[ad_1]
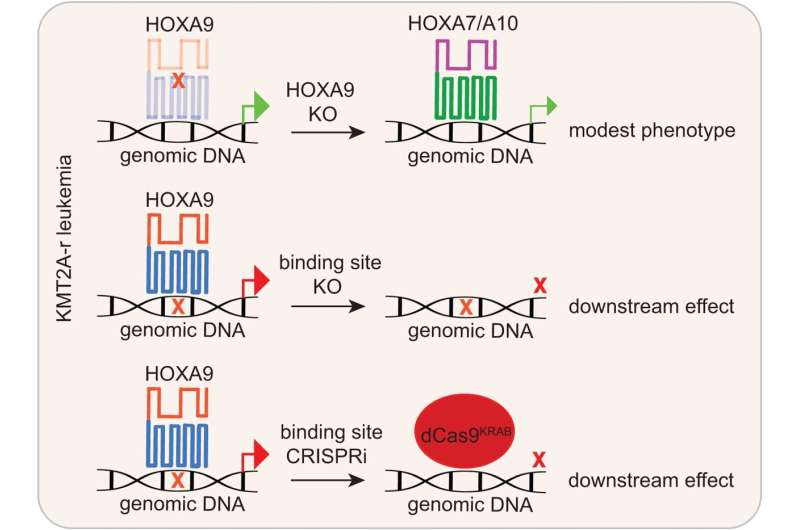
Schematic diagram summarizing this examine. Our work interrogated the transcription issue operate of HOXA9 in MLL-r leukemias by concentrating on HOXA9-bound websites by genomic enhancing (CRISPR/Cas9 and CRISPRi). It could overcome the frequent concern noticed by HOXA9 protein perturbation and HOX compensation. Credit score: Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-43264-5
Scientists at St. Jude Youngsters’s Analysis Hospital have comprehensively recognized genes immediately regulated by a protein related to high-risk pediatric leukemias. Excessive-risk leukemias, significantly MLL-rearranged (MLL-r) leukemia, typically overexpress the homeodomain transcription issue HOXA9 protein, which can not at present be focused with medication.
This examine gives a basis for revealing the HOXA9 regulation community and discovering novel drug targets downstream of HOXA9 that may kind the premise of recent remedies. The findings have been published right this moment (Nov. 28) in Nature Communications.
HOXA9 is a transcription issue, a sort of protein that binds DNA to manage the expression of different genes. Overexpression of HOXA9 is a trademark in lots of cancers, together with high-risk leukemias, such because the MLL-r subtype. Discovering the genes regulated by HOXA9 might reveal new methods to deal with leukemia by undermining how the protein helps cancers develop and survive.
As a result of technical challenges of working with HOXA9, the downstream regulation community of the protein was poorly understood. The St. Jude staff established a singular system to seek out these genes regulated by HOXA9.
“We confirmed two main identified targets, FLT3 and CDK6,” stated corresponding creator Chunliang Li, Ph.D., St. Jude Division of Tumor Cell Biology. “Each genes will be therapeutically focused by medication, which reveals good outcomes in preclinical fashions with HOXA9 overexpression. Our outcomes offered direct proof to help the enhancer regulation of FLT3 and CDK6 via HOXA9.”
Along with these well-studied genes, the scientists discovered 227 different goal websites sure by HOXA9. Lots of these websites have been positioned at noncoding regulatory areas, seemingly enhancers. They validated the highest 10 candidates in cell-based experiments performed in collaboration with computational biologists from the St. Jude Heart for Utilized Bioinformatics.
A number of of those hits defined earlier outcomes noticed utilizing present Meals and Drug Administration-approved medication, which lends credibility to the opposite outcomes from the display screen and suggests they might be productive targets for novel leukemia medication.
To carry out the display screen, the St. Jude group established a TetOn-inducible system to precise tagged HOXA9 in MLL-r leukemia cell strains. Utilizing this distinctive analysis instrument adopted with chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) know-how, they efficiently recognized the place within the genome HOXA9 binds DNA in MLL-r leukemic cells.
“Utilizing state-of-the-art analysis instruments and chic mannequin programs, we have now a greater understanding of how HOXA9 works in high-risk leukemia cells,” stated co-first creator Shaela Fields, St. Jude Division of Tumor Cell Biology. “Now, we will begin the lengthy course of to seek out and develop new medication to make our sufferers more healthy by profiting from that info.”
Overcoming a HOXA9 household drawback
Whereas it was beforehand identified that HOXA9 is overexpressed in high-risk pediatric leukemias, it has traditionally been difficult to check and goal. The HOX household of proteins accommodates 39 members, that are all similar to one another. The similarity additionally makes it difficult to check as a result of present methods have bother distinguishing between the HOX proteins. Functionally, different HOX members of the family might probably compensate for HOXA9 operate upon concentrating on.
With that in thoughts, the researchers created a system that recognized the genes sure particularly by HOXA9 in a sure leukemia subtype (mixed-lineage leukemia rearrangement or MLL-r) by inserting a tag onto HOXA9.
“Think about you’re in a canine park and have to discover a sure golden retrieverhowever there are a bunch of them working round, and you do not know which one is yours as a result of all of the canines look the identical,” stated Li. “If you happen to put a neon pink harness in your canine beforehand, it is simple to seek out among the many group. That’s how we might observe in all places HOXA9 went.”
The small tag doesn’t have an effect on HOXA9’s common operate and makes HOXA9 straightforward to hint in cells. The researchers then sequenced the connected DNA to determine the leukemia-related genes sure by HOXA9, permitting scientists to check this comparatively small checklist of genes that could be amenable to therapeutic improvement.
“We narrowed lots of of hundreds of targets to only over 2 hundred by evaluating to controls,” stated Fields. “And once we can examine the regulation mechanism and community of HOXA9, and what’s taking place within the cells, that is the place hopefully we will discover methods to assist youngsters with high-risk cancers get higher.”
Extra info:
Shaela Wright et al, Systematic characterization of the HOXA9 downstream targets in MLL-r leukemia by noncoding CRISPR screens, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-43264-5
Offered by
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital
Quotation:
Analysis reveals useful targets of oncogenic HOXA9 protein in high-risk pediatric leukemia (2023, November 28)
retrieved 28 November 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-11-reveals-functional-oncogenic-hoxa9-protein.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post