aDiagram of COMPLETE-seq RNA liquid-biopsy know-how, highlighting using repeat-derived cell-free RNAs aggregated right into a tractable function set to allow diagnostic modeling. Created with BioRender.com. bComparability of mapping charges between use of a repeat-naive (GENCODE v.39) reference annotation (**P = 0.0039) and repeat-aware reference annotation (Wilcoxon, paired, two-sided). cComparability of gene detection distributions for every cohort throughout coding genes (GENCODE_coding; *P = 0.043), lncRNAs (GENCODE_lncRNA; *P = 0.035) and TE subfamilies (Wilcoxon, two-sided). For the field plots, the middle line represents the median, the field limits are higher and decrease quartiles and whiskers signify 1.5× interquartile vary. NS, not vital; panc., pancreatic most cancers. Credit score: Nature Biomedical Engineering (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41551-023-01081-7
Most cancers is most treatable in its early levels, so discovering revolutionary and non-invasive strategies to diagnose most cancers early on is essential for combating the illness. Liquid biopsies, which require only a easy blood draw, are an rising know-how for non-invasively testing for most cancers utilizing DNA or RNA sequencing of a affected person’s blood.
Assistant Professor of Biomolecular Engineering Daniel Kim and his lab are creating extra correct and highly effective liquid biopsy applied sciences that benefit from alerts from RNA “darkish matter,” an understudied space of the genome. Kim’s new analysis exhibits that this genetic materials is current within the blood of individuals with cancer and could be recognized to diagnose particular most cancers varieties corresponding to pancreatic, lung, esophageal, and others early in the midst of the illness.
Kim’s lab developed an RNA liquid biopsy platform that detects each protein-coding RNA and RNA darkish matter within the blood, and confirmed that this new strategy considerably improves the efficiency of liquid biopsy for cancer diagnosis. This analysis was printed in the present day within the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering.
Deal with ‘darkish matter’
Whereas most researchers and firms are pursuing DNA-based liquid biopsy for most cancers analysis, Kim’s strategy is exclusive in its concentrate on RNA “dark matter,” particularly noncoding and repetitive RNA.
A lot of the three billion base pairs of DNA that make up the human genome are transcribed into RNA, and the entire RNA is collectively generally known as the transcriptome. Essentially the most generally acknowledged operate of RNA is to code for proteins within the physique, however 75% of the human genome generates noncoding RNA that doesn’t code for proteins.
A considerable portion of those noncoding RNAs are derived from repetitive components, and these RNAs can journey out of the cell from which they originate and into the bloodstream. A wholesome particular person’s blood sometimes would have only a few of those repetitive noncoding RNAs. Nonetheless, Kim’s research has shown that even on the earliest levels of most cancers, many of those repetitive RNAs are secreted out of cancer cellsmaking them potent biomarkers of early-stage illness.
RNA liquid biopsy know-how developed by the Kim lab goals to detect most cancers by sequencing “cell-free RNA” in a affected person’s blood to check for the presence of each protein-coding and repetitive noncoding RNA.
Kim’s lab created a cell-free RNA sequencing and evaluation platform referred to as COMPLETE-seq to determine repetitive noncoding RNAs which might be sometimes ignored. After a affected person’s blood is drawn, this complete strategy analyzes the pattern for the entire annotated areas of the transcriptome—the tens of hundreds of RNAs which have already been well-documented— plus the entire 5 million noncoding repetitive components that Kim’s lab additionally focuses on.
“In the event you take a look at these completely different cancers, every has its personal attribute cell-free RNA profile, however lots of these RNAs are coming from the tens of millions of repeat components which might be discovered all through the genome,” Kim mentioned.
“What we discovered was that once we skilled machine studying fashions for most cancers classification, the fashions carry out higher while you introduce these repetitive cell-free RNAs as extra options. We see larger sensitivity when it comes to detecting most cancers, so we expect that these repeat components are literally offering lots of wealthy cell-free RNA info that folks beforehand hadn’t appeared for.”
Enhancing exams
Different current liquid biopsy exams haven’t been very delicate for early stage most cancers, with some exams lacking as much as 75% of stage I cancers, when the organic sign is low because of the small tumor dimension. Kim’s paper exhibits that incorporating repetitive RNA into their liquid biopsy platform enormously will increase the organic sign and boosts the efficiency of machine studying fashions tasked to determine most cancers. For example, utilizing COMPLETE-seq improved efficiency to 91% sensitivity for figuring out colorectal most cancers.
“The worth of our examine is that we have now proven the potential of those repeat components for diagnosing illness, so hopefully there will be lots of curiosity in leveraging repetitive RNAs to spice up the sensitivity of those multi-cancer early detection exams,” Kim mentioned.
The analysis findings present that this know-how can be utilized to determine a wide range of most cancers varieties. The lab initially targeted on pancreatic most cancers for this examine, as there may be an pressing scientific want for pancreatic most cancers early detection, as late detection results in worse outcomes for sufferers. Pancreatic most cancers can also be identified to be pushed by mutations within the KRAS gene, which can also be a spotlight of Kim’s lab.
After verifying findings in pancreatic cancerthe researchers additionally checked out a wide range of different cancers, and plan to take a look at many extra most cancers varieties with extra samples throughout the progressive levels of most cancers. The staff is fascinated with collaborating with clinicians and firms to do that.
Kim’s objective is to develop an RNA liquid biopsy take a look at for multi-cancer early detection, utilizing the wealthy info from repetitive RNAs to determine and diagnose illness with excessive sensitivity and specificity. Kim hopes his platform won’t solely diagnose most cancers on the earliest levels but additionally assist information individualized, exact remedy methods when the most cancers is extra treatable.
Furthermore, his take a look at may assist to determine a recurrence of most cancers, and in addition be used to check getting older and to diagnose different varieties of ailments that alter the repetitive RNA panorama, corresponding to Alzheimer’s illness. He lately gave the UCSC Kraw Lecture on “Precision Well being for All By means of RNA” that laid out his imaginative and prescient for early detection and exact remedy of illness utilizing RNA.
The researchers additionally used nanopore sequencing to learn the cell-free RNAs floating within the blood, which allowed them to generate long-reads and decide the true size of those cell-free RNAs. Kim believes his lab is the primary to make use of nanopore sequencing, a method pioneered at UC Santa Cruz, for RNA liquid biopsies to diagnose most cancers and to find out the total size of those cell-free RNAs.
Nanopore sequencing could be carried out on a handheld machine developed by Oxford Nanopore Applied sciences referred to as the MinION. This holds promise for finishing up most cancers screening in distant or resource-poor settings the place bigger, dearer sequencers usually are not available.
“This examine wouldn’t have been doable with out the robust help of the American Most cancers Society and all of its beneficiant donors, management, workers, and volunteers, in addition to the entire arduous work of my Ph.D. scholar Roman Reggiardo (an NIH F99/K00 Fellow now at HHMI Investigator Howard Chang’s lab at Stanford College) and all of our Kim lab members and collaborators,” Kim mentioned.
Along with his function as an Assistant Professor within the Baskin Faculty of Engineering related to the Institute for the Biology of Stem Cells, the Genomics Institute, and the Heart for Molecular Biology of RNA at UC Santa Cruz, Kim can also be an Affiliate Member of the Canary Heart at Stanford for Most cancers Early Detection and a Analysis Scholar of the American Most cancers Society.
Extra info:
Daniel Kim et al, Profiling of repetitive RNA sequences within the blood plasma of sufferers with most cancers, Nature Biomedical Engineering (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41551-023-01081-7 www.nature.com/articles/s41551-023-01081-7
Offered by
University of California – Santa Cruz
Quotation:
New blood take a look at for noncoding RNA considerably improves most cancers detection (2023, August 31)
retrieved 3 September 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-08-blood-noncoding-rna-significantly-cancer.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post