[ad_1]

Immunologist Ming Li, PhD. Credit score: Memorial Sloan Kettering Most cancers Middle
Investigator Ming Li, Ph.D., has devoted his profession to understanding the intricate workings of the immune system—each usually and for the crucial function it performs in most cancers.
Examine by examine, his lab at Memorial Sloan Kettering Most cancers Middle (MSK) is sharing new insights into the molecular and mobile mechanisms concerned in immune regulation—a kind of knowledge-building that scientists name “fundamental science” or “discovery science.” However Dr. Li is equally centered on making use of that information to harness the facility of the immune system towards most cancers.
“Immunotherapy has change into a very vital space in cancer research,” says Dr. Li, a member of the Immunology Program on the Sloan Kettering Institute, a hub for fundamental and translational analysis inside MSK. “The concept we will have interaction the immune system to regulate most cancers is one thing that many most cancers biology labs are actually pursuing.”
For instance, in a new study in ImmunityDr. Li and his colleagues describe a tumor suppression pathway they imagine might type the premise for a brand new immunotherapy strategy.
On this interview, Dr. Li discusses the brand new findings and his analysis program at MSK.
What are the massive questions your lab is making an attempt to reply to grasp the immune system and make most cancers immunotherapy more practical?
Before everything, we’re fascinated about how the immune system is regulated at a mechanistic degree. Meaning doing experiments to grasp in exact element the mechanisms by which immune cells work together and coordinate to mount an immune response towards threats to a person’s well being.
Most cancers cells pose a novel problem for the immune system. They’re an individual’s personal cells, however they’ll act like overseas invaders. And most cancers has methods of hijacking the immune system for its personal profit.
How the immune system acknowledges micro organism and different infections has been nicely studied. However the way it acknowledges a wholesome cell that is remodeling right into a most cancers cell continues to be a comparatively new self-discipline.
I began my lab in 2007, and over the previous 16 years we have investigated the varied ways in which the immune system perceives and responds to cell transformation.
Throughout this identical interval, the event of immunotherapy has revolutionized most cancers remedy worldwide—that’s, tapping into the facility of an individual’s immune system to battle towards their most cancers. When it really works, it could actually have superb outcomes. The problem is making it work for extra individuals and extra kinds of most cancers.
In my lab, we’re uncovering new organic insights with the goal of doing precisely that.
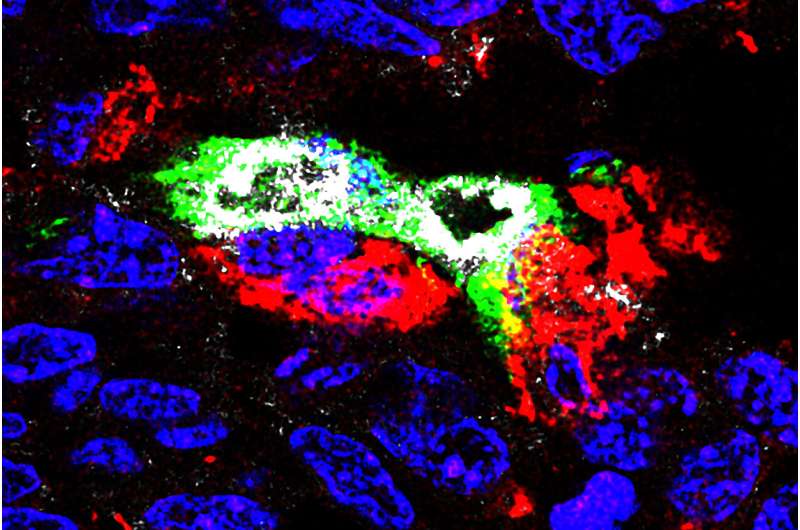
Tumor-associated macrophages (pink) outcompeting endothelial progenitor cells (inexperienced), resulting in cell demise (white). Credit score: Ming Li Lab, Memorial Sloan Kettering Most cancers Middle
Inform us about among the vital discoveries out of your lab and the way they could inform future therapies.
I feel our work has helped to broaden concepts about how we’d go about concentrating on the immune system for most cancers remedy.
My lab is primarily centered on a kind of white blood cells known as lymphocytes, together with T lymphocytes. T cells acknowledge irregular cells and goal them for destruction. They play a central function within the immune response that is called “adaptive,” as a result of it learns to determine the invader and might bear in mind find out how to assault it.
We found {that a} kind of adaptive T cells known as “helper T cells” are regulated by the TGF-beta pathway to regulate the tumor immune response. Blocking TGF-beta signaling in helper T cells creates a defensive response that could possibly be used towards most cancers. This strategy underscores the concept of focused immunotherapy approaches for advanced regulators akin to TGF-beta.
As we speak, adaptive lymphocytes are the principle focus of packages to develop checkpoint inhibitor therapiesto which the helper T cell-directed TGF-beta blockade belongs. However we found that two further kinds of tumor-resident lymphocytes known as “kind 1 innate lymphoid cells” and “killer innate-like T cells” play an vital function in most cancers immune surveillance. That is the method by which the immune system detects and eliminates newly reworked cancer cells to forestall the event of tumors.
Our first paper on this matter was printed in 2016, and we have had a number of further follow-up research that took our preliminary findings in mouse fashions right into a human context, and recognized interleukin-15 as a pivotal regulator of those newly found most cancers immune surveillance responses. These embody current papers in Nature, Nature Immunologyand Science Immunology.
We’re optimistic that the power to activate these tissue-resident innate lymphocytes and innate-like T cells could possibly be developed right into a next-generation immunotherapy.
In the meantime, there’s a complete separate arm of our analysis program that’s trying on the function of macrophages in most cancers. Macrophages are a special kind of white blood cell that engulfs and digests invaders, like micro organism and most cancers cells.
Macrophages play an advanced function in most cancers as a result of macrophages present in and round tumors—what we name tumor-associated macrophages—can truly help tumor progress.
We printed a paper this summer season in Nature that confirmed tumor-associated macrophages could be reprogrammed to outcompete sure most cancers cells for assets. And these findings recommend that this pathway could be harnessed towards aggressive cancers which might be fueled by cell competitors.
What concerning the new examine, what did it reveal concerning the function of macrophages in most cancers?
The brand new examine in Immunity was additionally one which centered on tumor-associated macrophages, which we name TAMs for brief.
The work—which was co-led by former lab members Mytrang Do, MD, Ph.D., and Wei Shi, Ph.D., and present postdoc Liangliang Ji, Ph.D.—confirmed how tumors make a good setting for his or her progress by selling the infiltration of TAMs into the tumor.
Utilizing a mouse mannequin of breast most cancers, we discovered that TAMs discovered inside tumors had low exercise of a key metabolic regulator known as mTORC1. We additionally discovered that depleting a protein that blocks mTORC1 exercise in these cells helped to cut back tumor progress by blocking blood vessel progress and slicing off most cancers cells from entry to oxygen.
So we see this as one other alternative to harness the facility of the immune system to battle most cancers—on this case, by growing mTORC1 signaling inside these tumor-associated macrophages to forestall the technology of a supporting tumor tissue blood vasculature.
In the end, we imagine there’s nice hope for precision immuno-oncology—that’s, utilizing the varied immunotherapy weaponry tailor-made to the precise most cancers risk of a person affected person. This can be a very thrilling time in immunotherapy discovery, and I am privileged to have the ability to contribute to creating immunotherapy work higher and for extra individuals.
Extra data:
Mytrang H. Do et al, Reprogramming tumor-associated macrophages to outcompete endovascular endothelial progenitor cells and suppress tumor neoangiogenesis, Immunity (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.10.010
Supplied by
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Quotation:
Q&A: How one lab is working to harness the facility of the immune system towards most cancers (2023, November 14)
retrieved 15 November 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-11-qa-lab-harness-power-immune.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post