[ad_1]
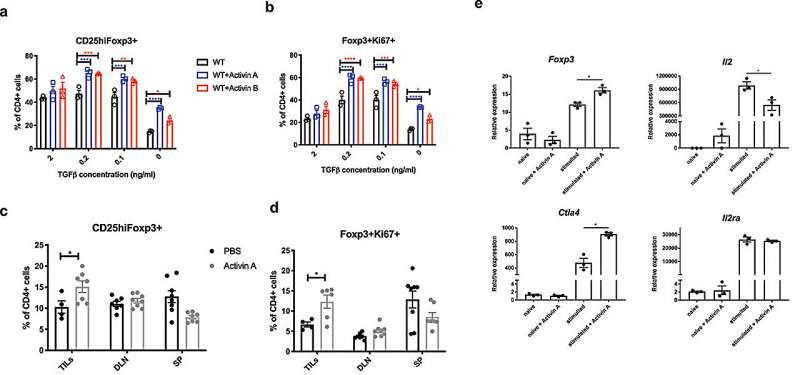
Activins promote the event of induced Tregs (iTregs) in vitro and in vivo. (a-b) naive CD4+ T cells have been remoted from WT C57BL/6J mice, after which cultured in vitro with plate-bound anti-CD3, soluble anti-CD28, recombinant IL-2 and the indicated gradient concentrations of TGF-b for 3 days. The proportion of CD25excessiveFoxp3+ (a) and Foxp3+Ki67+ (b) in CD4+ cells have been analyzed by movement cytometry. (c-d) WT C57BL/6J mice have been inoculated with B16F10 tumors and handled with 50ng per mouse recombinant activin A or PBS each different day for 21 days. TILs and specified organs (draining lymph nodes proven as DLN, spleens proven as SP) have been harvested from these mice and analyzed for the frequency of CD25excessiveFoxp3+ (c) and Foxp3+Ki67+ (d) in CD4+ cells by movement cytometry. (e) naive CD4+ T cells have been remoted from WT C57BL/6J mice, after which stimulated with plate-bound anti-CD3, soluble anti-CD28, recombinant IL-2 within the absence or presence of recombinant activin A. 36 hours later, RNA was analyzed for the expression of indicated genes utilizing qRT-PCR. Credit score: OncoImmunology (2024). DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2023.2297503
Medication that focus on a receptor on immune cells known as activin receptor 1C might fight tumor-induced immune suppression and assist sufferers’ immune programs combat again in opposition to most cancers, in accordance with a examine by investigators on the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Most cancers Heart and its Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Most cancers Immunotherapy.
The examine, published in Oncoimmunologyidentifies a brand new technique most cancers cells use to guard themselves from immune system assault, and suggests remedies that would counteract it.
It reveals that tumor cells and a few immune cells produce proteins known as activins that trigger immune cells known as CD4+ T helper cells—which ship alerts to different immune cells to destroy infectious particles—to rework into one other kind of T cell (regulatory T-cells, or Tregs), which performs the alternative operate, suppressing immune system exercise.
Nevertheless, blocking activin receptor 1C on CD4+ T cells helps forestall the buildup of immune-suppressing Tregs in tumors and slows tumor progress.
“We’ve got recognized a brand new goal for anticancer immunotherapy,” says the examine’s senior investigator, Drew Pardoll, M.D., P.h.D., director of the Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Most cancers Immunotherapy and professor of oncology on the Johns Hopkins College Faculty of Medication. “Our discovery might result in a completely new class of immunotherapies which will improve the consequences of present most cancers therapies and additional personalize cancer care.”
Tregs are important in stopping the immune system from attacking the physique’s cells and inflicting autoimmune ailments. However tumors co-opt this usually protecting cell to defend themselves in opposition to destruction by the immune system, suppressing the physique’s built-in defenses to most cancers. Sufferers with extra Tregs have worse most cancers outcomes, however research in mice have proven that blocking Tregs inhibits tumor progress, and lowering Treg numbers causes tumors to shrink.
A couple of decade of analysis by Johns Hopkins researchers on the function of a transcription issue known as YAP in Treg manufacturing in tumor cells led to the invention that YAP boosts activin receptor 1C numbers on Tregs. The truth that this receptor solely happens on cells produced within the bone marrowsimilar to immune or blood cells, reduces the chance of dangerous off-target results.
Within the examine, the investigators demonstrated that mice genetically engineered to lack the activin receptor 1C are wholesome, capable of reproduce, and naturally immune to tumor growth. Treating mice with an antibody that blocks the receptor additionally had anticancer results. When mixed with antibodies to a second inhibitory immune receptor, PD-1, which is used clinically to deal with many cancers, the antibody had an excellent larger affect on tumors, even these that don’t normally reply to anti-PD-1 therapies.
As a result of the human activin receptor 1C is sort of an identical to the mouse activin receptor 1C, Pardoll is hopeful that comparable efficacy can be achieved in people. The similarity will even assist expedite preclinical research testing anti-activin receptor 1C antibody remedy candidates. Pardoll and colleagues are partnering with Immunomic Therapeutics to develop a number of potential candidate antibodies.
“We hope to have an antibody accessible for clinical trials in 2025,” he says.
If medical trials are profitable, the anti-activin receptor 1C antibodies might be a potent addition to the arsenal of anticancer medicine. Combining them with PD-1 inhibitors might enhance therapy effectiveness. Pardoll explains that blood assessments can determine sufferers with excessive ranges of activin who could also be extra more likely to profit from anti-activin receptor 1C antibody therapies, permitting extra exact identification of sufferers more likely to profit from the remedy.
Extra info:
Ying Zheng et al, Concentrating on the activin receptor 1C on CD4+ T cells for most cancers immunotherapy, OncoImmunology (2024). DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2023.2297503
Supplied by
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
Quotation:
Immune cell receptor gives promising immunotherapy goal (2024, February 22)
retrieved 23 February 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-02-immune-cell-receptor-immunotherapy.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post