[ad_1]
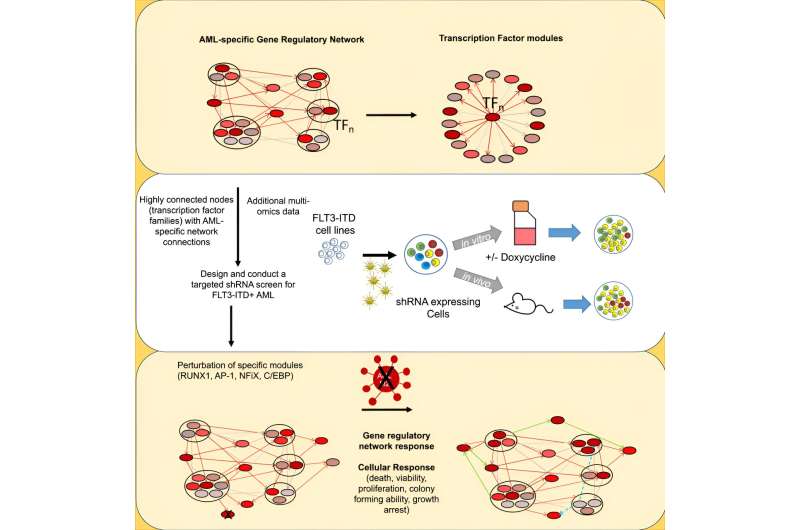
A extremely aggressive widespread type of leukemia which is activated by mutations in signaling molecules is maintained by an internet of regulatory proteins downstream of those alerts.
New analysis printed in Cell Reports reveals {that a} complicated community of interacting genes activated by this altered signaling might be able to be manipulated to kill off Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) most cancers cells.
This examine by a global crew of researchers from the College of Birmingham, Newcastle College, the Princess Maxima Heart of Pediatric Oncology in Utrecht and the College of Virginia, U.S. has used superior screening instruments to establish how gene regulatory networks (GRNs) keep a sub-type of blood most cancers referred to as FLT3-ITD mutated AML.
Utilizing this AML mannequin, the researchers have recognized connections between proteins referred to as transcription factors (TF) and the genes they bind to that collectively type a complex network (GRN) that’s extremely particular for FLT3-ITD AML cells as in comparison with wholesome cells.
Utilizing a screening method developed in Newcastle, the researchers recognized about 100 genes inside this GRN which can be necessary for AML progress and survival. They homed in on a number of of those genes to check the impact of focusing on them. The TF RUNX1 was studied in effective element and the analyses confirmed that RUNX1 is a key consider conserving the GRN steady.
Considerably, the RUNX1 protein could possibly be blocked through the use of a small molecule inhibitor developed by Prof John Bushweller of the College of Virginia, resulting in the collapse of the community that maintains FLT3-ITD AML.
Professor Constanze Bonifer from the Institute of Most cancers and Genomic Sciences on the College of Birmingham and senior creator of the paper stated, “The FLT3-ITD sub-type of acute myeloid leukemia that now we have been learning has very poor outcomes with excessive relapse charges amongst those that do go into remission. We got down to establish very particular targets which can be required for AML most cancers cells to manage themselves, that would doubtlessly result in new therapies.
“We’re delighted to have recognized a number of elements, together with TFs and signaling proteins which have key roles in sustaining these gene regulation networks the place TFs and genes are wired in an AML-specific method. Such networks act a bit like a pc program that runs processes to keep up AMLs and that are totally different to these networks present in normal cells. Our analysis has discovered that knocking out such elements resulted within the community shutting down, and which can result in the most cancers cells dying off as they’re unable to copy.”
Modeling AML
To establish potential protein targets that regulate AML most cancers cells, the researchers mapped the transcription elements and their genes. The crew used a mixture of regular and malignant cells to then work out which gene expressions had been selling AML survival.
The crew then used a kind of screening approach referred to as shRNA to take a look at particular transcription elements’ position in sustaining the community for AML. Because the TFs are clustered collectively in an interactive community, the crew then noticed the impact of focusing on particular person elements on the entire community, and located that particular proteins together with RUNX1 had been essential for the upkeep of the GRN as a complete.
Professor Olaf Heidenreich who’s a co-grant holder on this venture together with his colleague Dr. Helen Blair from Newcastle and who’s now on the Princess Maxima Heart for Pediatric Oncology in Utrecht stated, “Many researchers on the planet use methods referred to as ‘genome broad screening’ the place they remove each gene in most cancers cells to establish these genes which can be important for the expansion of those cells.
“Nonetheless, this technique identifies many genes which can be additionally required for healthy cells. Subsequently, discovering genes which can be solely necessary for most cancers cells is a bit like discovering a needle in a haystack. Figuring out the gene regulatory networks which can be particular for cancer cells makes this talks a lot simpler.
“Moreover testing the impact of choose targets on AML progress, our work will present an necessary useful resource for the scientific community to house in on the targets that actually matter.”
Extra data:
Daniel J.L. Coleman et al, Gene regulatory community evaluation predicts cooperating transcription issue regulons required for FLT3-ITD+ AML progress, Cell Studies (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113568
Quotation:
Discovering and focusing on a tumor’s candy spot to eradicate aggressive type of leukemia (2023, December 20)
retrieved 20 December 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-12-tumor-sweet-eradicate-aggressive-leukemia.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post