[ad_1]
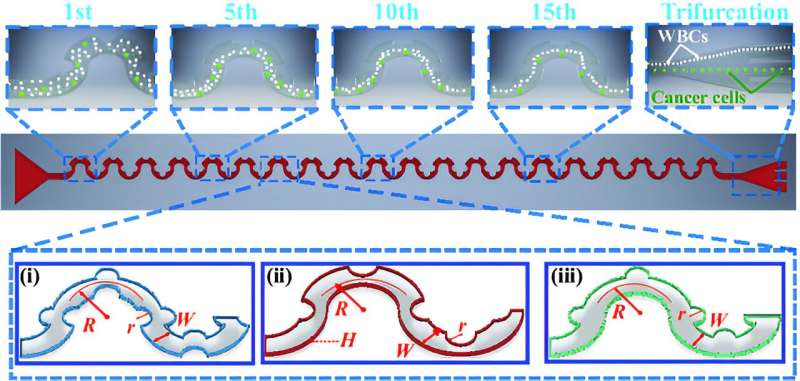
Schematics of particle unilateral focusing and separation in sinusoidal microchannels with uneven obstacles: (i) concave and convex obstacles on every respective sidewall (concave–convex impediment channel), (ii) concave obstacles on one sidewall (one-sided concave impediment channel), and (iii) convex obstacles on one sidewall (one-sided convex impediment channel). Credit score: Cyborg and Bionic Techniques (2023). DOI: 10.34133/cbsystems.0036
Early detection permits for well timed intervention in lots of ailments earlier than they progress to a extreme stage, usually at a decrease therapy value. That is significantly essential within the case of most cancers, because the stage of most cancers growth on the time of preliminary prognosis considerably influences the affected person’s prognosis and survival price.
Subsequently, common medical check-ups can guarantee higher survival and high quality of life. Nonetheless, the multitude of medical examination objects makes the expertise each liked and loathed. With numerous assessments and procedures to endure, the method can usually devour a considerable portion of 1’s day.
At this level, one would possibly marvel how handy it could be if all ailments may very well be indicated by way of a easy three-minute blood take a look at. The development of contemporary medical know-how is progressively turning this want right into a actuality. Certainly, the presence of a substantial variety of cancers could be advised by inspecting circulating tumor cells (CTCs) within the blood. Nonetheless, the focus of those CTCs is commonly extraordinarily low, falling beneath the detection restrict of present devices. To deal with this concern, cell separation know-how reveals nice promise.
Cell separation refers back to the technique of isolating a particular group of cells from a organic pattern, similar to blood or tissue, by eradicating different cell populations. Via cell separation methods, the amount and focus of a selected cell kind in a organic pattern could be enhanced, which is why this course of is also referred to as cell enrichment.
This know-how finds intensive purposes in numerous fields, together with biological researchillness prognosis, cell remedy, drug screening, and gene evaluation. As an example, by enriching the CTCs in blood, it turns into possible to conduct blood assessments for early-stage most cancers screening, considerably enhancing the diagnostic worth of such examinations.
Not too long ago, a analysis crew from Griffith College printed a analysis article titled “Asymmetrical Obstacles Allow Unilateral Inertial Focusing and Separation in Sinusoidal Microchannel” within the journal Cyborg and Bionic Techniques as a part of the China Science and Know-how Journal Wonderful Motion Plan. Of their examine, they proposed a novel cell enrichment methodology that makes use of asymmetrical obstacles in curved microchannels to realize unilateral inertial focusing, leading to a rise of tumor cell focus from 1% to over 90%.
How did they obtain such a excessive degree of cell enrichment? The reply lies within the utilization of a sinusoidal microchannel with asymmetrical obstacles buildings.
The idea of separation
To elucidate the mechanism behind the cell sorting impact of the sinuous microchannel, a comparability could be drawn with an identical phenomenon noticed within the pure world: meandering river channels. In straight river programs, the obstructive impact of sedimentation alongside each banks results in decrease circulation velocities on the sides, whereas the central circulation reveals greater velocities. Nonetheless, in meandering river channelsthe outer banks of convex bends expertise greater circulation velocities in comparison with the inside banks.
Consequently, the elevated circulation velocity on the outer aspect facilitates better erosion of the financial institution, leading to an extra enhance within the diploma of meandering within the river course.
Even with out contemplating the erosion impact of the riverbank, the precept of sedimentation in the direction of the convex financial institution because of the stress distinction and inertia attributable to the circulation velocity distinction remains to be relevant. This precept is employed in microfluidic channels for cell separation. In curved channels, cells are inclined to accumulate on the outer aspect of the bend (the place the circulation velocity is greater) because of inertia and stress variations.
Furthermore, as a result of cells of various sizes expertise completely different forces from inertia and stress, they progressively separate. The smaller cells have a tendency to remain nearer to the boundaries of the channel, whereas the bigger cells are extra inclined to occupy the central area. Subsequently, by implementing a number of bends within the channel, cells of various sizes could be successfully separated based mostly on the mixed results of circulation velocity-induced stress variations and inertia.
Simulation
The innovation of this examine lies within the incorporation of varied protrusions or indentations throughout the channel to additional improve cell separation effectivity induced by velocity variations. Researchers initially performed simulations to research the speed discipline distribution of the fluid in curved channels with completely different obstacles.
Via numerical simulations, they found that the introduction of protrusions or indentations as obstacles resulted in an enhancement of the intermediate circulation velocity throughout the channel, resulting in a extra asymmetrical distribution of the speed discipline. They hypothesized that this uneven velocity discipline distribution would possibly facilitate the preferential accumulation of cells on one aspect of the channel (unilateral focusing).
Experiment validation
Subsequently, they experimentally validated this speculation by confirming that the presence of obstacles within the curved microchannel certainly precipitated cell specializing in one aspect of the channel. Moreover, they noticed that this unilateral focusing impact was depending on the dimensions of the cells, indicating the potential to separate cells of various sizes based mostly on this attribute. To confirm their conjecture, the analysis crew initially performed separation experiments utilizing 10-micrometer and 15-micrometer polystyrene microspheres.
Below bright-field microscopy, it may be noticed that on the inlet, small particles (in blue) and huge particles (in crimson) are combined collectively. Nonetheless, on the center outlet, predominantly giant particles are seen, whereas on the different aspect outlet, solely small-sized particles are noticed.
Subsequently, can this attribute be utilized to separate white blood cells (8-12 micrometers) and tumor cells (16-18 micrometers), which have distinct dimension variations? To confirm this speculation, the researchers performed the next experiment. They ready a combination of U87MG most cancers cell line and white blood cells (WBCs) in a 1:100 ratio and injected it into the microchannel.
On the outlet of the channel, it was noticed that considerably larger-sized most cancers cells aggregated on the center outlet, whereas the smaller-sized WBCs accrued on the higher aspect of the channel. Quantitative evaluation revealed that after passing by way of this microchannel, the focus of most cancers cells elevated from 1.01% to 90.13%, making it appropriate for subsequent detection and evaluation.
Abstract and outlook
This examine proposes a novel method to regulate and cut back the inertial focusing place in microchannels by embedding uneven obstacles.
By incorporating uneven impediment patterns, similar to single-sided concave, single-sided convex, and concave-convex patterns, into symmetric curved channels, the researchers noticed distinctive one-sided focusing patterns close to the sidewalls of the channels within the case of single-sided concave and concave-convex impediment channels, which weren’t evident within the case of single-sided convex impediment channels. Moreover, the place of one-sided focusing was delicate to particle dimension.
In essence, by introducing concave-convex patterns into curved channels, particles within the fluid are directed in the direction of one aspect of the channel, and this aggregation phenomenon can be depending on particle dimension; smaller particles are inclined to accumulate nearer to the channel boundary. Leveraging this phenomenon, the researchers achieved the separation of cells with completely different sizes.
As an example, they have been capable of isolate tumor cells from blood samples containing white blood cells with excessive purity (over 90%), making it possible to display screen numerous sorts of most cancers based mostly on blood assessments.
With developments in microfluidic know-how and medical detection strategies, it’s conceivable that within the close to future, routine blood assessments might present monitoring and early detection of nearly all of ailments, reworking the panorama of medical diagnostics.
Extra info:
Haotian Cha et al, Asymmetrical Obstacles Allow Unilateral Inertial Focusing and Separation in Sinusoidal Microchannel, Cyborg and Bionic Techniques (2023). DOI: 10.34133/cbsystems.0036
Supplied by
Beijing Institute of Know-how Press Co., Ltd
Quotation:
Vital progress in cell separation know-how (2023, August 24)
retrieved 26 August 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-08-significant-cell-technology.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
Source link




Discussion about this post