[ad_1]
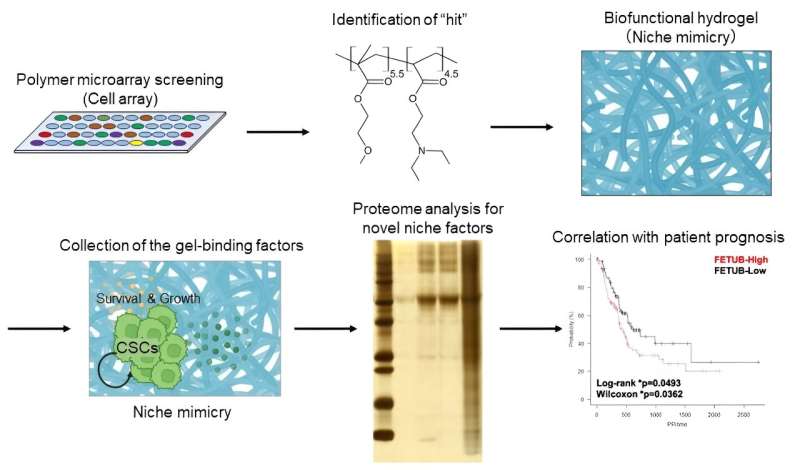
One of many largest challenges in biomedical analysis is discovering a option to seize the complexity of the human physique in laboratory-based methods, to allow them to be investigated precisely. Now, researchers from Japan report an strategy for exactly imitating a key function of aggressive cancers within the laboratory.
In a examine revealed lately in Irritation and Regenerationresearchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental College (TMDU) have revealed {that a} artificial scaffold mimicking the cancer microenvironment may very well be a robust software for understanding cancer progression and remedy.
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma is a very lethal most cancers, partially as a result of it’s troublesome to detect within the early levels, and partially due to the presence of persistent most cancers stem cells (CSCs), that are accountable for metastasis, resistance to remedy, and relapse. These CSCs exist inside a specialised most cancers microenvironment referred to as a distinct segment, and disrupting this CSC area of interest may impair most cancers development.
“CSCs talk with their area of interest by numerous cues, reminiscent of biological factorsphysicochemical components, and inflammatory components,” says lead writer of the examine Yoshitaka Murota. “The complexity of the CSC area of interest makes it difficult to establish helpful remedy targets, significantly in affected person samples, so we sought to design a laboratory-based synthetic area of interest that will recapitulate this intricate microenvironment.”
To do that, the researchers utilized pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells to an intensive array of artificial biofunctional supplies. They then assessed mobile development on every of the candidate supplies to pick out the one that almost all strongly supported development of CSCs, however not non-CSCs.
“The outcomes had been unequivocal,” explains Kouichi Tabu, senior writer. “Once we embedded the chosen polymer in hydrogel to create a niche-mimicking scaffold, it particularly supported substantial development and proliferation of human pancreatic CSCs.”
Subsequent, the researchers analyzed the serum proteins that had been enriched on the hydrogel the place the pancreatic cells had been rising and in contrast them to components recognized to advertise pancreatic cancer. The evaluation confirmed that the niche-mimicking biomaterial trapped a number of serum components, one in all which is carefully related to poor prognosis in sufferers with pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
“Taken collectively, our findings present that the polymeric hydrogel that we fabricated precisely mimics the pancreatic CSC area of interest and can be utilized to establish therapeutic targets that correlate considerably with affected person survival,” says Murota.
On condition that CSCs and the most cancers microenvironment are just about common options of most cancers, it’s doubtless that the findings from this examine will be utilized to different most cancers sorts. Utilizing this kind of artificial polymer materials to create synthetic CSC niches might assist establish vital most cancers biomarkers and remedy targets sooner or later.
Extra data:
Yoshitaka Murota et al, A distinct segment-mimicking polymer hydrogel-based strategy to establish molecular targets for tackling human pancreatic most cancers stem cells, Irritation and Regeneration (2023). DOI: 10.1186/s41232-023-00296-0
Supplied by
Tokyo Medical and Dental University
Quotation:
Discovering your area of interest: An artificial most cancers stem cell microenvironment (2023, November 9)
retrieved 10 November 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-11-niche-synthetic-cancer-stem-cell.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]




Discussion about this post