[ad_1]
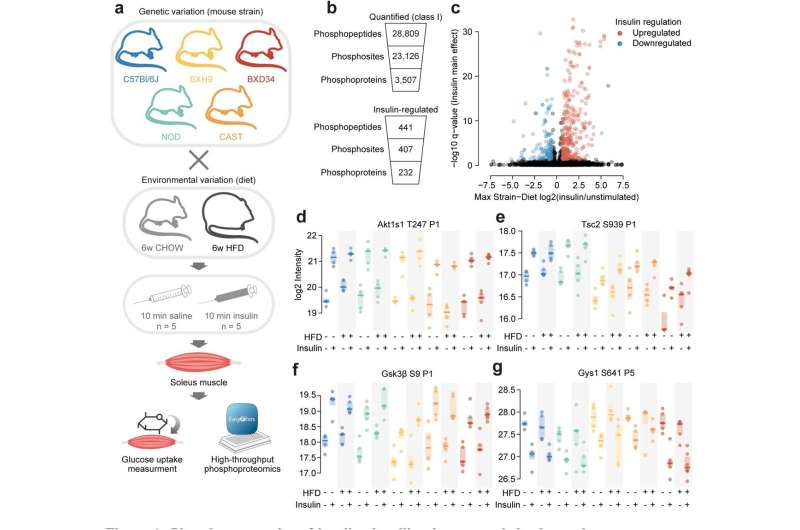
Researchers have produced a complete image of insulin signaling in mice and recommend that it’s formed by entangled results of genetics and weight loss plan.
The analysis, revealed right now as a Reviewed Preprint in eLife, is described by the editors as a elementary examine of considerable significance. They are saying the authors share compelling proof that sheds mild on the interaction between genetic attributes and environmental conditions in shaping insulin signaling in skeletal muscle—a vital regulator of metabolism.
The examine additionally supplies a singular software for assessing the vary of phosphorylation in insulin reactions and is anticipated to supply inspiration for additional analysis into metabolic illness and diabetes.
“Insulin resistance—the failure of insulin to advertise glucose uptake in its goal tissues—is triggered by genetic and environmental factors comparable to family history and high-calorie diets,” says lead writer Julian van Gerwen, throughout the examine an undergraduate on the Faculty of Life and Environmental Sciences, College of Sydney, Australia. “Though insulin resistance is a serious precursor of metabolic illness, together with sort 2 diabetes, its mechanistic foundation stays unresolved.”
Insulin usually tells the physique to soak up glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream by way of a fancy and dynamic signaling pathway. These alerts are enabled by a course of referred to as phosphorylation—the addition of a phosphate group to a protein at a really particular place (referred to as a phosphosite).
It’s thought that insulin signaling controls 1000’s of phosphosites, however many are nonetheless uncharacterized. As well as, though it’s well-known that particular person individuals range significantly of their physiological response to insulin, it stays unclear how genetics or weight loss plan affect the phosphorylation standing of mobile proteins—often known as the phosphoproteome.
To deal with this, van Gerwen and colleagues studied mice with well-characterized however totally different genetic backgrounds, so they might decipher the precise results of genetics and weight loss plan on insulin signaling.
They fed 5 strains of mice both a traditional or high-fat and high-sugar weight loss plan, and took samples of their skeletal muscle—the location of best insulin-triggered glucose uptake after consuming. Then they measured phosphorylation of the 1000’s of proteins current in every muscle pattern utilizing mass spectrometry. Their evaluation recovered many well-known insulin-regulated phosphosites, and lots of extra novel websites that had not beforehand been related to insulin signaling.
To discover the affect of genetic and environmental variation, the group developed an algorithm to research which adjustments may very well be attributed to genetics, weight loss plan, or their mixture. Virtually half of all insulin-regulated phosphosites had been affected by the pressure of the mice when fed a traditional weight loss plan, both having a stronger or weaker response to insulin. General, every genetic background displayed a singular fingerprint of insulin signaling.
Against this, though there have been adjustments in insulin signaling attributable to weight loss plan, the overwhelming majority of those had been formed by the genetic background of the mice. Many phosphosites even modified in the other way between a number of strains, highlighting that the molecular impacts of a high-fat weight loss plan are strongly managed by genetics.
To discover whether or not these adjustments in phosphorylation amounted to an altered insulin response within the mice, the group additionally measured glucose uptake in the identical muscle groups used for the phosphoproteome evaluation. By linking all insulin-regulated phosphosites with the extent of glucose uptake, the researchers narrowed down on a set of key phosphosites prone to management the insulin response. Impressed by one among these phosphosites, the group discovered that modulating a particular protein may reverse insulin resistance in a cell-based mannequin.
The authors level out that the genetic and diet-driven adjustments in phosphorylation largely couldn’t be predicted by the present mannequin of the insulin signaling pathway. This highlights that our data of this pathway is much from full, and so they say that the subsequent step is to analyze underlying biomolecular mechanisms that would hyperlink frequent adjustments. In addition they recommend that incorporating feminine mice and a wider vary of genetic backgrounds will strengthen their analysis.
“The protein phosphorylation panorama is huge and complicated, akin to an evening sky crammed with stars,” explains senior writer David James, a professor on the Faculty of Life and Environmental Sciences and School of Medication and Well being, College of Sydney. “Many groups have sought to arrange these stars into constellations and chart those who collapse in illness. Nevertheless, most have solely used cell traces and lab animals of restricted genetic backgrounds.”
“On this examine, after we examined genetic and environmental variation—as happens within the human inhabitants—we noticed a whole rearrangement of the evening sky, marked by a fading of the acquainted constellations and the emergence of totally new galaxies. To actually comprehend how ailments manifest from signaling aberrations, we should adapt to this newfound complexity. Our work supplies a launching pad for future research to deal with this complexity for insulin resistance and diabetes.”
Extra info:
Julian van Gerwen et al, The genetic and dietary panorama of the muscle insulin signalling community, eLife (2023). DOI: 10.7554/eLife.89212.1 elifesciences.org/reviewed-preprints/89212
Quotation:
Complete insulin signaling map exhibits interaction between genes and weight loss plan (2023, September 12)
retrieved 12 September 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-09-comprehensive-insulin-interplay-genes-diet.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post