[ad_1]
When making vital selections about illness prevention, who do you take heed to? Medical establishments? Or maybe the folks round you? Your reply would possibly reveal extra about your private circumstances than you’d count on.
In a research published this month within the Worldwide Journal of Catastrophe Threat Discount, researchers from Osaka College have revealed that, when taking steps to stop the unfold of disease, we’re affected by sure elements surrounding us, similar to the place we get our data and whether or not we at present dwell below a pandemic. The research is titled “Exploration of things related to mask-wearing and hand disinfection in Japan after the coronavirus illness outbreak: A longitudinal study.”
In response to the coronavirus illness (COVID-19) outbreak, many nations carried out social measures, similar to lockdowns, and mandated preventive behaviors, similar to mask-wearing, for his or her residents. In Japan, behaviors that stop an infection, similar to hand sanitizing and mask-wearing, have been left to particular person discretion because the starting of the COVID-19 outbreak.
“Since COVID-19 continues to flow into globally, you will need to decide the associations between particular person traits and preventive behaviors to know how one can promote discretion-based preventive behaviors,” explains Michio Murakami, lead creator of the research. “We’re significantly fascinated about creating a threat communication technique for selling infection-preventive behavior in a well timed method.”
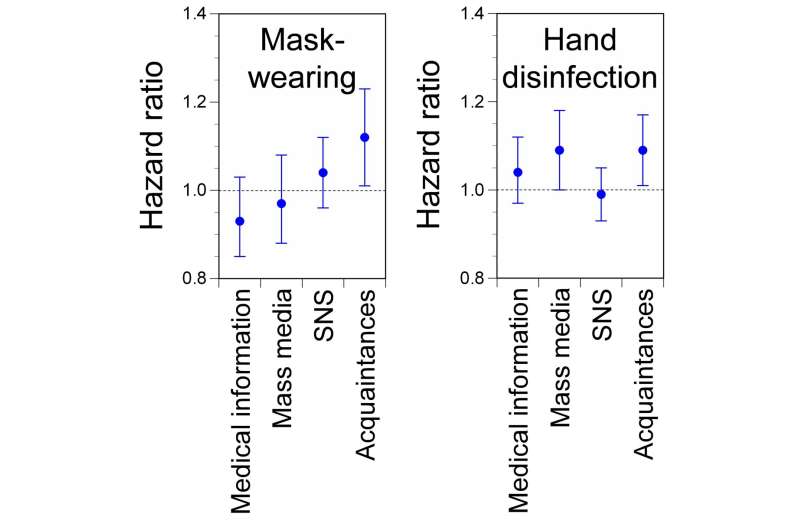
To handle this, the researchers investigated the affiliation between sure particular person traits earlier than and after the outbreak of COVID-19. Utilizing 23 waves of panel information from January 2020 to January 2023, the researchers examined whether or not people consumed medical information on authorities or medical establishment web sites, whether or not they wore masks, and whether or not they disinfected their palms.
“The outcomes have been intriguing,” explains Asako Miura, senior creator. “We discovered that, whereas medical data had the sturdy impact on infection-preventive conduct earlier than the COVID-19 outbreak, individuals who exchanged data with acquaintances have been extra more likely to newly begin mask-wearing and hand disinfection after the COVID-19 outbreak.”
The researchers discovered that individuals who consumed medical data have been extra more likely to put on masks and disinfect palms even earlier than the COVID-19 outbreak. There have been additionally slight variations within the charges of infection-preventive conduct and gender, with males much less more likely to implement preventive behaviors than ladies.
“Our findings clearly present that, in Japan, mask-wearing and hand-disinfection behaviors have been the results of completely different data sources earlier than and after the outbreak,” says Murakami.
On condition that infection-preventive behaviors defend not solely in opposition to COVID-19, but in addition seasonal and rising infectious diseases, the insights from this research are a helpful contribution to public well being. Specifically, implementing the suitable communication methods for sure demographics might be an efficient help to disease prevention.
Extra data:
Michio Murakami et al, Exploration of things related to mask-wearing and hand disinfection in Japan after the coronavirus illness outbreak: A longitudinal research, Worldwide Journal of Catastrophe Threat Discount (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2023.104107
Quotation:
What leads folks to take motion on illness prevention? (2023, November 17)
retrieved 17 November 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-11-people-action-disease.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post