[ad_1]
Credit score: Science Advances (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adi2012
Programmed cell dying 1 (PD-1) is a vital goal for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies that block its signaling and increase T-cell exercise. PD-1 inhibitors have been accepted for treating varied kinds of most cancers.
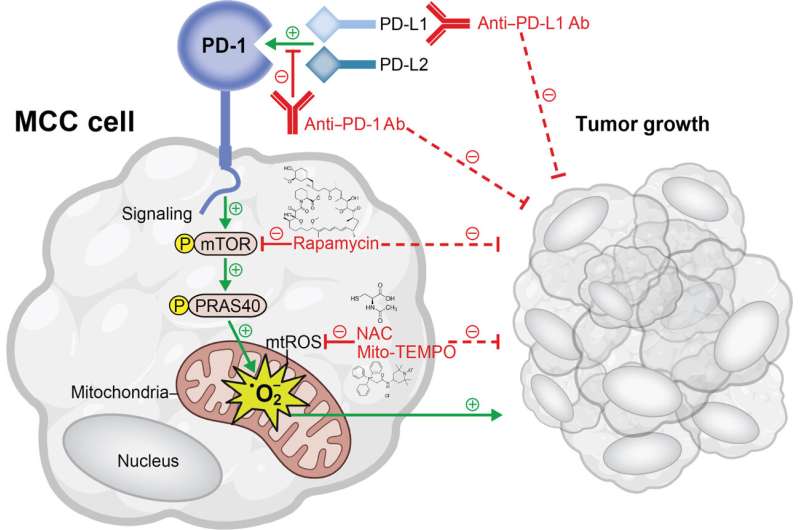
Nevertheless, PD-1 features can range between completely different cell and most cancers varieties, both selling or suppressing disease progression. Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC), a uncommon and aggressive type of pores and skin most cancers, responds effectively to immune checkpoint inhibitor remedy. Nevertheless, it was beforehand unknown if MCC cells categorical PD-1 themselves, and unclear how precisely most cancers cell-intrinsic PD-1 contributes to tumor progress.
A research led by investigators from Brigham and Girls’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass Basic Brigham well being care system, recognized a brand new mechanism by way of which PD-1 promotes MCC development. By means of a sequence of experiments, the researchers demonstrated PD-1 expression on MCC cells in preclinical fashions and affected person tumor samples. They discovered that MCC-PD-1 receptor binding to its ligands accelerated tumor progress by activating the mammalian goal of the rapamycin (mTOR) pathway and producing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mtROS) to advertise MCC progress.
The authors subsequently confirmed that inhibiting mTOR signaling and neutralizing mtROS suppressed MCC-PD-1-mediated tumor proliferation in mice. These findings, they counsel, may assist in the event of latest therapies to halt MCC development even in sufferers missing T-cell immunity.
“For the primary time, our work identifies PD-1 as an MCC-intrinsic receptor that promotes tumor growth by way of downstream mTOR signaling and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species manufacturing,” mentioned corresponding creator Tobias Schatton, PharmD, Ph.D., of the Division of Dermatology. “Focusing on this tumor-intrinsic PD-1 signaling community might assist optimize immune checkpoint remedy regimens and enhance MCC affected person outcomes.”
The analysis is published within the journal Science Advances.
Extra info:
Christina Martins et al, Tumor cell–intrinsic PD-1 promotes Merkel cell carcinoma progress by activating downstream mTOR-mitochondrial ROS signaling, Science Advances (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adi2012
Offered by
Brigham and Women’s Hospital
Quotation:
Examine identifies new PD-1 immune checkpoint mechanism selling Merkel cell carcinoma progress (2024, January 20)
retrieved 20 January 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-01-pd-immune-checkpoint-mechanism-merkel.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post