[ad_1]
Queen Mary College of London researchers have found a brand new immune mechanism in osteocytes, the commonest kind of bone cell, that might result in new medicine for breast and prostate most cancers.
The studyprinted in Superior Sciencediscovered that osteocytes can use this mechanism to suppress the expansion of invading breast and prostate cancer cells. Nevertheless, most cancers cells can intervene to forestall bone cells from creating this function, leading to a promotion of tumor development.
Whereas survival rates in breast and prostate most cancers—the 2 commonest cancers—have elevated because of enhancements in screening and remedy, these sufferers have excessive ranges of ache and decrease survival probabilities if the cancers unfold (metastasize) into their bones, a standard development.
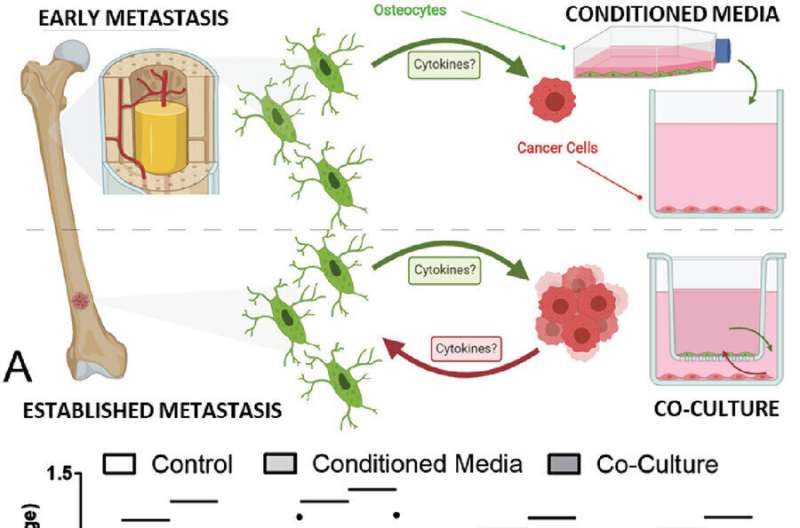
The interplay between bone cells and most cancers cells has beforehand been poorly understood, so the research aimed to research how breast and prostate cancers unfold to, and develop inside bones. Utilizing cell tradition and organ-on-a-chip technologyit recognized a brand new mechanism by way of which they hijack our bone cells as a way to develop sooner.
The research discovered that osteocytes, by far the commonest bone cell kind making up greater than 90% of our bone cells, possess an immune mechanism that they’ll use to suppress the expansion of invading breast or prostate most cancers cells. Nevertheless, a vicious suggestions loop is created when the most cancers cells intervene to forestall the bone cells from creating this function and subsequently block this suppression, ensuing as a substitute in a promotion of tumor development.
It’s possible that this preliminary inhibition of the most cancers cells by osteocytes might in some half clarify why breast and prostate cancers typically go dormant earlier than establishing metastatic colonies in bone tissue.
The invention of this new molecular mechanism demonstrates the significance of most cancers cell to osteocyte signaling in regulating breast and prostate bone metastases, and additional helps the event of therapies which goal and disrupt this pathway.
Most notably, these findings reveal two particular new drug targets which could possibly be used to both help the osteocyte suppression of the most cancers cells by TNF-α, or forestall the cancer cells from blocking this suppression through TGF-β.
Dr. Stefaan Verbruggen, Lecturer in Medical Know-how within the College of Engineering and Supplies Science at Queen Mary College says, “Most significantly and unusually, as this mechanism impacts each breast and prostate cancerthe commonest cancers, the variety of sufferers who could profit is huge.”
Persevering with work with the bone metastasis organ-chip mannequin will enable the crew to develop a extra advanced 3D human tumor microenvironment and subsequently additional examine and check these new recognized therapies.
The work was a part of a Marie Curie Fellowship for Stefaan Verbruggen and a collaboration between Professor Martin Knight at Queen Mary College of London and Professor Chris Jacobs at Columbia College, who sadly handed away from most cancers earlier than the research was accomplished. The paper accommodates a dedication to his reminiscence.
Extra info:
Stefaan W. Verbruggen et al, A Novel Main Cilium‐Mediated Mechanism By way of which Osteocytes Regulate Metastatic Habits of Each Breast and Prostate Most cancers Cells, Superior Science (2023). DOI: 10.1002/advs.202305842
Offered by
Queen Mary, University of London
Quotation:
Immune mechanism present in osteocyte cells might result in drug goal to forestall unfold of most cancers to bones (2023, November 17)
retrieved 18 November 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-11-immune-mechanism-osteocyte-cells-drug.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]




Discussion about this post