[ad_1]
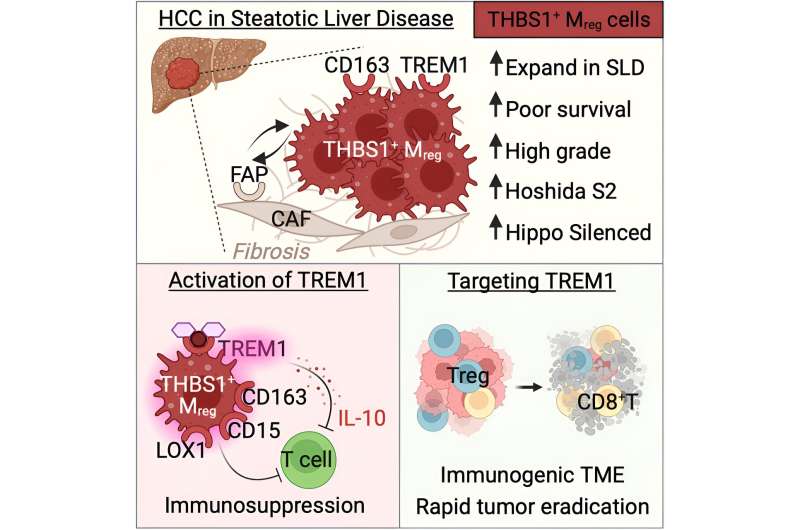
Graphical summary. Credit score: Cell Reviews (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.11377
A analysis staff of Canadian and French scientists, led by INRS professor Maya Saleh, has been investigating immunotherapy resistance in sure sufferers with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) related to steatotic liver illness. The findings are published within the journal Cell Reviews.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is related to recognized risk factors corresponding to power hepatitis B or C an infection, alcohol abuse, and metabolic dysfunction. It’s the commonest kind of liver most cancers. Regardless of main advances in immunotherapy, this most cancers is usually deadly: round 75% of sufferers with superior HCC fail to answer the sort of remedy for causes which have but to be clarified.
This inspired the analysis staff to discover the hyperlink between metabolic dysfunction-associated liver illness, a power inflammatory illness of the liver, and therapeutic resistance to immunotherapy in HCC sufferers.
“We’ve got recognized an immune biomarker for HCC related to steatotic liver illness, which is able to enable us to develop new immunotherapies,” explains Professor Maya Saleh, a global specialist in immuno-oncology. “We might envisage immunotherapies that restore an efficient immune response towards HCC by attenuating the damaging liver irritation.”
Discovery of a possible therapeutic goal
HCC stays a serious public well being concern; in North America, its incidence has doubled previously three a long time. Previous to the approval of immunotherapy, the treatment options for superior HCC have been restricted and ineffective. For example, sorafenib improves imply total survival by simply 3 months and is related to vital unwanted effects.
Immunotherapies, when administered in combos, improve the common survival of HCC sufferers by 17 months on common.
Because of the usage of “omics” applied sciences, which permit massive portions of organic information to be analyzed in a brief timeframe, the staff developed an immune map of the tumor and adjoining non-tumoral liver in 10 sufferers. These preliminary immune maps led them to check databases of a whole bunch of sufferers so as to validate the immune profiles associated to threat components and related to illness severity.
These preliminary outcomes point out that the power irritation from steatotic liver illness makes the liver most cancers atmosphere distinctive, with an enlargement of immunosuppressive cells that paralyze the immunological assault of the tumor.
The analysis staff has demonstrated that the immunosuppressive cells categorical an inflammatory receptor named TREM1, which makes them extra harmful. They, subsequently, highlighted TREM1 as a possible therapeutic goal in HCC related to steatotic liver illness.
Attention-grabbing implications for immunotherapy analysis
By figuring out this biomarker, which might clarify remedy failure in folks with HCC, the staff has paved the way in which for a brand new method to classifying sufferers. This could enable them to find out who can be extra possible to answer immunotherapy earlier than remedy even begins.
Such a scientific breakthrough would ease the psychological burden for sufferers who do not reply to immunotherapy. Essential bodily impacts, together with unwanted effects, is also prevented.
“It is a promising avenue for the following few years. We are going to proceed the evaluation by characterizing the immune element of tumors in a bigger cohort of sufferers, together with complete imaging of tumor cell composition and the usage of synthetic intelligence to hyperlink immune profiles to response to remedy. This might have a big impression on the sector,” concludes Professor Saleh.
Extra info:
Julie Giraud et al, THBS1+ myeloid cells develop in SLD hepatocellular carcinoma and contribute to immunosuppression and unfavorable prognosis via TREM1, Cell Reviews (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.11377 www.cell.com/cell-reports/full … 2211-1247(24)00101-3
Quotation:
Liver most cancers: A promising avenue for simpler immunotherapies (2024, February 14)
retrieved 14 February 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-02-liver-cancer-avenue-effective-immunotherapies.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post