[ad_1]
A couple of hundred key genes linked to DNA harm have been uncovered by means of systematic screening of practically 1,000 genetically modified mouse traces in a brand new research published in Nature.
The work offers insights into most cancers development and neurodegenerative diseases in addition to a possible therapeutic avenue within the type of a protein inhibitor.
The genome comprises all of the genes and genetic materials inside an organism’s cells. When the genome is secure, cells can precisely replicate and divide, passing on appropriate genetic data to the following era of cells. Regardless of its significance, little is known concerning the genetic components governing genome stability, safety, restore, and the prevention of DNA harm.
On this new research, researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and their collaborators on the UK Dementia Analysis Institute on the College of Cambridge got down to higher perceive the biology of mobile well being and determine genes key to sustaining genome stability.
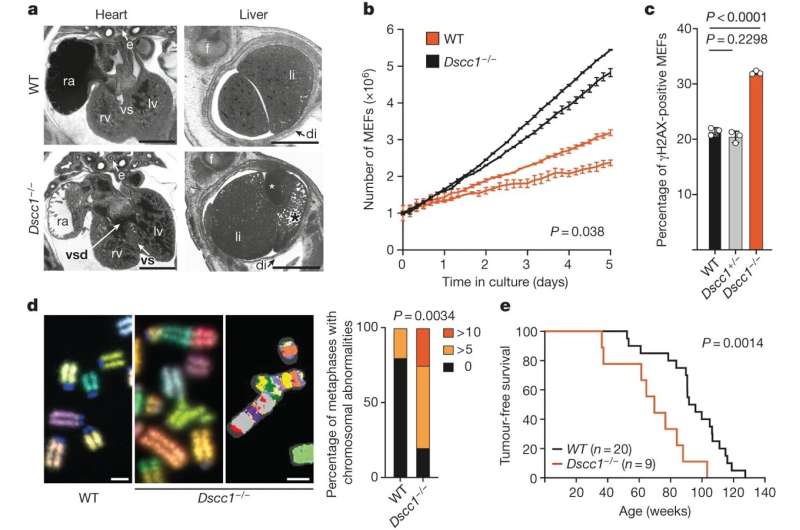
Utilizing a set of genetically modified mouse traces, the workforce recognized 145 genes that play key roles in both growing or reducing the formation of irregular micronuclei buildings. These buildings point out genomic instability and DNA harm, and are widespread hallmarks of getting older and illnesses.
Probably the most dramatic will increase in genomic instability have been seen when the researchers knocked out the gene DSCC1, growing irregular micronuclei formation five-fold. Mice missing this gene mirrored traits akin to human sufferers with cohesinopathy problems, additional emphasizing the relevance of this analysis to human well being.
Utilizing CRISPR screening, researchers confirmed this impact triggered by DSCC1 loss might be partially reversed by means of inhibiting protein SIRT1. This presents a extremely promising avenue for the event of latest therapies.
The findings assist make clear genetic components influencing the well being of human genomes over a lifespan and illness improvement.
Professor Gabriel Balmus, senior creator of the research on the UK Dementia Analysis Institute on the College of Cambridge, previously on the Wellcome Sanger Institute, stated, “Continued exploration on genomic instability is important to develop tailor-made therapies that deal with the foundation genetic causes, with the purpose of enhancing outcomes and the general high quality of life for people throughout numerous circumstances.”
“Our research underscores the potential of SIRT inhibitors as a therapeutic pathway for cohesinopathies and different genomic problems. It means that early intervention, particularly concentrating on SIRT1, might assist mitigate the organic modifications linked to genomic instability earlier than they progress.”
Dr. David Adams, the primary creator of the research on the Wellcome Sanger Institute, stated, “Genomic stability is central to the well being of cells, influencing a spectrum of illnesses from most cancers to neurodegeneration, but this has been a comparatively underexplored space of analysis.”
“This work, 15 years within the making, exemplifies what will be discovered from large-scale, unbiased genetic screening. The 145 recognized genes, particularly these tied to human disease, provide promising targets for growing new therapies for genome instability-driven illnesses like most cancers and neurodevelopmental problems.”
Extra data:
David Adams, Genetic determinants of micronucleus formation in vivo, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-07009-0. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-07009-0
Quotation:
Key genes linked to DNA harm and human illness uncovered (2024, February 14)
retrieved 14 February 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-02-key-genes-linked-dna-human.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post