[ad_1]
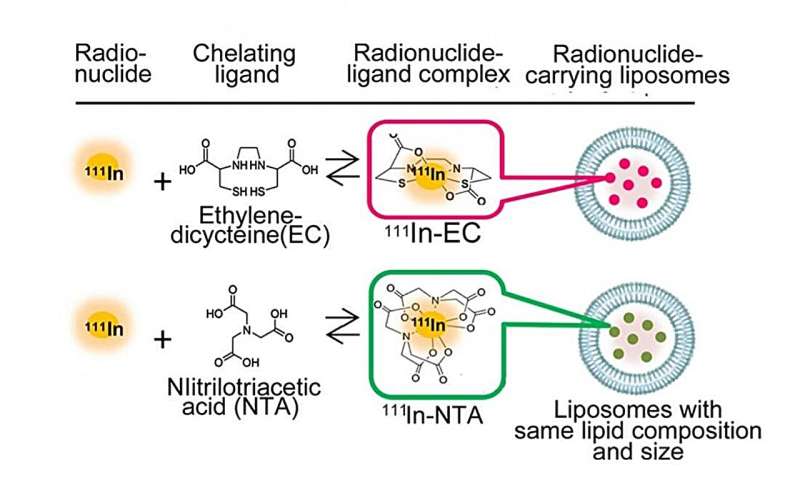
Determine 1. The radionuclide-encapsulated liposomes, together with the main target of the examine, a ligand referred to as ethylenedicysteine (EC). Credit score: Umeda et al
A workforce of researchers has developed a brand new methodology that suppresses the distribution of medication to wholesome tissues and in addition quickly removes the medicine as soon as distributed within the physique, which might enhance the accuracy of imaging analysis of adverse cancers, cut back toxicity to wholesome tissues, and additional enhance the effectiveness of therapy. They report their findings in a latest examine published within the Journal of Managed Launch.
Radiopharmaceuticals have been attracting consideration as the following technology of most cancers imaging and most cancers therapy medicine. Till now, most analysis has centered on growing the expertise to ship medicine to most cancers lesions, however it has been inconceivable to keep away from distributing medicine to wholesome tissues.
A workforce of researchers, led by Nationwide Most cancers Middle Exploratory Oncology Analysis & Scientific Trial Middle Purposeful Diagnostics Improvement Area researchers Izumi Umeda, who on the time was additionally a Mission Researcher on the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Arithmetic of the Universe (Kavli IPMU), and Hirofumi Fujii, alongside researchers from Chiba College, Kavli IPMU, and Kyoto School of Medical Science, mixed parts in nuclear medicine, drug supply techniques (DDS) and complicated chemistry to develop a way that controls the in vivo dynamics of radionuclides post-administration.
The workforce’s methodology permits radiopharmaceuticals to build up sufficiently in most cancers lesions, whereas shortening the time the medicine are involved with wholesome tissues. This implies medicine can think about the most cancers lesions, enhancing their results in comparison with standard strategies.
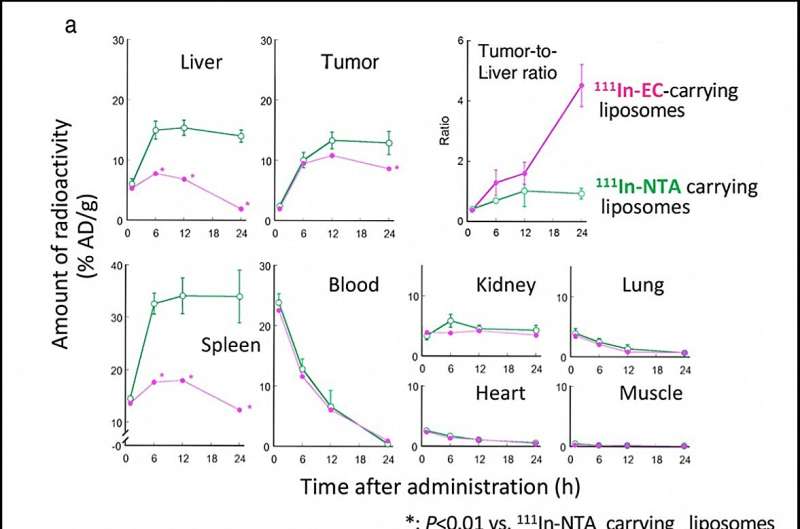
Determine 2. Time-dependent biodistribution of 111In-radioactivity in tumor-bearing mice after administration of 111In-EC- and 111In-NTA-carrying liposomes. (a) reveals time-dependent uptake, retention, and clearance of 111In radioactivity in every organ and tumor, whereas (b) reveals collected excretion of 111In radioactivity with time within the urine and feces. (c) HPLC evaluation of radioactive materials in urine. Credit score: Umeda et al
The 2 kinds of radiopharmaceuticals, or RI-encapsulated liposomes (Determine 1), have the identical liposome composition and particle measurement, and the RI is identical 111In, differing solely within the ligand. Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) is a typical ligand, and ethylenedicysteine (EC) is the brand new ligand on the heart of the workforce’s experiment.
Two kinds of 111In-ligand-containing liposomes got to mice with tumors, and researchers monitored the uptake and accumulation of 111In in most cancers and wholesome tissues, particularly the liver and spleen (Determine 2). There was little distinction within the tumors in each mice, however within the liver and spleen, 111In-EC-liposomes have been as soon as taken up however then quickly cleared out, whereas standard 111In-NTA-liposomes remained for a very long time. The 111In-EC-liposomes additionally promoted excretion into feces, and the chemical type in urine was 111In-EC not within the liposomes.
The workforce discovered that within the liver, the liposomes have been damaged up, releasing the 111In-ligand complexes inside, whereas within the tumor, liposomes persevered intact for a very long time and the 111In-ligand complexes remained in liposomes. The distinctive complicated, 111In-EC, allowed for speedy clearance from the liver after being launched from the liposomes.
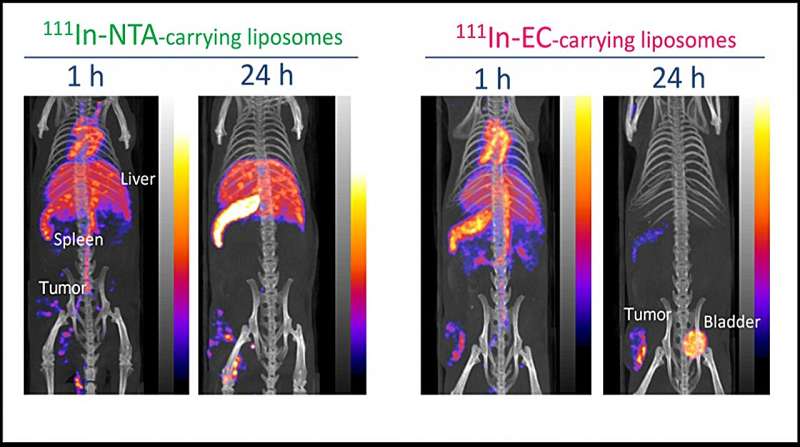
Determine 3. In vivo SPECT/CT pictures of the 2 kinds of 111In-carrying liposomes in-tumor-bearing mice at 1 and 24 h after administration. Credit score: Umeda et al
Within the in vivo SPECT/CT pictures of tumor-bearing mice after administration of 111In-EC- or 111In-NTA-liposomes (Determine 3), the distribution of the 2 liposomes within the physique was virtually similar to start with. Nevertheless, later, the 111In-EC-liposomes appeared clearly in tumor websites as a result of a negligible sign from the liver and spleen, whereas 111In-NTA-liposomes have been unable to selectively picture tumors as a result of their low clearance from the above organs. The photographs have been in line with the biodistribution research described above.
Primarily based on the outcomes of this examine, the workforce proposed a scheme explaining the in vivo destiny of radionuclide-carrying liposomes (Determine 4). After intravenous administration, standard 111In-NTA-liposomes and new 111In-EC-liposomes flow into within the bloodstream and accumulate to an identical extent in tumors. Most liposomes stay intact throughout the tumor for a very long time, and consequently, the encapsulated radionuclide-ligand complexes are retained inside liposomes. Moreover, liposomes are taken up by the liver, the place they’re quickly degraded and launch their encapsulated 111In-ligand complexes.
After their launch from liposomesstandard 111In-ligand complexes, reminiscent of 111In-NTA, remained within the liver for a very long time. In distinction, 111In-EC have been in a position to escape from the liver and have been quickly excreted within the urine in its unique type. The researchers say speedy urinary excretion with out accumulation in different tissues will enable radioactivity to be cleared swiftly from the physique and decrease injury.
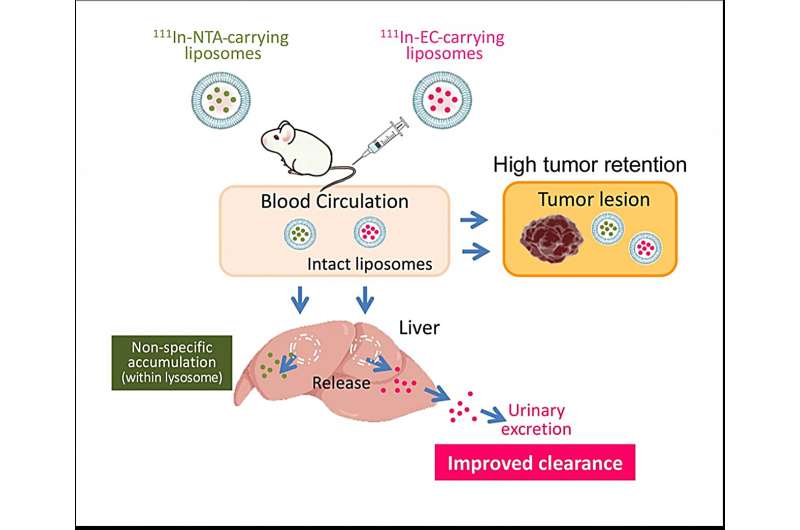
Hypothesized in vivo destiny of radionuclide-carrying liposomes in tumor-bearing mice. Credit score: Umeda et al
“The truth that a brand new method to drug improvement has been developed at the moment from a brand new perspective to take care of the focus of medication in most cancers lesions whereas defending wholesome tissue is vital when contemplating the position high-precision most cancers therapy, or theranostics, will play within the therapy of the intractable. Sooner or later, we hope that additional analysis will result in medicine that keep solely in cancer lesions, which has by no means been achieved earlier than,” mentioned Umeda.
Extra info:
Izumi O. Umeda et al, New liposome-radionuclide-chelate mixture for tumor focusing on and speedy wholesome tissue clearance, Journal of Managed Launch (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.07.060
Offered by
Kavli IPMU
Quotation:
Researchers develop new methodology of exactly focusing on most cancers lesions whereas defending wholesome tissues (2023, November 21)
retrieved 21 November 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-11-method-precisely-cancer-lesions-healthy.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post