[ad_1]
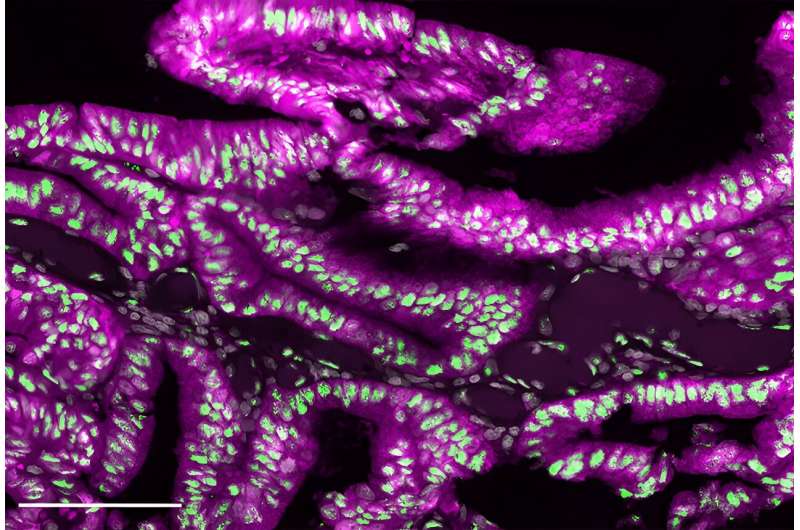
Multiplex immunofluorescence picture of cholesterol-rich human serrated colorectal most cancers. Extremely aggressive tumoral cells (inexperienced and magenta) are adverse for each aPKCs (turquoise). The nuclear accumulation of SREBP2 (the most important enzyme of ldl cholesterol biosynthesis) is labeled in inexperienced, and nuclei in gray. Credit score: Anxo Martinez-Ordoñez
Arduous-to-detect colorectal pre-cancerous lesions often known as serrated polyps, and the aggressive tumors that develop from them, rely closely on the ramped-up manufacturing of ldl cholesterol, in response to a preclinical examine from researchers at Weill Cornell Drugs. The discovering factors to the opportunity of utilizing cholesterol-lowering medicine to stop or deal with such tumors.
Within the examine published in Nature Communicationsthe researchers analyzed mice that develop serrated polyps and tumors, detailing the chain of molecular occasions in these tissues that results in elevated cholesterol production.
They confirmed their findings in analyses of human serrated polyps and tumors and confirmed in mouse fashions that replicate the human cancer that blocking cholesterol manufacturing prevented the development of some of these intestinal tumors.
“Serrated-type polyps and tumors at present should not handled in another way from different colorectal neoplasias, however as our work reveals, they’ve this particular metabolic vulnerability that may be focused,” stated examine co-senior creator Dr. Jorge Moscat, a Homer T. Hirst III Professor of Oncology in Pathology, Vice-Chair for Cell and Most cancers Pathobiology within the Division of Pathology and Laboratory Drugs and a member of the Sandra and Edward Meyer Most cancers Heart at Weill Cornell Drugs.
The opposite co-senior creator is Dr. Maria Diaz-Meco, additionally a Homer T. Hirst III Professor of Oncology in Pathology and a member of the Meyer Most cancers Heart at Weill Cornell Drugs. The examine’s first creator is Dr. Yu Muta, a postdoctoral affiliate within the Moscat/Diaz-Meco laboratories.
Ldl cholesterol is usually thought-about a pro-growth molecule, being a constructing block for cell membranes and having different growth-supporting features. Prior research have linked excessive blood levels of cholesterol to numerous cancers, together with colorectal cancers. Nonetheless, it hasn’t been clear that reducing ldl cholesterol, for instance, with frequent statin medicine, can forestall colorectal cancers.
“Trials of statins to stop colorectal cancer have had conflicting outcomes,” Dr. Diaz-Meco stated. “Our findings counsel that it’s because focusing on ldl cholesterol has a preventive however selective impact solely towards polyps and tumors of this serrated kind.”
Serrated polyps are so-called due to their sawtooth look below a microscope. They’re flatter than abnormal colorectal polyps and might typically be missed throughout colonoscopies. But the tumors into which they develop, which account for roughly 15 to 30 % of colorectal cancers, comprise many “metaplastic” cells which might be notably invasive and immune to remedies.
A number of years in the past, the Moscat/Diaz-Meco crew linked serrated polyps and tumors to low ranges of two enzymes often known as aPKCs. They confirmed that mice engineered to lack these aPKC enzymes of their intestine linings reliably kind serrated polyps after which aggressive tumors.
Within the new examine, the scientists discovered that in serrated-type tumors in these mice, and even in intestinal tissue poised to develop some of these cancerous lesions, ldl cholesterol synthesis was strikingly upregulated, suggesting that ldl cholesterol could also be an early driver of tumor improvement.
The researchers revealed how the absence of aPKC enzymes, particularly in metaplastic tumor cells, unleashes the activation of a transcription issue referred to as SREBP2, which switches on ldl cholesterol manufacturing. Assessments on colorectal polyp and tumor samples from human patients dovetailed with the mouse findings. They discovered, for instance, that solely serrated-type tumors had low aPKC ranges concomitant with the buildup of SREBP2, a driver and a marker of upregulated ldl cholesterol biosynthesis within the serrated most cancers cells.
Lastly, the researchers examined a mix of two ldl cholesterol synthesis-blocking medicine, together with the extensively used atorvastatin. The remedy, delivered when the low-aPKC mice had been nonetheless fairly younger, considerably lowered the speed at which each serrated polyps and tumors later shaped—and the serrated-type tumors that did kind had been much less aggressive than these usually arising within the untreated mice.
The outcomes point out that focusing on ldl cholesterol may very well be a viable technique for treating and stopping serrated-type colorectal tumors. The Moscat and Diaz-Meco labs are actually hoping to arrange an preliminary medical trial of a cholesterol-lowering intervention in sufferers from whom serrated colorectal polyps have been eliminated.
“Presently, when these polyps are detected early with colonoscopy, they’re eliminated, and sufferers need to hope that they do not come again,” Dr. Moscat stated. “Sooner or later, we hope to have a extra energetic methodology to stop this very aggressive type of cancer earlier than it’s absolutely developed and tougher to deal with.”
Extra info:
Yu Muta et al, Enhanced SREBP2-driven ldl cholesterol biosynthesis by PKCλ/ι deficiency in intestinal epithelial cells promotes aggressive serrated tumorigenesis, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-43690-5
Supplied by
Weill Cornell Medical College
Quotation:
Ldl cholesterol-lowering remedy could hinder aggressive kind of colorectal tumor (2023, December 13)
retrieved 13 December 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-12-cholesterol-lowering-therapy-hinder-aggressive-colorectal.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post