[ad_1]
Credit score: Most cancers Cell (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.07.007
Endometrial carcinoma, a most cancers of the liner of the uterus, is the most typical gynecologic malignancy in developed nations. Over the previous decade, its incidence has steadily elevated (roughly 1% yearly) and mortality has progressively worsened.
“Regardless of many makes an attempt to enhance this cancer‘s remedy, important challenges stay. On this examine, we centered on gaining new insights to enhance remedy of endometrial most cancers,” mentioned co-first creator Dr. Yongchao Dou, postdoctoral affiliate in Dr. Bing Zhang’s lab at Baylor Faculty of Drugs’s Lester and Sue Smith Breast Heart. “We used 10 genomics and proteomics platforms to establish biological markers and pathways that might be used to develop improved therapies for this situation.”
The examine seems within the journal Cancer Cell.
Earlier genomic research have depicted the mutational panorama of endometrial most cancers. Nonetheless, how mutations drive most cancers traits have remained elusive. In 2020, Zhang and colleagues within the Nationwide Most cancers Institute’s Scientific Proteomic Tumor Evaluation Consortium (CPTAC) revealed the primary integrative proteogenomic characterization of endometrial most cancers within the journal Cell. They revealed the affect of genetic aberrations on proteins and their chemical modifications, comparable to phosphorylation, resulting in a extra complete molecular understanding of this most cancers.
“Primarily based on the 2020 examine, we suggest that not-yet recognized molecules concerned in endometrial carcinoma development might be efficient targets to regulate or cease tumor growth,” mentioned co-corresponding creator Zhang, professor of molecular and human genetics, the Lester and Sue Smith Breast Heart and a McNair Scholar at Baylor. He is also a member of the Dan L Duncan Complete Most cancers Heart.
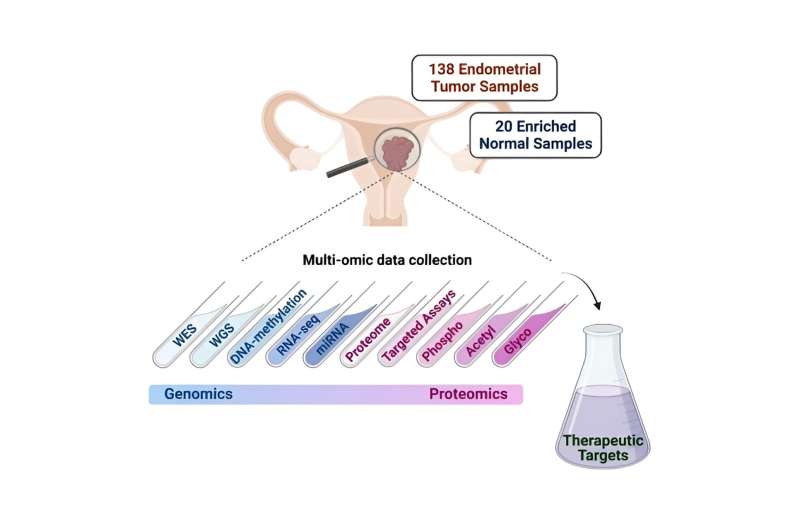
A complete investigation
To establish potential new endometrial carcinoma targets, the crew performed a complete proteogenomic investigation—the identification of each genetic elements and proteins produced by most cancers cells—of 138 prospectively collected endometrial carcinoma tumors and 20 regular endometrium samples.
First, the findings supplied purposeful validation of beforehand described results of regularly noticed gene mutations, protein markers of medical and genomic tumor subgroups and the affect of defects in antigen presentation—an essential step in triggering an immune response—on patterns of immune infiltrates in some tumors.
“Importantly, our present examine additionally expands our earlier work in endometrial most cancers in a number of methods, together with the exploration of extra protein varieties comparable to glycoproteins, contributing additional insights into endometrial most cancers biology,” Dou mentioned. “We additionally developed focused mass spectrometry-based assays, which give a path to the event of medical assays.”
Highlighted findings
The researchers explored intimately the function of mutations referred to as in-frame indels within the PIK3R1-AKT pathway which were related to worse most cancers outcomes. The researchers hypothesized that in-frame indels remove PIK3R1’s skill to suppress most cancers development. PIK3R1 is assumed to suppress most cancers development by stopping AKT1 phosphorylation, the addition of a phosphate chemical group to the enzyme AKT1. Phosphorylated AKT1 is assumed to activate pathways that assist most cancers develop.
To realize extra proof supporting their commentary of the potential function PIK3R1 proteins with in-frame indels in selling AKT phosphorylation, the Zhang lab collaborated with Dr. Yi Li, professor of molecular and mobile biology and of molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor. He is also member of Baylor’s Lester and Sue Smith Breast Heart and the Dan L Duncan Complete Most cancers Heart.
“We used CRISPR to engineer in cell lines a selected in-frame indel mutation that’s current in a affected person’s endometrial cancer cells,” Li mentioned. “Then, the most cancers cell line grew to become precisely because the Zhang lab had predicted based on their proteogenomic evaluation of most cancers samples from sufferers. We noticed large activation of protein AKT, which supported the speculation that in-frame indels in PIK3R1 promote AKT phosphorylation. Additional research are wanted to guage the significance of this mutation in activating AKT resulting in most cancers development in residing animals, and importantly, whether or not the tumors will grow to be conscious of the medication the Zhang group discovered to be efficient for sure sufferers.”
“Altogether, our findings recommend that PIK3R1 in-frame indel mutations are potential markers of the AKT inhibition response and is perhaps used to establish sufferers who might reply to AKT inhibitors, transferring a step towards future improved medical purposes,” Zhang mentioned. “The thought of this examine is to disclose biomarkers that may establish sufferers who would reply higher to remedy. On this massive observational examine, we’ve generated an inventory of potential therapeutic targets for the scientific neighborhood to check for his or her potential medical worth.”
Extra data:
Yongchao Dou et al, Proteogenomic insights recommend druggable pathways in endometrial carcinoma, Most cancers Cell (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.07.007
Supplied by
Baylor College of Medicine
Quotation:
Analysis reveals new potentialities to enhance remedy of endometrial carcinoma (2023, October 12)
retrieved 15 October 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-10-reveals-possibilities-treatment-endometrial-carcinoma.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post