[ad_1]
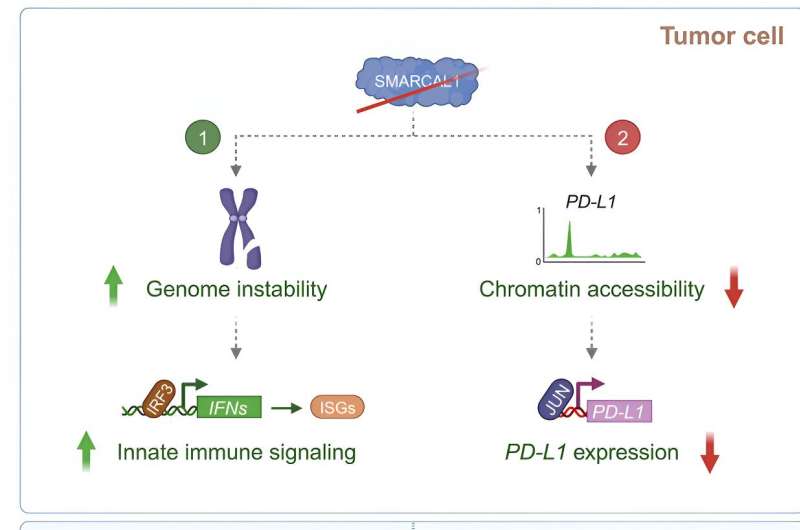
Graphical summary. Credit score: Cell (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.01.008
A multinational crew of researchers led by Columbia College has found that tumors can repurpose a single mobile protein to cover themselves from the immune system in two distinct methods. Medicine focusing on that protein might strike a double blow in opposition to many cancers, and make immunotherapy, one of many latest kinds of tumor therapies much more efficient.
One of many hallmarks of most cancers is genome instabilityan elevated tendency of the genome to accumulate mutations throughout cell division. This genome instability in flip triggers innate immune sensors inside the cell, who then acknowledge the bits of genetic materials that leak outdoors the cell nucleus into the encircling cytoplasm.
“This may be useful within the context of most cancers remedy as a result of it may result in the discharge of chemokines that appeal to immune cells into the tumor,” says Alberto Ciccia, affiliate professor of genetics and improvement at Columbia and a member of the Herbert Irving Complete Most cancers Heart. The responding immune cells can then kill the cancerous cell earlier than it will get uncontrolled.
Sadly, some cancers handle to activate an immune checkpoint response, primarily a “nothing to see right here” sign, to evade the preliminary response. Lately developed therapies, a kind of immunotherapy known as checkpoint inhibitors, can overcome that drawback by suppressing the checkpoint response, however these immune checkpoint blockade therapies nonetheless fail in some sufferers.
SMARCAL1: A one-molecule immune evasion system
“We have been to review the interaction between the innate immune response and the immune checkpoint response,” says Ciccia, who’s the senior writer on the paper describing the brand new outcomes, published within the journal Cell. A postdoctoral fellow in Ciccia’s lab, Giuseppe Leuzzi, led the research, utilizing a intelligent genetic display to determine mobile proteins linked to each responses. “We have been anticipating to seek out elements that may up-regulate each responses,” says Ciccia. Nevertheless, the crew found a subset of proteins with reverse results on the 2 responses.
One protein particularly, known as SMARCAL1, appears to suppress innate immune signaling whereas inducing the manufacturing of immune checkpoint proteins; it is a one-molecule immune evasion system. “Whenever you inactivate this issue, you activate the innate immune pathway, and cut back the expression of one of many immune checkpoint proteins,” says Ciccia.
Working with a world crew of collaborators at a number of different establishments, the investigators demonstrated that the 2 features work by two distinct mechanisms. SMARCAL1 operates as an element that maintains genome stability throughout DNA replication, and likewise as a transcription regulator that may induce the manufacturing of immune checkpoint proteins.
A promising goal for brand spanking new therapies
“By focusing on this issue, we might obtain a twin profit, growing innate immunity and infiltration of tumors by immune cellsand limiting the flexibility of the cancer cells to evade the immune system by immune checkpoints,” says Ciccia. The crew examined that concept in a mouse mannequin of tumor immune responses, with promising outcomes. In addition they analyzed affected person information from The Most cancers Genome Atlas, and located that top SMARCAL1 expression correlates with poor scientific outcomes.
“We hope to have the ability to develop small-molecule inhibitors of SMARCAL1 and see whether or not we will recapitulate the results that we’re observing in our genetic fashions,” says Ciccia. Although he emphasizes that many hurdles stay to turning the brand new findings into efficient therapies, Ciccia is optimistic concerning the prospects. Certainly, SMARCAL1 wasn’t the one potential goal the crew recognized within the preliminary display. “These are elements that if you inactivate them, they may assist you to obtain a number of totally different responses that may very well be useful,” says Ciccia.
Extra info:
Giuseppe Leuzzi et al, SMARCAL1 is a twin regulator of innate immune signaling and PD-L1 expression that promotes tumor immune evasion, Cell (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.01.008
Offered by
Columbia University Irving Medical Center
Quotation:
A one-molecule immune evasion system: New discovery might land one-two punch in opposition to most cancers (2024, February 2)
retrieved 2 February 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-02-molecule-immune-evasion-discovery-cancer.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post