[ad_1]
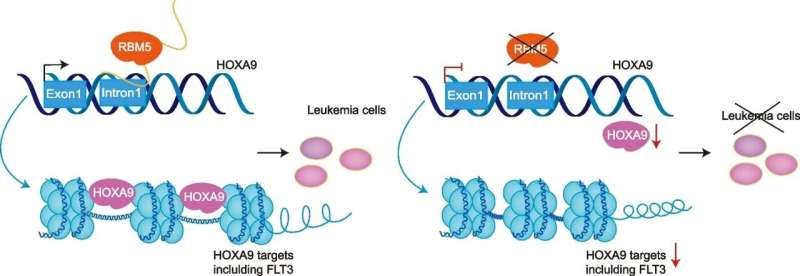
Mannequin for the brand new regulatory axis RBM5-HOXA9 in AML. RBM5 straight regulates the transcriptional exercise of the HOXA9 locus, which maintains correct downstream signaling transduction, together with the FLT3-responsive targets in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Credit score: Genome Biology (2024). DOI: 10.1186/s13059-023-03149-8
The protein HOXA9 is overexpressed in most acute myeloid leukemia (AML) instances and is related to poor affected person outcomes. Nonetheless, HOXA9 is a troublesome protein to focus on therapeutically, so researchers at St. Jude Youngsters’s Analysis Hospital regarded for tactics to extinguish it not directly.
Utilizing CRISPR/Cas9 screening, the researchers recognized RBM5, demonstrating a causative hyperlink between RBM5 expression and leukemia cell proliferation. This hyperlink is pushed by a novel twin perform of RBM5 as each a DNA and RNA handler in gene expression. The analysis was published in the present day in Genome Biology.
Overexpression of the protein HOXA9 is a trademark of AML, current in over 70% of instances, typically with poor prognosis. Whereas this is able to implicate it as a helpful drug goal, the protein’s position as a transcription issue has left it “undruggable” as a result of a drug that interferes with HOXA9 would seemingly have quite a few different off-target results.
This impressed researchers to strategy the issue in another way by investigating the proteins HOXA9 works alongside and depends on to perform. Chunliang Li, Ph.D., St. Jude Division of Tumor Cell Biology, co-corresponding creator on this paper, is one such researcher. Via his latest work devising an unbiased CRISPR screening technique to establish targets of HOXA9, he uncovered a community of alternatives.
“This has been a continued effort since my lab was established in 2017,” mentioned Li, “We constructed up this distinctive reporter system in early 2019, which is the primary reporter authentically representing HOXA9 expression in these leukemia programs.”
The CRISPR/Cas9 screening strategy is elegantly easy in design however extremely efficient. It entails attaching a fluorescent tag to the HOXA9 gene and inserting it into leukemia cell strains. This permits researchers to trace variations in expression levels by taking a look at fluorescence in cells.
“We needed to establish a extra targetable or novel regulator. So, we carried out an unbiased entire genome CRISPR screening to focus on all of the genes expressed in cells,” Li acknowledged. This allowed the researchers to look at totally different pathways the place HOXA9 left its fluorescent fingerprint.
To the researchers’ shock, splicing factors seemed to be probably the most represented pathway.
“This was fairly shocking to us as a result of splicing elements regulate totally different combos of the transcript, however not often the extent. Our knowledge urged these proteins management the HOXA9 expression stage,” mentioned Li. “So, we hypothesized possibly the splicing elements have one other perform, like a twin perform.”
The protein that stood out was the RNA-binding protein RBM5. The researchers discovered that RBM5 is extremely expressed in leukemia cells versus different cell types and that each the DNA- and RNA-binding websites are important to its oncogenic features. Whereas the RBM household includes important RNA splicing elements, their perform in DNA transcription was unknown. To deal with the direct transcriptional regulation of RBM5/HOXA9, the researchers generated a system to permit the acute degradation of RBM5.
“Instantly after RBM5 protein was faraway from cells, HOXA9 mRNA ranges had been considerably decreased,” Li defined, “This discount occurred as early as two hours later however didn’t impression splicing occasions of HOXA9.” Moreover, leukemia cells stripped of their potential to provide RBM5 had been rescued via overexpression of HOXA9, additional demonstrating the hyperlink between the 2 proteins.
These outcomes have Li trying to discover the protein as a drug goal to deal with AML.
“We expect RBM5 is an excellent dependency gene, which must be a superb goal based mostly on our purposeful assays,” he mentioned. “If we will particularly goal the DNA binding affinity of those proteins, we should always be capable of mix with different present therapies in synergy to focus on HOXA9-driven leukemia.”
Extra info:
Mengli Zhang et al, RNA-binding protein RBM5 performs a vital position in acute myeloid leukemia by activating the oncogenic protein HOXA9, Genome Biology (2024). DOI: 10.1186/s13059-023-03149-8
Offered by
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital
Quotation:
HOXA9 monitoring reveals RBM5 twin perform and therapeutic potential for acute myeloid leukemia (2024, January 12)
retrieved 12 January 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-01-hoxa9-tracking-reveals-rbm5-dual.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link



Discussion about this post