[ad_1]
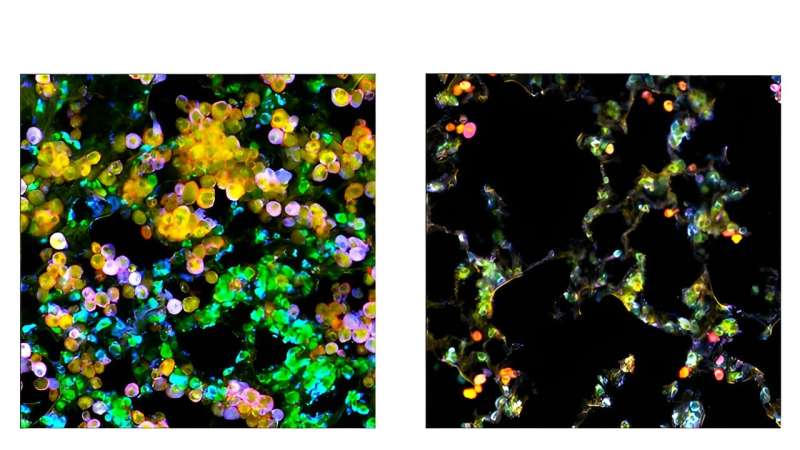
Lung adenocarcinoma tumor cells (inexperienced) and macrophages (pink) accumulate within the lungs of management mice (left), however enlargement of the tumor cells is hindered in macrophage PPARγ knockout mice (proper), because the macrophages cannot be metabolically coopted by tumor cells. Mobile ldl cholesterol is visualized in yellow. Credit score: Salk Institute
Lung adenocarcinoma is the most typical lung most cancers and the reason for most cancer-related deaths in the US. There are a number of methods lung adenocarcinoma can come up, one in all which is a mutation in a protein referred to as EGFR (epidermal progress issue receptor). Non-mutated EGFR helps cells develop in response to harm, however mutated EGFR promotes out-of-control progress that may flip into most cancers.
Trendy immunotherapies do not work towards EGFR-driven lung adenocarcinoma, and whereas some medication exist to deal with the most cancers, sufferers sometimes develop a resistance to them inside just some years. This hole within the remedy software chest impressed Salk Institute researchers to probe for weak spots within the most cancers’s progress pathway.
The workforce found that EGFR-driven lung adenocarcinoma hijacks a specialised inhabitants of lung-resident immune cells referred to as macrophages, that are designed to get rid of diseased and broken cells, in addition to keep a fragile stability of protecting lipids (fat) round lung alveoli, that are important for respiration.
The lung most cancers cells pull macrophages into the tumor microenvironment and alter their lipid metabolism to show them into most cancers fuel-suppliers. The newly energized tumor cells then spur additional macrophage proliferation to produce extra gas—a novel self-perpetuating most cancers mechanism.
The findings, published in Most cancers Discoverypresent new inspiration for lung adenocarcinoma interventions that disrupt this tumor cell-macrophage relationship. The researchers recommend that therapies utilizing EGFR inhibitors could also be extra profitable when paired with statins, a category of medicine generally used to decrease cholesterol levels.
“We have now found a novel approach that lung most cancers cells manipulate their native atmosphere and different cell varieties surrounding them to advertise their very own progress. On this case, the tumor cells exploit lung-resident macrophages—reworking them to offer vitamins, like ldl cholesterol, to the most cancers cells and stimulate tumor growth,” says senior and co-corresponding creator Susan Kaech, professor, director of the NOMIS Heart for Immunobiology and Microbial Pathogenesis, and holder of the NOMIS Chair at Salk. “One thrilling implication of this work is that lung most cancers therapies could also be improved by merely including statins, an already extensively used class of medicine, to the affected person’s remedy plan.”
Lungs depend on tiny bulbs referred to as alveoli, which increase and deflate with our breath, to facilitate the change of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air and our blood. Alveoli are essential to human survival, and their well being depends on a lipid-rich atmosphere created by alveolar cells and sustained by macrophages. Lipids, similar to ldl cholesterol, are fatty compounds that help bodily perform by serving to cells transfer, retailer vitality, and soak up nutritional vitamins.
This distinctive means of lung-resident macrophages to take care of lipid stability turns into extra sophisticated when tumor cells start to use these lipids to assist themselves develop. A greater understanding of the mechanisms macrophages use to control their metabolism and lipid manufacturing can present perception into how tumor cells selfishly manipulate these mechanisms to assist themselves.
“The tumor cells excrete much more of a progress issue referred to as GM-CSF (granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating issue), which then causes the macrophages to develop alongside them and alter their metabolism, leading to extra lipids that the tumor cells use to strengthen themselves,” says first creator Alexandra Kuhlmann-Hogan, former postdoctoral researcher in Kaech’s lab and present postdoctoral researcher at UC Los Angeles. “The most cancers was successfully hijacking this regular macrophage means of sustaining the lungs with wholesome lipids so as to gas itself.”
“Not solely have been the tumor cells metabolically reprogramming the macrophages—they have been additionally instigating a feedback loop that inspired an optimum metabolic state within the tumor cells themselves,” says co-corresponding creator Katerina Politi, scientific director of the Heart for Thoracic Cancers at Yale Most cancers Heart and professor of pathology at Yale Faculty of Medication.
When the EGFR-driven lung adenocarcinoma cells secreted GM-CSF, it stimulated a gene within the macrophages referred to as PPARγ (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma), which jump-started their metabolic reprogramming and subsequent secretion of lipids. Along with utilizing these macrophage-curated lipids to develop, the tumor cells additionally use the lipids to energy the continued activation of the EGFR-drive that helps the most cancers develop.
Kaech predicts that disrupting this loop might be a novel intervention for slowing down EGFR-driven most cancers progress. Precisely how the supply of lipids like ldl cholesterol to tumor cells powers the EGFR oncogenic pathway, the researchers aren’t but certain.
“Our outcomes reveal new therapeutic prospects for immunotherapy-resistant EGFR-driven lung adenocarcinomas,” says co-corresponding creator Christian Metallo, professor and holder of the Daniel and Martina Lewis Chair at Salk. “We have now recognized a key metabolic relationship between macrophages and alveoli that’s exploited by tumor cells to help the most cancers’s metabolic calls for—now we simply need to disrupt that exploitation.”
In future medical trials, the researchers advocate pairing PPARy inhibitors, which might disrupt macrophage hijacking, with statins, which might restrict out there ldl cholesterol together with the presently used EGFR inhibitors. They’re additionally curious whether or not comparable immunological hijacking happens in different tumor microenvironments across the physique, suggesting these outcomes could immediate additional discoveries throughout different most cancers varieties and immune cells.
Different authors embrace Ziyan Xu, Ramya Kuna, Kacie Traina, Anna-Maria Globig, and Reuben Shaw of Salk; Thekla Cordes of Technishe Universität Braunschweig in Germany; Elizabeth Kwong and Sandra Leibel of UC San Diego Faculty of Medication and Sanford Consortium for Regenerative Medication; Matthew Nobari and George Cheng of UC San Diego Division of Medication; and Camila Robles-Oteíza, Deborah Ayeni, Stellar Levy, and Robert Homer of Yale Faculty of Medication.
Extra info:
Alexandra Kuhlmann-Hogan et al, EGFR-Pushed Lung Adenocarcinomas Co-opt Alveolar Macrophage Metabolism and Operate to Help EGFR Signaling and Progress, Most cancers Discovery (2024). DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-23-0434
Supplied by
Salk Institute
Quotation:
How lung most cancers hijacks immune cell metabolism to gas its personal progress (2024, February 7)
retrieved 8 February 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-02-lung-cancer-hijacks-immune-cell.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post