[ad_1]
Credit score: Molecular & Mobile Proteomics (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100702
By revolutionary exploratory work, scientists have recognized a brand new strategy to research proteins which are concerned within the improvement of the vast majority of breast cancers.
This research was initiated by the Molecular Endocrinology Group at The Institute of Most cancers Analysis, London, in collaboration with the institute’s Purposeful Proteomics Analysis Group. It’s published within the journal Molecular & Mobile Proteomics.
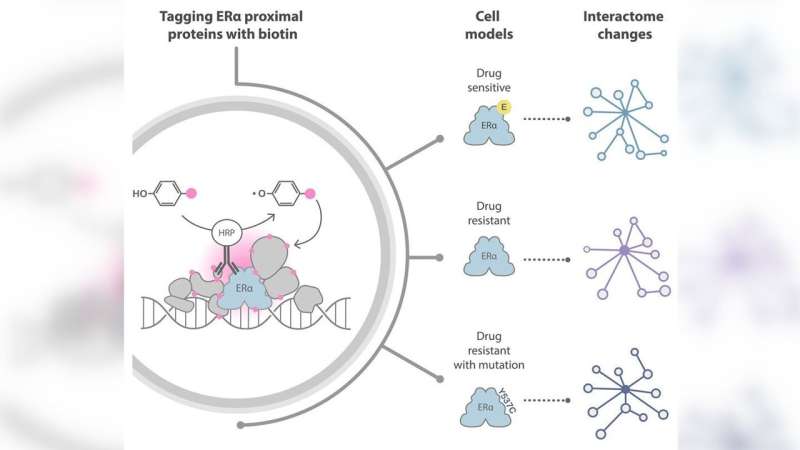
The analysis group efficiently used a cutting-edge method to detect many of the proteins identified to work together with estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), which is expressed in about 70% of breast cancers and promotes the event of the illness by rising cell growth and survival. Additionally they uncovered potential new therapeutic targets within the type of novel proteins that work together with ERα.
Researchers worldwide can now use this method to assist them work towards growing new focused therapies for ERα-positive breast cancer. They’ll additionally use it to review the proteins that work together with key receptors in different sorts of most cancers.
ERα is a vital goal
It has lengthy been identified that estrogen has a key function in breast most cancers development. That is largely on account of ERα, which is activated by this hormone. Upon activation, ERα crosses into the nucleus of the most cancers cell the place it interacts with numerous proteins to extend the variety of most cancers cells and lengthen their survival.
Though scientists have already developed remedies that forestall ERα from binding to estrogen, many sufferers discover that their most cancers turns into resistant to those therapies over time. One of many mechanisms behind this resistance includes irregular interactions between ERα and the proteins surrounding it.
By understanding the intricacies of those interactions, researchers imagine that it is going to be doable to higher perceive the mechanisms underlying resistance and to develop extra focused therapies.
Taking a brand new method
Not too long ago, a novel method to investigating protein interactions has remodeled the protein interplay area. This methodology known as proximity labeling, and it makes use of enzymes to label endogenous interplay companions of particular proteins of curiosity with biotin. An analytical technique referred to as mass spectrometry permits scientists to determine biotin-labeled proteins.
This labeling helps reveal proximal proteins inside cells, however it isn’t particular sufficient to disclose the molecular particulars of how interactions happen. As an example, it can’t distinguish between proteins being subsequent to one another and proteins being instantly certain collectively. Nonetheless, it’s an especially great tool for acquiring details about the spatial panorama of proteins.
The group at The Institute of Most cancers Analysis (ICR) determined to attempt a unique approach referred to as biotinylation by antibody recognition (BAR), which makes use of antibodies joined with enzymes to focus on the protein of curiosity, thereby avoiding genetic manipulation of the cells.
For the primary experiment, the researchers examined epitope tagging, choosing a brief sequence of amino acids (an epitope) that’s identified to pair with a sure antibody with very excessive affinity and tagging it onto the proteins of curiosity in order that the antibody may goal them. They then used a secondary antibody conjugated with the enzyme to deposit biotin on adjoining proteins within the presence of a biotin substrate and hydrogen peroxidase.
This experiment allowed them to optimize their methodology for the second a part of the research, during which they wished to focus on the endogenous protein—protein that has not been genetically modified with the epitope tag. They did this utilizing an antibody capable of goal the complete size of the ERα protein with excessive affinity.
Confirming BAR’s effectiveness
The mass spectrometry findings revealed that BAR efficiently recognized 329 proteins identified to work together with ERα and revealed 22 new ones.
The researchers had been ready to make use of the information from their experiments to determine a number of the protein candidates prone to play an element within the improvement of resistance to therapy. Additionally they refined a listing of proteins of curiosity to 97 that ought to be prioritized for additional scientific investigation.
First creator Dr. Camilla Rega, a Postdoctoral Coaching Fellow on the ICR, mentioned, “That is the primary time BAR has been used to research ERα’s proximal protein interactions. This method offers worthwhile insights into how proteins are spatially organized within the cells and identifies transient interactions which are difficult to detect with conventional approaches.
“Now we’ve confirmed that we will use BAR efficiently, we plan to use it to scientific samples from most cancers sufferers in order that we will examine these protein interactions within the context of the illness. A greater understanding of those interactions will contribute to the event of focused therapies for ERα-positive breast most cancers and probably different ailments associated to estrogen signaling.”
Senior creator Professor Jyoti Choudhary, Professor of Most cancers Proteomics and Head of the Proteomics Core Facility on the ICR, mentioned, “Our research has supplied robust proof that BAR can be utilized successfully to additional our understanding of ERα’s function in selling most cancers development and resistance to therapy. It reveals new proteins which are concerned in necessary processes inside breast most cancers cells.
“This work has opened thrilling alternatives within the area to determine new biomarkers and has the potential to achieve insights into precision therapy methods. Our method may also be used to review the protein interactions that happen with different receptors throughout most cancers sorts.”
Extra info:
Camilla Rega et al, Exploring the Spatial Panorama of the Estrogen Receptor Proximal Proteome With Antibody-Primarily based Proximity Labeling, Molecular & Mobile Proteomics (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100702
Offered by
Institute of Cancer Research
Quotation:
Examine identifies new strategy to research proteins concerned in breast most cancers (2024, February 13)
retrieved 14 February 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-02-proteins-involved-breast-cancer.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post