[ad_1]
Sepideh Dolatshahi, an assistant professor of biomedical engineering on the College of Virginia, is spearheading an exploration of programs immunology in its essential improvement part—throughout being pregnant.
Programs immunology is about unraveling hid patterns throughout the human immune system, mentioned Dolatshahi, whose approaches to her analysis span computational modeling, programs serology and cutting-edge spatial evaluation strategies to research immune interactions between mom and fetus throughout being pregnant that might later assist early childhood immunity.
Designing tailor-made and efficient vaccine plans
Infants are immunocompromised and depend on antibodies from their moms to safety towards infections. Moms are vaccinated throughout being pregnant to assist enhance and customise the antibodies handed on to the child. Whereas early vaccines resembling tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis (TDAP), and just lately respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), have proven astounding success, the variety of vaccines out there to moms is proscribed and infants stay susceptible to many pathogens.
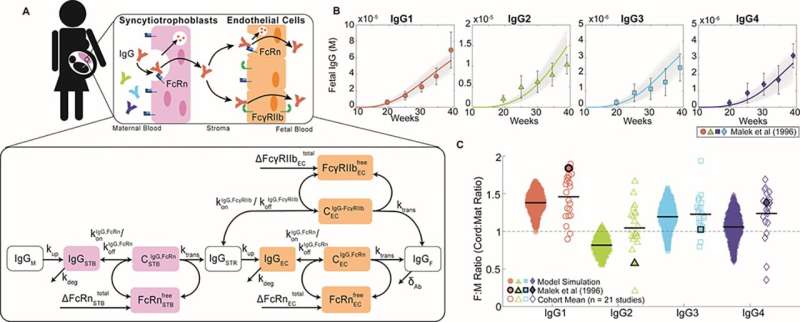
The Dolatshahi lab is working to make clear how vaccines given to pregnant women work together with each their altering immune system and the growing placenta to confer immune safety within the child. The staff’s objective is to design customized vaccination methods that may be particularly useful to susceptible sufferers, for instance, those that have genetic problems or compromised immune programs.
To perform this, Dolatshahi and her colleagues developed the primary computer-based predictive mannequin of maternal vaccination and placental antibody switch. This mannequin now serves as a instrument to assist medical doctors and pre-clinical researchers take a look at totally different vaccination strategies in silico earlier than embarking on expensive, tedious scientific trials, and to shorten the timeline for when sufferers may profit from the ensuing immunization protocols.
The significance of placental improvement
The placenta is a protecting gatekeeper that safeguards the fetus, governing which substances can attain the rising child. Shockingly, little is understood in regards to the specifics of how the placenta regulates the passage of antibodies from mom to child.
To make clear this course of and perceive which interactions are accountable for conferring switch of protecting antibodies to the child, Dolatshahi’s staff is taking a more in-depth take a look at the vital molecules expressed by placental cells and the way they work collectively to move antibodies.
By inspecting this particular course of utilizing spatial evaluation instruments, they hope to uncover info that can establish new targets of maternal vaccines that can maximize the profit to the child.
Uncovering variability throughout the inhabitants
Throughout being pregnant the mom’s immune system is in fixed flux, so there isn’t a motive to consider that vaccination throughout being pregnant needs to be a one-size-fits-all strategy. Dolatshahi and her staff hope to uncover key variables affecting placental antibody switch which may contribute to variations throughout the inhabitants.
By defining what causes some infants to obtain extra maternal antibodies than others, Dolatshahi’s work will assist medical doctors establish sufferers who might profit from specifically designed vaccines to greatest assist their child’s immune system. Extra broadly, this investigation will make clear the organic and socioeconomic components which make some ladies extra susceptible to immune-related being pregnant problems.
This analysis stands as a milestone to understanding the nuances of how maternal antibodies traverse the placenta and confer safety in new child infants, and to uncovering particular immune-related mechanisms of being pregnant problems resembling preterm beginning and preeclampsia. Dolatshahi’s analysis units the stage for a extra profound comprehension of the immune system‘s conduct throughout pregnancy, providing a promising trajectory for additional developments on this important area.
The staff’s publication about this analysis, “Quantitative mechanistic model reveals key determinants of placental IgG transfer and informs prenatal immunization strategies,” has been accepted for publication by PLOS Computational Biology.
Extra info:
Remziye E. Wessel et al, Quantitative mechanistic mannequin reveals key determinants of placental IgG switch and informs prenatal immunization methods, PLOS Computational Biology (2023). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011109
Quotation:
Biomedical engineers unveil the dynamics of maternal immune responses (2023, December 16)
retrieved 17 December 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-12-biomedical-unveil-dynamics-maternal-immune.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post