[ad_1]
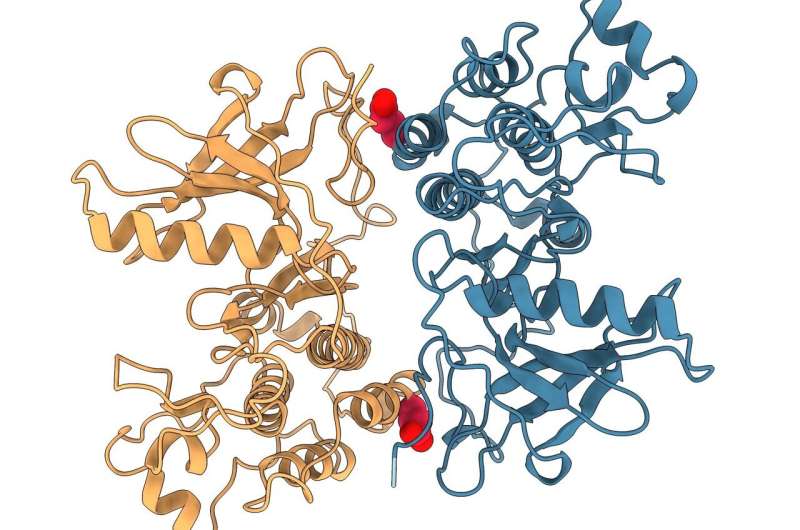
Rendering of interface within the mutant EGFR studied that was proven to be crucial for EGFR-driven tumor progress. The K946E mutation proven in crimson was utilized by the workforce to verify that this interface is implicated in tumor progress within the examine. Credit score: Ioannis Galgadas, College of Geneva
Researchers have proven for the primary time {that a} essential interface in a protein that drives most cancers progress might act as a goal for more practical remedies.
The examine was led by the Science and Know-how Amenities Council (STFC) Central Laser Facility (CLF) and used superior laser imaging methods to establish structural particulars of a mutated protein that assist it to evade medicine that focus on it.
The analysis is published within the journal Nature Communications and lays the groundwork for future analysis into more practical, long-lasting most cancers therapies.
The Epidermal Development Issue Receptor (EGFR) is a protein that sits on the floor of cells and receives molecular alerts that inform the cell to develop and divide. In sure varieties of most cancers, mutated EGFR stimulates uncontrolled progress, leading to tumors. Numerous most cancers remedies block and inhibit mutant EGFR to forestall tumor formation, however these are restricted, as finally cancerous cells generally develop additional EGFR mutations which can be proof against therapy.
Till now, how precisely these drug-resistant EGFR mutations drive tumor progress has not been understood, hindering our means to develop remedies that focus on them.
On this newest examine, scientists at CLF have obtained super-resolution photographs of a drug-resistant EGFR mutation recognized to contribute to lung most cancers. This was achieved utilizing a sophisticated laser imaging approach developed by STFC for this objective and known as Fluorophore Localization Imaging with Photobleaching, or FLImP.
FLImP evaluation revealed structural particulars as small as two nanometers and confirmed for the primary time with this stage of precision how molecules within the drug-resistant EGFR mutation work together.
Further evaluation by the Biomolecular & Pharmaceutical Modeling Group at College of Geneva (UNIGE) used advanced computer simulations that—mixed with the FLImP evaluation—offered atomistic particulars of the mutant EGFR complexes. From this, the workforce was in a position to evaluate the structural particulars of the mutated and wholesome EGFR to establish interfaces between interacting molecules within the drug-resistant mutation crucial for tumor progress.
Professor Marisa Martin-Fernandez, Chief of the Octopus Group at CLF, which led the examine, stated, “This discovering is the end result of years of analysis and technological development at CLF and our companion establishments and we’re extraordinarily enthusiastic about its potential to tell the course of most cancers analysis going ahead. If this interface proves to be an efficient therapeutic goal, it might present a completely new method to a lot wanted pharmaceutical growth.”
The workforce then launched extra mutations to the drug-resistant EGFR in in cultured lung cells and in mice that interfered with the newly found interfaces.
In these experiments, one of many extra EGFR mutations was proven to dam cancer growthwith mice creating no tumors, additional indicating that the flexibility of this EGFR mutation to advertise most cancers certainly is determined by these interfaces.
Dr. Gilbert Fruhwirth, Chief of the Imaging Therapies and Most cancers group at King’s School London who validated leads to dwell animals, remarked, “This analysis has turn out to be potential by means of the mixture of a wide range of completely different imaging applied sciences, starting from single molecules to complete animals, and demonstrates the ability of imaging to raised perceive the internal workings of most cancers. We’re extraordinarily happy about this profitable collaboration and look ahead to develop this pharmaceutical alternative additional as a part of this workforce.”
Researchers hope that these interfaces might act as potential targets for brand new most cancers therapies that overcome resistance acquired by EGFR mutations.
Professor Francesco Luigi Gervasio, Chief of the Biomolecular & Pharmaceutical Modeling Group at UNIGE, commented, “This breakthrough was made potential by a mixture of state-of-the-art simulations and experimental methods that may now ‘visualize’ the construction and dynamics of necessary most cancers targets akin to EGFR in unprecedented element.”
Dr. Yiannis Galdadas at UNIGE, who carried out the simulations, added, “The simulations had been in a position to push the efficient decision of the microscope past the boundaries of creativeness. It is virtually potential to ‘contact’ the mutation website and see its impact.”
Additional research at CLF are presently testing the analysis technique on different EGFR mutations recognized to contribute to lung most cancers. In addition they hope to ascertain whether or not this interface performs a job within the growth of different cancers together with mind most cancers.
Extra data:
Drug-resistant EGFR mutations promote lung most cancers by stabilizing interfaces in ligand-free kinase energetic EGFR oligomers, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46284-x. www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-46284-x
Offered by
UK Research and Innovation
Quotation:
Scientists establish Achilles heel of lung most cancers protein (2024, March 19)
retrieved 19 March 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-03-scientists-achilles-heel-lung-cancer.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post