[ad_1]
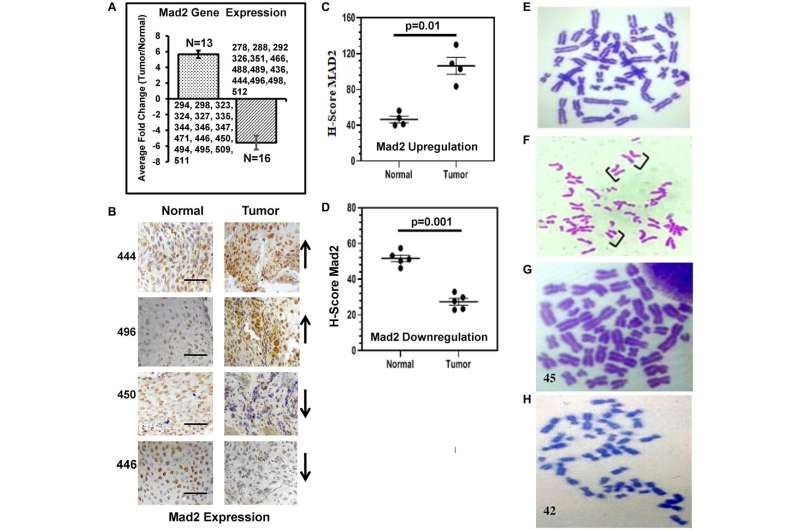
Expression evaluation of the human Mad2 gene and karyotype evaluation of genomic instability in esophageal most cancers sufferers. (A) Expression of Mad2 gene in esophageal most cancers tissues analyzed by qRT-PCR. Sufferers ID numbers are proven. (B) Consultant photographs of an immunohistochemical (IHC) evaluation of tumor and adjoining regular tissues in ESCC achieved with anti-Mad2 antibody. Sufferers ID numbers are proven within the left aspect. Arrows point out the upregulation and down regulation of Mad2 expression within the tumor tissues. The magnification of all these photographs is 40x. (C, D) Scatterplot of H-scores based mostly on IHC for Mad2 optimistic cells in Mad2 upregulation and Mad2 downregulation teams, respectively. (E) Regular metaphase unfold from human PBLs. Information had been analyzed utilizing one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s a number of comparability post-tests. P values lower than 0.05 are thought-about important. The dimensions bar: 200 μm. (F) Untimely sister-chromatid separation in PBL of esophageal most cancers sufferers. Brackets present sister chromatids mendacity separated in mitotic figures that present the phenotype. (G, H) Metaphase unfold confirmed 45 and 42 chromosomes in PBLs of esophageal most cancers sufferers, respectively. Credit score: Oncotarget (2024). DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.28554
A brand new analysis paper titled “Differential expression of Mad2 gene is consequential to the patterns of histone H3 post-translational modifications in its promoter area in human esophageal most cancers samples” has been published in Oncotarget.
Uncooked areca nut (AN) consumption will increase esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) as a result of overexpression of securin (pituitary tumor remodeling gene1), inflicting chromosomal instability. Mitotic arrest poor protein 2 (Mad2), an important spindle meeting checkpoint protein, is susceptible to aneuploidy and tumor growth when overexpressed or underexpressed.
On this new research, researchers Chongtham Sovachandra Singh, Nabamita Boruah, Atanu Banerjee, Sillarine Kurkalang, Pooja Swargiary, Hughbert Dakhar, and Anupam Chatterjee from The Assam Royal World College, College of Pennsylvania, LN Mithila College, College of Chicago Medication, Nazareth Hospital, Laitumkhrah, and North-Japanese Hill College evaluated Mad2 standing in human ESCC with AN consumption habits, revealing unclear molecular mechanisms.
Human ESCC samples (n = 99) had been used for lack of heterozygosity evaluation at 4q25-28, whereas 32 samples had been used for expression evaluation of Mad2, E2F1 genes, and Rb-phosphorylation. Blood samples had been used for metaphase preparation. The Mad2 deregulation was assessed utilizing chromatin immunoprecipitation-qPCR assay within the core promoter area, establishing its affiliation with the pRb-E2F1 circuit for the primary time.
“The research revealed overexpression and underexpression of Mad2, untimely anaphase, and chromosome missegregation in all of the samples,” the researchers write.
LOH sample recognized a deletion in D4S2975 in 40% of ESCC samples. The research reveals the deregulation of pRb-E2F1 circuit in all samples. 4q27 disruption might be an element for Mad2 underexpression in AN-induced esophageal carcinogenesis, whereas overexpression could also be because of the deregulation of the Rb-E2F1 circuit and consequently elevation of H3K4me3 and H3K9ac.
“Mad2 expression levels with chromosomal abnormalities generally is a scientific biomarker, however additional analysis is required to know pRb’s position in Mad2 down-regulation,” the researchers conclude.
Extra info:
Chongtham Sovachandra Singh et al, Differential expression of Mad2 gene is consequential to the patterns of histone H3 post-translational modifications in its promoter area in human esophageal most cancers samples, Oncotarget (2024). DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.28554
Supplied by
Impression Journals LLC
Quotation:
Differential expression of Mad2 gene in human esophageal most cancers (2024, February 12)
retrieved 12 February 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-02-differential-mad2-gene-human-esophageal.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post