[ad_1]
Bettering the way in which scientists can see the microscopic constructions of the mind can enhance our understanding of a number of mind ailments, like Alzheimer’s or a number of sclerosis. Learning these ailments is difficult and has been restricted by accuracy of accessible fashions.
To see the smallest components of cells, scientists typically use a method referred to as electron microscopy. Electron microscopy traditionally includes including chemical substances and bodily reducing the tissue. Nonetheless, this method can change the way in which the cells and constructions look, perturbing their pure state, and may restrict decision.
An alternate technique, referred to as cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET), offers clearer photographs of the mind’s smallest components in a extra native state, nevertheless, it requires freezing. Freezing samples to cryogenic temperatures should be finished fastidiously or ice crystals can type, disrupting the native anatomy.
However new analysis by Benjamin Creekmore in Yi-Wei Chang and Edward Lee’s labs on the College of Pennsylvania exhibits a brand new approach to review the human mind’s ultrastructure. They current their analysis on the 68th Biophysical Society Annual Meeting, held February 10–14, 2024 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
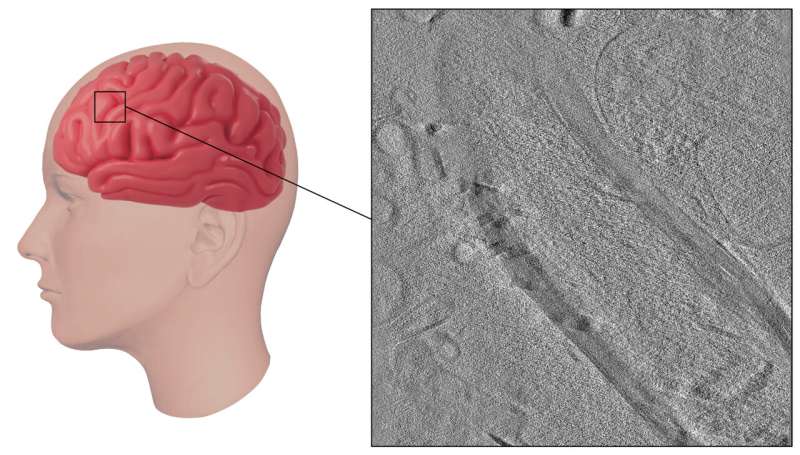
Creekmore and colleagues obtained mind tissue from autopsies, flash froze it immediately on particular grids with liquid ethane, and used a robust device referred to as a xenon plasma centered ion beam (FIB) to chop skinny slices for imaging. This technique allowed them to take a look at the mind tissue in its near-natural state with out reducing with a knife blade, including chemical substances, or slower freezing, all of which may result in modifications within the constructions.
“The commonest method to protect tissue at a time of post-mortem is to place it in a freezer after which use it later. However letting it freeze slowly after which warming it up after which refreezing it additionally disturbs the tissue. Membranes break and you may lose the conventional structure,” Creekmore defined.
One shocking a part of the brand new technique is that it lets them extra simply and quickly freeze a lot thicker samples—up to now samples have been restricted to 10 microns utilizing comparable approaches. “We have been capable of freeze samples as much as 250 microns thick with out ice crystals,” Creekmore stated. The method of getting thick samples prepared for high-resolution imaging is far quicker than with different strategies. This speed-up can enable evaluation of a wider array of samples.
By making use of this method to mind tissue from people with Alzheimer’s disease, they have been capable of observe intact constructions inside cells, equivalent to tau fibrils, an indicator of Alzheimer’s illness, and mobile parts that attempt to break down these fibrils. The staff additionally visualized and measured myelin, a sheath that is essential for nerve operate however that breaks down in sure ailments, equivalent to a number of sclerosis.
“Methods for imaging human tissue traditionally have been comparatively low decision they usually disturb the native structure. We needed to attempt to provide you with a manner that we might mannequin and examine mind ailments of their pure context,” Creekmore stated.
Their revolutionary technique offers a primary glimpse into the pure state of human brain tissue, providing useful insights into its anatomy at a excessive stage of element. This new technique can begin to present distinctive info to find out disease-causing mechanisms of a broad array of brain-related ailments.
Quotation:
Utilizing ion beams to enhance mind microscopy (2024, February 10)
retrieved 10 February 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-02-ion-brain-microscopy.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post