[ad_1]
Credit score: Blood Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023011076
Selections on remedy for sufferers with acute myeloid leukemia (AML)—a extremely aggressive type of leukemia—are based mostly, amongst different issues, on a sequence of sure genetic options of the illness; however on the time when a analysis is made, this data is just not accessible. Proof of those genetic anomalies is essential in offering focused remedy for sufferers at an early stage. As genetic testing is pricey and time-consuming, there’s a nice want for cheap, quick and broadly accessible checks to foretell such anomalies.
A workforce of IT specialists and physicians on the College of Münster and the College Hospital Münster has now revealed a examine displaying how a way based mostly on artificial intelligence (AI) can be utilized to foretell numerous genetic options on the premise of high-resolution microscopic pictures of bone marrow smears. Because of this, choices on a extra exact remedy might be made straight on the day of the analysis, with out the necessity to watch for genetic analyses. These outcomes have been published within the journal Blood Advances.
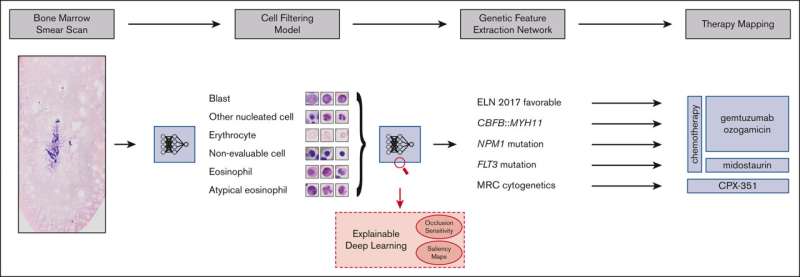
On this new methodology, the genetic aberrations had been extracted straight from extraordinarily high-resolution multi-gigabyte scans from entire bone marrow smears taken from greater than 400 AML sufferers. The scans had a decision of 270,000 occasions 135,000 pixels on common, with one picture being a number of gigabytes in dimension. Continuing from this huge dataset, it was potential to extract greater than 2 million single-cell pictures.
“We developed a brand new sort of deep studying methodology, absolutely computerized, which was educated for a fancy activity via machine studying know-how,” explains Prof. Benjamin Risse, who headed the work on algorithmic developments on the IT facet. “In our case, the essential algorithm can robotically acknowledge the genetic options and the very positive patterns in massive cytological pictures. The strategy then filtered the single-cell pictures into classes of various cell sorts, and it additionally confirmed any genetic aberrations.
“Apparently, a number of patterns acknowledged by the algorithm cannot be recognized by human observers. That is for instance as a result of the patterns could also be too faint or as a result of extraordinarily positive textures are concerned which stay hidden to the human eye, regardless of wonderful imaging,” says Risse.
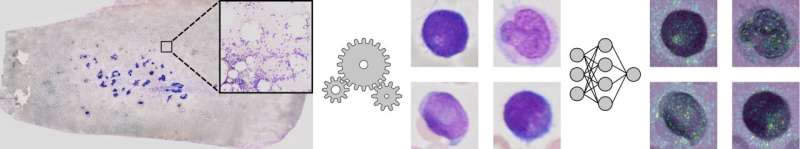
AI-based processing of bone-marrow smears to assist leukaemia analysis. Credit score: AG Risse
One key benefit of the tactic introduced is within the end-to-end AI pipeline which permits monitoring of the (interim) outcomes and reduces to a minimal the guide preliminary work usually crucial for machine learning. That is made potential by a mixture of so-called unsupervised, self-supervised and supervised studying processes. The primary two processes require no guide knowledge choice in any respect however attempt to extract related content material robotically from the picture knowledge as a substitute.
“Utilizing a so-called incremental method, we carried out middleman steps with a human skilled to look at the pictures. That is crucial for instance in cell pictures categorized as problematic,” says Dr. Linus Angenendt, who heads the Personalised Most cancers Remedy and Digital Medication working group at Münster College Hospital. Problematic cell pictures can happen because of incorrect staining, for instance. The educated mannequin was subsequently evaluated on an impartial dataset referring to an extra 70 sufferers with greater than 440,000 single-cell pictures—as a take a look at cohort.
Though the brand new methodology can’t substitute genetic analyses, it however helps at a really early stage within the diagnostic clarification course of for a leukemia affected person by offering an thought of which genetic aberrations may underlie the illness. This could be particularly useful within the case of aggressive illnesses when there is no such thing as a time to attend for the entire genetic analyses.
The researchers are assured that sooner or later digital strategies and synthetic intelligence will develop into more and more essential for giant medical datasets when making personalised suggestions for remedy for sufferers with malignant illnesses. This examine contributes an essential foundation for this, for instance within the improvement of comparable approaches for different bone marrow illnesses.
Extra data:
Jacqueline Kockwelp et al, Deep studying predicts therapy-relevant genetics in acute myeloid leukemia from Pappenheim-stained bone marrow smears, Blood Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023011076
Supplied by
University of Münster
Quotation:
Leukemia: Synthetic intelligence offers assist in diagnostics (2024, January 9)
retrieved 9 January 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-01-leukemia-artificial-intelligence-diagnostics.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post