[ad_1]
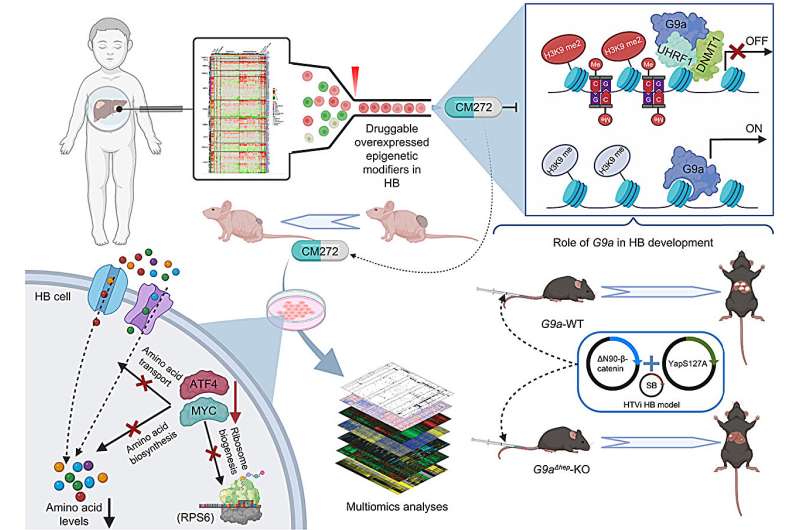
Graphical Summary. Credit score: Journal of Hepatology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.05.031
Hepatoblastoma is probably the most frequent liver most cancers in childhood. Regardless of the advances in its mixed remedy involving surgical procedure and chemotherapy, this illness presents vital therapeutic challenges, particularly for sufferers with aggressive tumors.
A collaborative research, led by Cima Universidad de Navarra, has recognized key epigenetic targets for its remedy. This analysis opens up new views for coping with numerous cancer kinds.
“Our work reveals that epigenetic alterations play a vital position within the improvement and development of the illness. Particularly, we have now recognized a promising therapeutic goal, the enzyme histone-lysine methyltransferase G9a, which actively participates in epigenetic regulation in these tumors,” notes Dr. Matías Ávila, co-director of the Strong Tumors Program at Cima and coordinator of the venture.
This work has been executed in collaboration with Dr. José Juan García Marín (USAL—Universidad de Salamanca and IBSAL), Dr. Maria Luz Martínez-Chantar (Heart for Cooperative Analysis in Biosciences—CIC bioGUNE), Dr. Pau Sancho-Bru ( August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Analysis Institute—IDIBAPS), and Dr. Carolina Armengol from the Germans Trias i Pujol Analysis Institute (IGTP).
“This discovery is a big step in understanding hepatoblastoma and gives new alternatives to develop focused therapies that may improve the standard of life for pediatric sufferers battling this illness,” states Dr. Carolina Armengol, who brings 20 years of expertise in hepatoblastoma analysis and leads the Childhood Liver Oncology (C-LOG) group at IGTP, a pioneering group within the research of childhood liver most cancers in Spain.
Based on Dr. Maite García, a researcher in Cima’s Hepatology Group, “this work not solely sheds gentle on hepatoblastoma but additionally means that therapies aimed on the G9a enzyme might be efficient for different tumor varieties depending on the identical oncogene (c-MYC).” The outcomes have been revealed within the Journal of Hepatology.
Cell progress blockage
The study discovered that, despite the fact that hepatoblastoma doesn’t exhibit many genetic mutations, it does show alterations in sure mechanisms that management gene exercise.
“These are often known as ‘epigenetic’ mechanisms, and their disruption is critical in most cancers improvement. Particularly, we discovered that an enzyme known as G9a was extremely lively in these tumors. Once we blocked this enzyme with inhibitory molecules in laboratory experiments, we may halt the expansion of hepatoblastoma most cancers cells,” the authors of the research level out.
Additionally they noticed that this childhood liver most cancers modifications the best way cells metabolize vitamins. By blocking G9a, they had been capable of reverse these metabolic modifications, which play a vital position in most cancers progress.
This research underscores the significance of epigenetic alterations in hepatoblastoma and means that G9a is a promising therapeutic goal. Moreover, it gives a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms concerned within the aggressiveness of childhood liver tumors and the shortage of response to pharmacological remedy. These findings may result in the event of recent and more practical instruments and therapies for treating this illness.
This multicenter research was carried out throughout the framework of the Biomedical Analysis Networking Heart in Hepatic and Digestive Illnesses (CIBEREHD), as a part of the Coordinated Challenge PMed4HB.
Figuring out new therapeutic targets for hepatoblastoma
Dr. Armengol has additionally participated, as a part of the coordinated venture “Customized Drugs for Childhood Liver Most cancers,” in another study revealed within the journal Nature Communications. The analysis addresses a brand new problem in understanding and treating hepatoblastoma: researchers have developed a mouse mannequin that precisely mimics the pathological traits of hepatoblastoma, particularly within the case of aggressive tumors that current decrease survival prospects.
Moreover, utilizing superior methods for single-cell RNA sequencing and complicated evaluation, scientists recognized completely different subpopulations of most cancers cells in hepatoblastoma, offering a extra detailed understanding of its biology.
Probably the most vital contributions of this research is the identification of genes important for most cancers progress, a few of that are potential therapeutic targets, corresponding to CDK7, CDK9, PRMT1, and PRMT5 by means of the event of cell traces from this mouse model.
Moreover, utilizing this experimental hepatoblastoma mannequin, researchers recognized the genes accountable for modulating the response to chemotherapy. These findings complement the earlier research and open the door to attainable focused therapies for probably the most aggressive hepatoblastoma, which lacks particular therapeutic choices.
Extra info:
Alex Clavería-Cabello et al, Identification and experimental validation of druggable epigenetic targets in hepatoblastoma, Journal of Hepatology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.05.031
Offered by
Germans Trias i Pujol Analysis Institute
Quotation:
Collaborative research identifies potential targets to deal with the commonest childhood liver most cancers (2023, October 24)
retrieved 24 October 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-10-collaborative-potential-common-childhood-liver.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post