[ad_1]
A research led by scientists at Duke-NUS Medical Faculty has recognized the pivotal however beforehand unknown position of an enzyme, referred to as FAXDC2, that’s suppressed in cancers with hyperactive Wnt signaling. FAXDC2 regulates the manufacturing of ldl cholesterol and cell signaling molecules, and its suppression causes irregular cell development. Restoring FAXDC2 operate might probably normalize cell conduct in these cancers. Credit score: Babita Madan
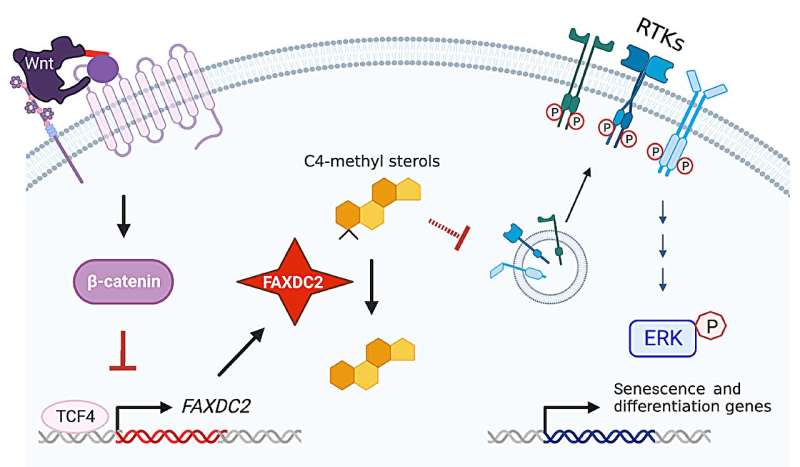
Scientists led by a group at Duke-NUS Medical Faculty have made a breakthrough in understanding the mechanisms that affect most cancers cell development and improvement. Publishing within the Journal of Scientific Investigationthe researchers illuminate the beforehand hidden position of a novel enzyme, referred to as fatty acid hydroxylase area containing 2 (FAXDC2), revealing its pivotal position in ldl cholesterol synthesis and most cancers development.
The research particulars the cascade of molecular occasions starting from the suppression of FAXDC2 to the disruption of regular ldl cholesterol synthesis to altered most cancers fates, highlighting a possible vulnerability in most cancers cells that could possibly be focused for therapeutic intervention.
“Our journey into the mobile drivers of most cancers began with an exploration of the Wnt signaling pathway, a vital participant in cell development and improvement,” defined Assistant Professor Babita Madan, first creator of the research from Duke-NUS’ Most cancers & Stem Cell Biology (CSCB) Program.
“It was throughout these research that we stumbled upon the enzyme FAXDC2, which emerged as a central determine in controlling most cancers and stem cells. Our discovery means that FAXDC2’s exercise, or its suppression, has profound implications for mobile development and differentiation, portray a posh image of the connection between cancer biology and ldl cholesterol synthesis.”
The analysis started with a deep dive into the Wnt signaling pathway, identified for its crucial position within the regulation of each regular and cancer cell growth. Wnt signaling is a key signaling pathway that regulates development and improvement and sustaining mind, pores and skin, hair and intestinal cells.
Nevertheless, hyperactive Wnt signaling—current within the most cancers fashions employed within the research—impairs cell differentiation and retains the cancers in a stem cell-like state. These undifferentiated most cancers stem cells proliferate quickly and uncontrollably, selling quicker tumor development, and are immune to anti-cancer therapies.
A research led by scientists at Duke-NUS Medical Faculty has recognized the pivotal however beforehand unknown position of an enzyme, referred to as FAXDC2, which is suppressed in cancers with hyperactive Wnt signaling. FAXDC2 regulates the manufacturing of ldl cholesterol and cell signaling molecules, and its suppression causes irregular cell development. Restoring FAXDC2 operate might probably normalize cell conduct in these cancers.
Using cutting-edge genomic applied sciences to unravel this advanced organic course of, the scientists’ consideration was drawn to the enzyme FAXDC2 after they discovered it elevated dramatically after pancreatic most cancers fashions have been handled with a made-in-Singapore Wnt inhibitor, ETC-159.
In-depth analyses of colorectal most cancers tissue samples corroborated this discovering, displaying a constant sample of FAXDC2 suppression and subsequent buildup of ldl cholesterol precursors, together with a constructing block of ldl cholesterol referred to as lophenol. The decrease the FAXDC2 expression, the upper the extent of lophenol.
“FAXDC2 is a beforehand unknown enzyme that helps make ldl cholesterol from the precursor lophenol. Importantly, how a lot FAXDC2 you’ve got in your cells adjustments the quantity of lophenol you’ve got,” defined Professor David Virshup, Director of the CSCB Program and the senior creator of the research.
“Lophenol seems to modulate the exercise of the differentiation pathway and, subsequently, we predict it helps to maintain most cancers cells in a extra stem cell-like state.”
Prof Virshup emphasised the broader implications of those insights, saying, “This research gives a captivating glimpse into the molecular equipment of most cancers cells. The position of FAXDC2 in regulating ldl cholesterol synthesis opens new pathways for future therapies. Understanding these advanced mechanisms paves the way in which for progressive approaches to fight most cancers, emphasizing the significance of ldl cholesterol biosynthesis intermediates as necessary signaling molecules and potential medication.”
The invention of FAXDC2’s position in most cancers biology marks just the start of an extended scientific journey. Additional analysis is important to totally perceive how the suppression of FAXDC2 and the ensuing adjustments in ldl cholesterol metabolism could be leveraged to develop new most cancers therapies.
The analysis group is eager on exploring the therapeutic potential of focusing on FAXDC2 in most cancers therapy, contemplating it as a potential avenue for the event of medication that might inhibit most cancers development by modulating cholesterol synthesis pathways.
Moreover, the findings spur curiosity in preventative methods that might mitigate the chance of most cancers improvement by sustaining the stability of ldl cholesterol precursors within the physique. Understanding the triggers that result in the suppression of FAXDC2 in most cancers cells might pave the way in which for novel prevention methodologies, probably providing new hope within the combat towards most cancers.
“These findings resonate with our unwavering dedication to enhancing patient care by way of pivotal discoveries,” commented Professor Patrick Tan, Senior Vice-Dean for Analysis at Duke-NUS.
“The street forward entails rigorous analysis and collaboration throughout varied disciplines, all geared toward translating these elementary insights into tangible medical breakthroughs that might sooner or later remodel most cancers therapy and prevention methods.”
Extra info:
Madan B, Wadia S, Patnaik S, et al. The ldl cholesterol biosynthesis enzyme FAXDC2 {couples} Wnt/β-catenin to RTK/MAPK signaling. Journal of Scientific Investigation (2023). DOI: 10.1172/JCI171222. www.jci.org/articles/view/171222
Offered by
Duke-NUS Medical School
Quotation:
Scientists uncover a vital hyperlink between ldl cholesterol synthesis and most cancers development (2024, February 2)
retrieved 4 February 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-02-scientists-uncover-crucial-link-cholesterol.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post