[ad_1]
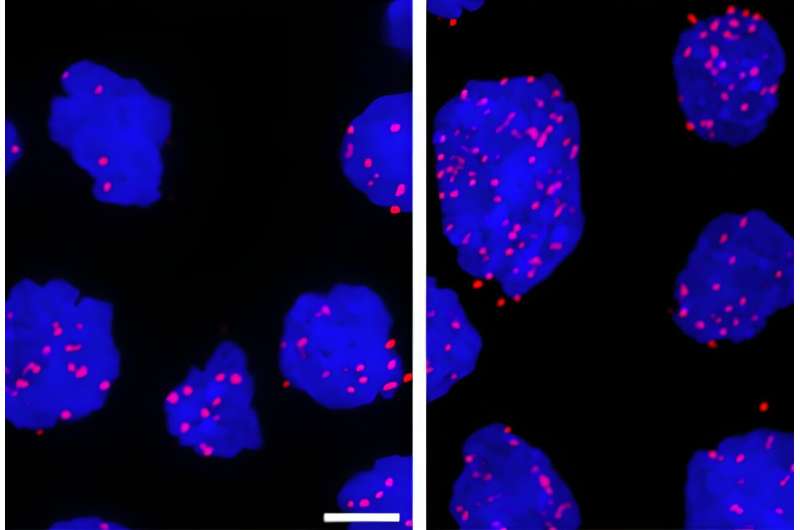
Diffuse massive B cell lymphoma cells which might be untreated (left panel) and handled with a DNA damaging agent (proper panel). The pink dots point out XPO-1 protein interacting with a protein that binds mRNAs and chaperones them from the nucleus. Credit score: Weill Cornell Drugs
A stunning mechanism that makes some cancers treatment-resistant has been found by Weill Cornell Drugs and NewYork-Presbyterian investigators. The mechanism, which includes the shuttling of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, finally facilitates DNA restore in most cancers cells. These most cancers cells can thereby thwart remedies geared toward damaging their DNA.
In a mission encompassing each elementary analysis and medical research they demonstrated {that a} mixture of accepted chemotherapies, certainly one of which targets the DNA repair-facilitating mechanism, might assist deal with these persistent instances. Whereas the workprinted in Most cancers Analysistargeted on diffuse massive B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the findings probably apply to different most cancers varieties as effectively.
DLBCL is the commonest type of lymphoma, affecting about 30,000 sufferers yearly in the US alone. First-line therapies remedy about two thirds of sufferers, “however for individuals who aren’t cured or who relapse, they traditionally had poor outcomes with customary chemotherapy-based remedy approaches,” mentioned co-lead creator Dr. Sarah Rutherford, an assistant professor of drugs at Weill Cornell Drugs and a hematologist/oncologist at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Middle. The opposite co-lead creator is Dr. Rossella Marullo, an teacher in drugs at Weill Cornell Drugs.
Earlier analysis had demonstrated that treatment-resistant DLBCL cells typically categorical excessive ranges of a protein referred to as XPO1. In 2019, the U.S. Meals and Drug Administration accepted a brand new drug, selinexor, that was designed to focus on XPO1 and inhibit its exercise. The drug, which hinders the expansion of lymphoma cells expressing excessive ranges of the protein, is used to deal with these refractory instances. Selinexor has helped many, however not all sufferers with treatment-resistant illness.
“Selinexor is efficient by itself, it is simply not as efficient as we might prefer it to be,” mentioned Dr. Rutherford, who can be a member of the Sandra and Edward Meyer Most cancers Middle at Weill Cornell Drugs. That is pushed her to seek for methods to enhance the drug’s efficacy.
In the meantime, Dr. Rutherford’s colleagues have been making an attempt to be taught extra about precisely how selinexor works. Its goal, XPO1, transports a whole lot of proteins, and sure RNAs, out of the cell nucleusprimarily to separate the pool of proteins that shouldn’t be current within the nucleus, resembling ribosomal proteins.
Nevertheless, the investigators discovered that a few of these XPO1-exported proteins are additionally sure to mRNA molecules; thus, these mRNAs are exported out of the cell nucleus into the cytoplasm the place they are often translated into proteins. This new mechanism signifies that the amount and exercise of XPO1 in a cell can due to this fact have an effect on the expression ranges of quite a few genes.
“We discovered that it isn’t simply regulating a couple of proteins, it is coordinating these huge packages, permitting cells to quickly alter their proteome and survive completely different sorts of stress that cancer cells encounter on a regular basis,” mentioned senior creator Dr. Leandro Cerchietti, the Richard Stratton Affiliate Professor of Hematology and Oncology and a member of the Meyer Most cancers Middle at Weill Cornell Drugs.
Taking some remedy resistant DLBCL cells from sufferers and grafting them into preclinical modelsthe researchers discovered that increased ranges of XPO1 finally will increase the expression of genes that defend cells towards demise from DNA harm. Inhibiting XPO1 in these fashions with selinexor elevated the lymphomas’ sensitivity to DNA-damaging chemotherapies and immune-based remedies.
“We have been excited, and primarily based on a few of Dr. Cerchietti’s analysis, we thought selinexor would probably synergize with different chemotherapies,” mentioned Dr. Rutherford. To check that in sufferers, she initiated a part 1 medical trial, aiming to find out whether or not such a mixture can be secure, and in that case at what doses. The trial, which primarily enrolled sufferers with treatment-resistant DLBCL, confirmed that the mixed routine isn’t solely secure, however seems to work. Although the information set is just too small to attract definitive conclusions, a number of sufferers had higher outcomes than anticipated.
Dr. Rutherford is keen to proceed testing and refining the brand new regimens in follow-up trials. “It has been a very distinctive time over the past 4 years or so on this illness, the place we now have many extra therapies than we did once we first began the trial,” she mentioned.
As a result of each cell within the physique expresses XPO1, the brand new outcomes are prone to have broader purposes. “There are different tumors wherein XPO1 is overexpressed, so it is actually a pleasant spine to construct on,” mentioned Dr. Cerchietti.
Extra data:
Rossella Marullo et al, XPO1 allows adaptive regulation of mRNA export required for genotoxic stress tolerance in most cancers cells, Most cancers Analysis (2023). DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-1992
Offered by
Weill Cornell Medical College
Quotation:
New technique assaults treatment-resistant lymphomas (2023, November 2)
retrieved 6 November 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-11-strategy-treatment-resistant-lymphomas.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post