[ad_1]
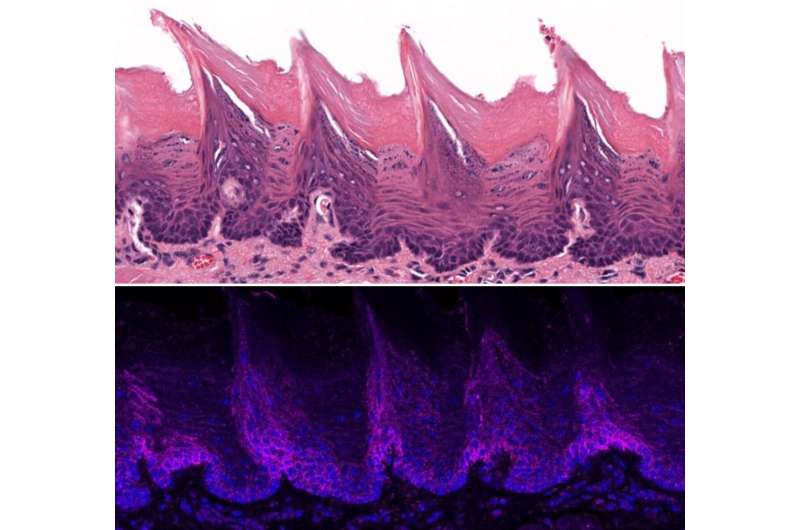
Tissue from a mouse tongue as seen beneath a microscope (high) and localization of the ORAI1 protein within the tissue on floor of the mouse tongue (backside). Credit score: Lacruz Lab/NYU
A vital protein that acts as a gatekeeper for calcium coming into cells promotes the expansion of oral most cancers and generates ache, in accordance with a brand new examine printed in Science Signaling led by researchers at New York College Faculty of Dentistry.
Concentrating on this protein—the ORAI1 calcium channel—may present a brand new method to treating oral most cancers, which causes persistent pain that worsens because it progresses.
“Our outcomes present that the ORAI1 channel fuels the expansion of oral most cancers tumors and produces an abundance of molecules that, as soon as secreted, work together with neurons leading to an elevated sensitivity to ache,” mentioned Ga-Yeon Son, a postdoctoral fellow within the Division of Molecular Pathobiology at NYU Faculty of Dentistry and the examine’s first creator.
The keepers of the gates of heaven
WEATHER calcium channels—named after the three sisters in Greek mythology who guarded the gates of heaven at Mount Olympus—play an vital function controlling how a lot calcium enters cells.
“These calcium channels is usually a supply of fine or unhealthy for cells,” mentioned Rodrigo Lacruz, professor of molecular pathobiology at NYU Faculty of Dentistry and the examine’s senior creator.
“Calcium coming into cells is important for a lot of good issues, however an excessive amount of calcium for a very long time has the other impact.”
Calcium channels have been linked to varied cancers, particularly most cancers development, however few research have appeared on the function of ORAI1 in most cancers and ache.
“Calcium inflow by ORAI1 channels has been well-known to contribute to the regulation of gene expression by activating gene transcription components within the cells. Notably, our investigation extends its perform in regulating gene expression to altering oral most cancers ache,” mentioned Son.
Much less ORAI1, much less most cancers progress and ache
The researchers first analyzed tissue samples from human oral most cancers tumors and wholesome tongues. They discovered that the ORAI1 gene, which accommodates directions for creating the ORAI1 calcium channel, was closely overexpressed within the tumors however not in wholesome tissue.
They then examined human oral cancer cells and located that activating the ORAI1 calcium channel (however not different calcium channels) induced a big inflow of calcium into most cancers cells. This inflow resulted within the enhance of a calcium-dependent enzyme referred to as matrix metalloprotease 1 (MMP1) that’s secreted outdoors of most cancers cells. MMP1 is ample in a number of forms of most cancers, together with oral most cancers, the place its overexpression is related to metastasis and poor prognosis.
Eradicating the ORAI1 gene from oral most cancers cells modified the course of the illness in animal research. When mice have been inoculated with most cancers cells missing the ORAI1 gene, tumors grew extra slowly and have been much less painful.
“These findings show an vital function for ORAI1 in oral most cancers development and ache, however what’s the mechanism? We questioned if MMP1 may very well be the messenger relaying ache,” mentioned Lacruz.
In collaboration with NYU Ache Analysis Heart scientists Rajesh Khanna and Yi Ye, the workforce appeared on the ranges of MMP1 expressed within the fluid surrounding oral most cancers cells and noticed that cells missing the ORAI1 gene secreted much less MMP1 into the encompassing fluid.
They mixed the fluid with neurons from the trigeminal ganglia, a set of nerves within the face that transmit ache in oral most cancers. The fluid from most cancers cells with out the ORAI1 gene didn’t elicit a powerful response from the neurons, however the MMP1-rich fluid from cells with ORAI1 evoked a rise in motion potentials, the required sign for ache transmission.
“This provides us proof that an abundance of MMP1 might generate elevated sensitivity to ache,” mentioned Lacruz.
The researchers additionally ran experiments with irregular however non-cancerous cells. Once they overexpressed the ORAI1 gene in these non-invasive cells, they turned invasive, elevating the likelihood that ORAI1 may play a task in cells switching from non-cancerous to cancerous cells.
Future analysis: Blocking ORAI
A number of FDA-approved medicine block the ORAI1 calcium channel, however they haven’t but been examined in oral most cancers. In future research, the researchers will see whether or not nanoparticles will be loaded with an ORAI-blocking drug and exactly delivered into the tongues of animal fashions to cease oral most cancers development and ache.
“In mild of the continued opioid disaster, our examine paves the way in which for validating novel ache therapies in oral most cancers,” mentioned Rajesh Khanna, director of the NYU Ache Analysis Heart, professor of molecular pathobiology at NYU Dentistry, and a co-author of the examine.
“Finally, our hope is that focusing on the ORAI1 channel in oral most cancers can stop or delay the development from oral epithelial dysplasia to oral most cancers tumors and concurrently alleviate the ache burden skilled by oral cancer sufferers,” added Son.
Extra examine authors embody Nguyen Huu Tu, Maria Daniela Santi, Santiago Loya Lopez, and Guilherme H. Souza Bomfim of NYU Faculty of Dentistry; Manikandan Vinu, Ariya Chaloemtoem, Rama Alhariri, and Youssef Idaghdour of NYU Abu Dhabi; and Fang Zhou of NYU Langone Well being.
Extra data:
Ga-Yeon Son et al, The Ca2+ channel ORAI1 is a regulator of oral most cancers progress and nociceptive ache, Science Signaling (2023). DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.adf9535
Offered by
New York University
Quotation:
‘Gates of Heaven’ calcium channel drives oral most cancers ache and progress, examine exhibits (2023, September 5)
retrieved 5 September 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-09-gates-heaven-calcium-channel-oral.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post