[ad_1]
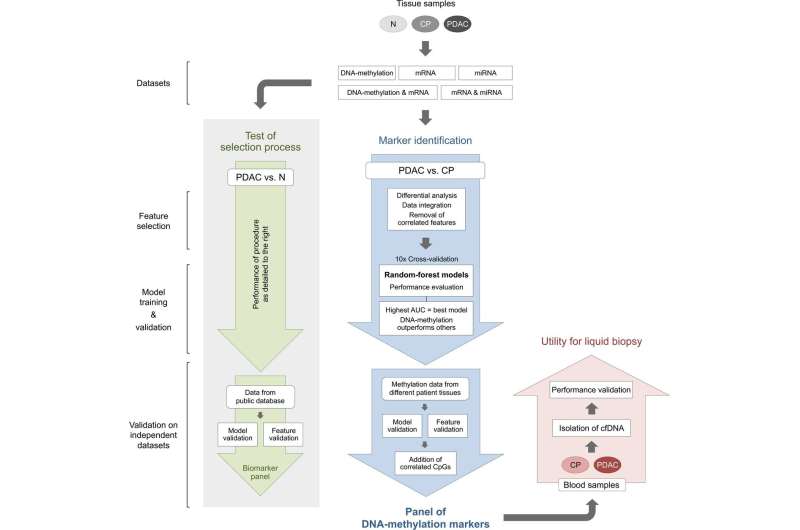
Schematic workflow of biomarker choice course of. Single-‘omic’ and multi-‘omic’ information from PDAC, CP and N tissue samples had been collected and analyzed. The workflow consists of 4 most important steps: characteristic choice, mannequin coaching, inner validation and validation on unbiased datasets. AUC, space underneath the curve; cfDNA, cell-free DNA; CP, persistent pancreatitis; mRNA, messenger RNA; miRNA, microRNA; N, wholesome people; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Credit score: Intestine (2023). DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330155
Present diagnostic strategies don’t all the time reliably distinguish between persistent irritation of the pancreas and pancreatic most cancers. About one third of all diagnoses are inconclusive. Scientists from the German Most cancers Analysis (DKFZ) and from the Heidelberg College Hospital (UKHD) subsequently looked for molecular markers that would specify this prognosis.
Supported by machine studying, they had been in a position to determine a sample of DNA methylations that allowed excessive accuracy in distinguishing between chronically infected and malignantly altered tissue samples. First preliminary outcomes recommend that prognosis might be carried out on blood samples.
Most cancers of the pancreas or PDAC for brief (“pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma”), has a dramatically poor prognosis. The explanations for this are its normally late detection at a complicated stage, misdiagnosis and its marked resistance to out there therapies.
Imaging strategies are normally used for prognosis. However these have the drawback that they can’t all the time reliably distinguish pancreatic most cancers from persistent pancreatic irritation. Power irritation is taken into account an necessary danger issue for pancreatic most cancers. About 6 to 9 p.c of sufferers affected by chronic inflammation of the pancreas later develop pancreatic most cancers. However imaging and even ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy too typically additionally present incorrect diagnoses.
“That is dramatic for the sufferers: if a malignant tumor is misdiagnosed as persistent irritation, they lose useful time to deal with the illness. Nonetheless, if medical doctors mistakenly suppose an irritation is a carcinoma, the affected person has to endure a critical surgical intervention unnecessarily,” says Jörg Hoheisel of the German Most cancers Analysis Middle.
To enhance this example and discover molecular markers to reach at extra exact differential diagnoses, Hoheisel has now joined forces with physicians at Surgical College Clinic Heidelberg to conduct a large-scale research of pancreatic tissue samples. The staff analyzed 345 tissue samples (PDAC, chronically infected and wholesome), after which validated the outcomes on an unbiased set of 48 further samples. Previous to this, the fabric used had been independently assessed twice by skilled pathologists.
The evaluation included genome-wide variations in DNA methylation in addition to mRNA and microRNA quantities. To filter out related variations between malignant tumors and persistent irritation from the wealth of knowledge, the researchers used machine learning approaches. Different, generally used strategies didn’t yield helpful outcomes. It turned out that variations in DNA methylation allowed considerably increased accuracy with far fewer biomarkers than the mRNA or microRNA information.
A signature of six methylation positions within the PRKCB gene offered the clearest discrimination. This allowed right identification of inflammatory and malignant tissues.
For clinical useit will be extra advantageous if the analyses might be carried out on blood as a substitute of tissue samples. Such blood analyses, which detect the small quantities of DNA that flow into within the blood, are also called “liquid biopsy.”
The Heidelberg staff subsequently additionally utilized the six methylation markers to a small variety of blood samples from sufferers with persistent pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer to display their applicability in blood as nicely. As beforehand in tissue, the methylation markers had been in a position to diagnose sufferers with excessive accuracy.
“After all, the process should be validated on a lot of blood samples and confirmed in a trial underneath scientific circumstances with a view to lastly assess its precise profit for clinical practice,” says Jörg Hoheisel, senior creator of the publication. “If the result’s confirmed on this course of, it may have a big impression on scientific care and affected person prognosis.”
Hoheisel assumes that the algorithm developed for this information evaluation can be useful within the seek for biomarkers for different ailments.
The paper is revealed within the journal Intestine.
Extra info:
Yenan Wu et al, DNA-methylation signature precisely differentiates pancreatic most cancers from persistent pancreatitis in tissue and plasma, Intestine (2023). DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330155
Offered by
German Cancer Research Center
Quotation:
Find out how to higher distinguish persistent irritation and most cancers of the pancreas (2023, September 20)
retrieved 21 September 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-09-distinguish-chronic-inflammation-cancer-pancreas.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post