[ad_1]
Researchers from Kyushu College, Japan have developed a novel deep-learning mannequin which might precisely estimate viable tumor cell density from pathological photos of osteosarcoma sufferers, and predict their prognosis following chemotherapy. Credit score: Dr. Makoto Endo/Kyushu College
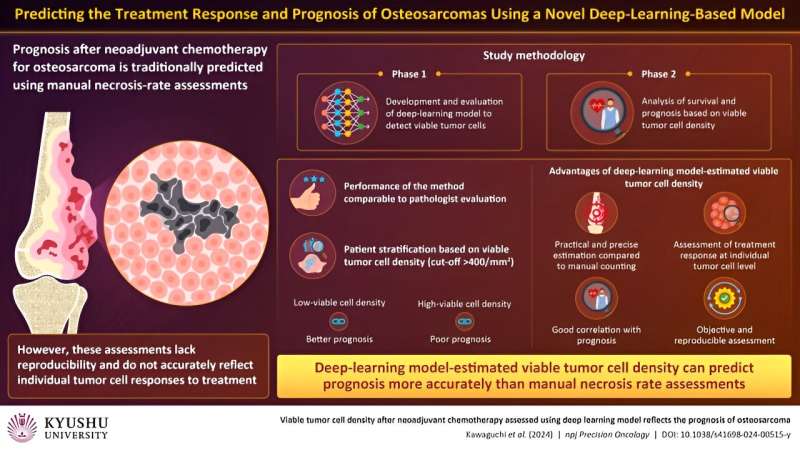
Researchers at Kyushu College have developed and validated a machine-learning mannequin that may precisely consider the density of surviving tumor cells after therapy in pathological photos of osteosarcoma—probably the most prevalent malignant bone tumor. The mannequin can assess how particular person tumor cells reply to therapy and may predict general affected person prognosis extra reliably than standard strategies.
Surgical procedure and chemotherapy have considerably improved the outcomes of sufferers with localized osteosarcoma. Nevertheless, sufferers with superior metastatic illness (the stage the place cancerous cells have unfold to distant tissues) have a low survival price. After a normal therapy of surgical procedure and chemotherapy, assessing the prognosis of sufferers is crucial for figuring out their subsequent particular person therapy plans. Nevertheless, predicting affected person outcomes has many challenges.
Presently, prognosis depends on necrosis price evaluation, which includes pathologists evaluating the proportion of lifeless tissue inside a tumor. Sadly, these strategies are restricted by variability between pathologists’ assessments and should not precisely predict therapy response.
Recognizing the necessity for quicker and extra correct prognoses, co-first authors Dr. Kengo Kawaguchi and Dr. Kazuki Miyama, from the Division of Orthopedic Surgical procedure, Graduate Faculty of Medical Sciences, Kyushu College, Japan, and Dr. Makoto Endo, a lecturer of Orthopedic Surgical procedure at Kyushu College Hospital, together with collaborators, turned to synthetic intelligence (AI) for a extra nuanced analysis. The multidisciplinary was staff headed by Dr. Endo included Kyushu College’s Professor Ryoma Bise, Professor Yoshinao Oda, and Professor Yasuharu Nakashima.
Explaining the rationale behind their analysis, which was published in npj Precision OncologyDr. Endo says, “Within the conventional methodology, the necrosis price is calculated as a necrotic space reasonably than particular person cell counts, which isn’t sufficiently reproducible between assessors and doesn’t adequately replicate the results of anticancer medicine. We due to this fact thought-about utilizing AI to enhance the estimation.”
In section 1 of the research, the staff skilled a sort of AI, referred to as a deep-learning mannequin, to detect surviving tumor cells and validated its detection efficiency utilizing affected person knowledge. The AI mannequin confirmed proficiency in detecting viable tumor cells in pathological photos, aligning with knowledgeable pathologists’ capabilities.
In section 2, the researchers analyzed two key measures: disease-specific survival, which tracks the length after analysis or therapy with out loss of life immediately brought on by the illness, and metastasis-free survival, which screens the time post-treatment with out most cancers cells spreading to distant physique components. Additionally they explored the correlation between AI-estimated viable tumor cell density and prognosis. Notably, the AI mannequin demonstrated comparable detection efficiency and precision to that of the pathologist, with good reproducibility.
Subsequent, the researchers sorted the sufferers into teams based mostly on whether or not the viable tumor cell density was above or under 400/mm2. The survival evaluation revealed that the high-density group confirmed a worse prognosis, whereas the low-density group confirmed a greater prognosis for disease-specific survival and metastasis-free survival.
Necrosis price, alternatively, was not related to disease-specific survival or metastasis-free survival. Moreover, evaluation of particular person circumstances revealed that AI-estimated viable tumor cell density was a extra dependable predictor of prognosis than necrosis price.
Total, these findings counsel that the AI-based measurement of viable tumor cells displays the inherent malignancy (means of the most cancers to unfold) and particular person tumor cell response of osteosarcomas. Incorporating AI within the evaluation of pathological photos improves detection accuracy, reduces inter-assessor variability, and allows well timed evaluation.
Furthermore, the estimation of viable tumor cells, which displays their means to maintain multiplying following chemotherapy, is a extra dependable predictor of therapy response than cell loss of life. Giant-scale validation of the AI mannequin developed on this research can help its wider software in real-life medical settings.
“This new strategy has the potential to boost the accuracy of prognoses for osteosarcoma sufferers handled with chemotherapy. Sooner or later, we intend to actively apply AI to uncommon illnesses similar to osteosarcoma, which have seen restricted developments in epidemiology, pathogenesis, and etiology.
“Regardless of the passage of a long time, notably in treatment methods, substantial progress stays elusive. By placing AI to the issue, this would possibly lastly change,” concludes Dr. Endo.
Extra info:
Kengo Kawaguchi et al, Viable tumor cell density after neoadjuvant chemotherapy assessed utilizing deep studying mannequin displays the prognosis of osteosarcoma, npj Precision Oncology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41698-024-00515-y
Offered by
Kyushu University
Quotation:
AI’s means to detect tumor cells might be key to extra correct bone most cancers prognoses (2024, April 2)
retrieved 3 April 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-04-ai-ability-tumor-cells-key.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post