[ad_1]
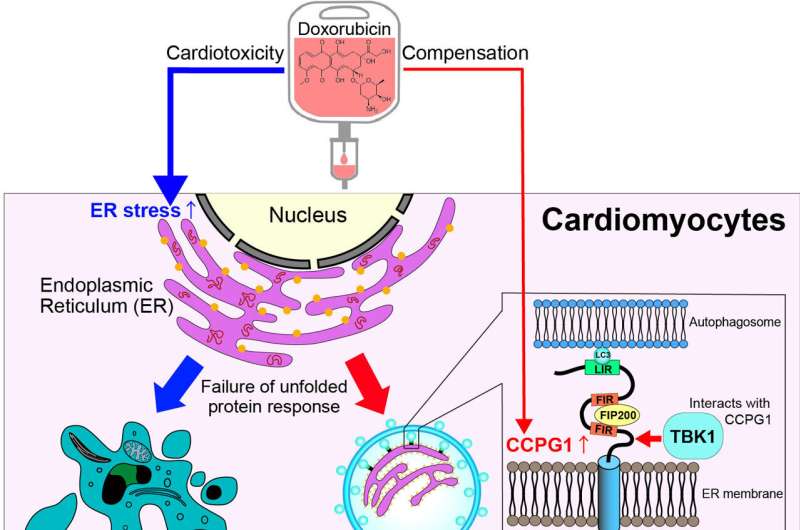
ER-phagy alleviates anthracycline cardiotoxicity. Credit score: Division of Cardiovascular Medication, TMDU
A cell accommodates many specialised subunits, referred to as organelles, that perform vital duties comparable to power era, protein synthesis, and calcium outflux. However what occurs when one thing goes mistaken with one of many organelles?
In a research just lately printed within the JACC: CardioOncologyresearchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental College have found how an organelle ‘eats itself’ for the nice of the complete cell when broken by chemotherapy drugs.
This act of focused degradation is known as autophagy and serves to take away faulty mobile elements. Autophagy is triggered by cellular stress and harm from dangerous molecules; emergency indicators then set off the regeneration of structural models, sustaining steadiness and performance within the human physique.
One potential supply of such harm is anti-cancer drugscomparable to anthracyclines. These medication are prescribed for varied varieties of most cancers however are related to an elevated danger of great cardiotoxicity. Doxorubicin (Dox), an anthracycline drug, can induce oxidative stress in a cells’ endoplasmic reticulum (ER), an important organelle that, amongst different issues, controls protein synthesis and calcium outflux in cardiomyocytes.
Extreme ER impairment in cardiomyocytes can finally result in cardiac dysfunction. The ER is the organelle that the researchers noticed finishing up autophagy throughout drug-induced stress.
“Endoplasmic reticulum-selective autophagy (ER-phagy) might be a helpful protecting mechanism in opposition to drug-induced cardiotoxicity,” explains first creator Shun Nakagama. “Nonetheless, there’s a lack of analysis displaying the presence of ER-phagy in cardiomyocytes. We subsequently aimed to find out whether or not ER-phagy helps to guard the center from drug-induced ER stress.”
The researchers developed a novel ER-phagy monitoring system in cardiomyocytes to visualise the activation of ER-phagy and determine protein regulators that management selective autophagy within the presence of Dox-induced ER stress. Moreover, a mouse model was used to find out an correct illustration of the cardioprotective position of ER-phagy in mammals.
“Our outcomes confirmed that ER-phagy certainly alleviates Dox-induced cardiomyopathy,” says corresponding creator Yasuhiro Maejima. “We decided that Dox-induced ER-phagy was activated by the interaction between two protein regulators: cell-cycle development gene 1 and TANK binding kinase 1. ER stress, attributable to Dox, was exacerbated with out this protein interplay, which then decreased cell survival.”
As anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity is widespread and severe in cancer patientsadditional analysis can elucidate the potential therapeutic efficacy of autophagy-promoting medication to alleviate Dox-associated coronary heart illness.
Extra data:
Shun Nakagama et al, Endoplasmic Reticulum Selective Autophagy Alleviates Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity, JACC: CardioOncology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2023.05.009
Offered by
Tokyo Medical and Dental University
Quotation:
Intracellular recycling: The important thing to surviving potent anti-cancer medication (2023, August 31)
retrieved 1 September 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-08-intracellular-recycling-key-surviving-potent.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post